Abstract
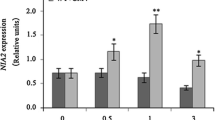
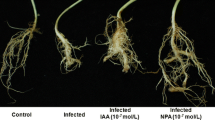
Nitrate reductase (NR) has emerged as a potential NO source in plants. Indeed, the Arabidopsis thaliana NR double-deficient mutant (nia1 nia2) produces low NO and develops abnormal susceptibility to bacterial infection. We have employed quantitative real-time polymerase chain reactions to analyze the effects of NO gas on the expression of defense-related genes in wild-type and nia1 nia2 A. thaliana plants that were inoculated with an avirulent strain of Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato. The pathogenesis-related gene 1 (PR1) was up-regulated by bacterial infection, and its expression was higher in the wild type than in nia1 nia2. Fumigation with NO attenuated the expression of PR1 and other salicylic acid-related genes in plants that had been inoculated with P. syringae. Nevertheless, NO inhibited the most intense bacterial growth and disease symptoms in nia1 nia2 leaves. The NO fumigation also directly modulated lignin biosynthesis-related gene expression (CAD1) and parts of the auxin (TIR1, ILL1, GH3) and ethylene (ACCS7) pathways, among other defense-related genes, and their modulation was more intense in the NR-deficient mutant. Pathogen inoculation induced delayed but intense H2O2 production in mutant leaves in comparison with the wild type. Hydrogen peroxide potentiated the microbicidal effects of NO against bacterial cultures. These results suggest that NO has a direct microbicidal effect in combination with H2O2 to allow for the attenuation of the SA-mediated defense response, thereby reducing the energy expenditure associated with defense-related gene transcription. Overall, these results highlight the importance of NR-dependent NO production in the establishment of disease resistance.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Arg:
-
l-Arginine
- Cfu:
-
Colony forming units
- HR:
-
Hypersensitive response
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NR:
-
Nitrate reductase
- PR:
-
Pathogenesis-related protein
- Pst:
-
Pseudomonas syringae pv. tomato
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
References
Ahuja I, Kissen R, Bones AM (2012) Phytoalexins in defense against pathogens. Trends Plant Sci 17:73–90
Alderton WK, Cooper CE, Knowles RG (2001) Nitric oxide synthases: structure, function and inhibition. Biochem J 357:593–615
Bari R, Jones JD (2009) Role of plant hormones in plant defence responses. Plant Mol Biol 69:473–488
Bellin D, Asai S, Delledonne M, Yoshioka H (2013) Nitric Oxide as a mediator for defense responses. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 26:271–277
Bethke PC, Badger MR, Jones RL (2004) Apoplastic synthesis of nitric oxide by plant tissues. Plant Cell 16:332–341
Chen GH, Chan YL, Liu CP, Wang LC (2012) Ethylene response pathway is essential for ARABIDOPSIS A-FIFTEEN function in floral induction and leaf senescence. Plant Signal Behav 7:457–460
Corpas FJ, Palma JM, del Rio LA, Barroso JB (2009) Evidence supporting the existence of l-arginine dependent nitric oxide synthase activity in plants. New Phytol 184:9–14
Czechowski T, Stitt M, Altman T, Udvardi MK, Scheible WR (2005) Genome-wide identification and testing of superior reference genes for transcript normalization in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 139:5–17
Delledonne M, Xia Y, Dixon RA, Lamb C (1998) Nitric oxide functions as a signal in plant disease resistance. Nature 394:585–588
Delledonne M, Zeier J, Marocco A, Lamb C (2001) Signal interactions between nitric oxide and reactive oxygen intermediates in the plant hypersensitive disease resistance response. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:13454–13459
Dixon RA, Paiva NL (1995) Stress-induced phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Cell 7:1085–1097
Durner J, Wendehenne D, Klessig DF (1998) Defense gene induction in tobacco by nitric oxide, cyclic GMP, and cyclic ADP-ribose. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:10328–10333
Durrant WE, Dong X (2004) Systemic acquired resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol 42:185–209
Ferrarini A, De Stefano M, Baudouin E, Pucciariello C, Polverari A, Puppo A, Delledonne M (2008) Expression of Medicago truncatula genes responsive to nitric oxide in pathogenic and symbiotic conditions. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 21:781–790
Gay C, Collins J, Gebicki JM (1999) Determination of hydroperoxides by the ferric-xylenol orange method. Redox Rep 4:327–328
Grant JJ, Loake GJ (2000) Role of reactive oxygen intermediates and cognate redox signaling in disease resistance. Plant Physiol 124:21–29
Gupta KJ, Fernie AR, Kaiser WM, van Dongen JT (2011) On the origins of nitric oxide. Trends Plant Sci 16:160–168
Kazan K, Manners JM (2009) Linking development to defense: auxin in plant-pathogen interactions. Trends Plant Sci 14:373–382
Keen NT (1990) Gene-for-gene complementarity in plant-pathogen interactions. Annu Rev Genet 24:447–463
Klessig DF, Durner J, Noad R, Navarre DA, Wendehenne D, Kumar D, Zhou JM, Shah J, Zhang S, Kachroo P, Trifa Y, Pontier D, Lam E, Silva H (2000) Nitric oxide and salicylic acid signaling in plant defense. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:8849–8855
Lamattina L, García-Mata C, Graziano M, Pagnussat G (2003) Nitric oxide: the versatility of an extensive signal molecule. Annu Rev Plant Biol 54:109–136
Lamb C, Dixon RA (1997) The oxidative bursts in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 48:251–275
Leon-Reyes A, Spoel SH, De Lange ES, Abe H, Kobayashi M, Tsuda S, Millenaar FF, Welschen RA, Ritsema T, Pieterse CM (2009) Ethylene modulates the role of nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes1 in cross talk between salicylate and jasmonate signaling. Plant Physiol 149:1797–1809
Leshem YY, Wills RBH, Ku VV (1998) Evidence for the function of the free radical gas—nitric oxide (NO•)—as an endogenous maturation and senescence regulating factor in higher plants. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:825–826
Lindermayr C, Saalbach G, Bahnweg G, Durner J (2006) Differential inhibition of Arabidopsis methionine adenosyltransferases by protein S-nitrosylation. J Biol Chem 281:4285–4291
Lindermayr C, Sell S, Müller B, Leister D, Durner J (2010) Redox regulation of the NPR1-TGA1 system of Arabidopsis thaliana by nitric oxide. Plant Cell 22:2894–2907
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and 2–ΔΔC T method. Methods 25:402–408
Modolo LV, Augusto O, Almeida IMG, Magalhaes JR, Salgado I (2005) Nitrite as the major source of nitric oxide production by Arabidopsis thaliana in response to Pseudomonas syringae. FEBS Lett 579:3814–3820
Modolo LV, Augusto O, Almeida IMG, Pinto-Maglio CAF, Oliveira HC, Seligman K, Salgado I (2006) Decreased arginine and nitrite levels in nitrate reductase-deficient Arabidopsis thaliana plants impair nitric oxide synthesis and the hypersensitive response to Pseudomonas syringae. Plant Sci 171:34–40
Moore JW, Loake GJ, Spoel SH (2011) Transcription dynamics in plant immunity. Plant Cell 23:2809–2820
Naoumkina MA, Zhao Q, Gallego-Giraldo L, Dai X, Zhao PX, Dixon RA (2010) Genome-wide analysis of phenylpropanoid defence pathways. Mol Plant Pathol 11:829–846
Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JD (2006) A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing auxin signaling. Science 312:436–439
Neill S, Bright J, Desikan R, Hancock J, Harrison J, Wilson I (2008) Nitric oxide evolution and perception. J Exp Bot 59:25–35
Oliveira HC, Justino GC, Sodek L, Salgado I (2009) Amino acid recovery does not prevent susceptibility to Pseudomonas syringae in nitrate reductase double-deficient Arabidopsis thaliana plants. Plant Sci 176:105–111
Perchepied L, Balagué C, Riou C, Claudel-Renard C, Rivière N, Grezes-Besset B, Roby D (2010) Nitric oxide participates in the complex interplay of defense-related signaling pathways controlling disease resistance to Sclerotinia sclerotiorum in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 23:846–860
Raes J, Rohde A, Christensen JH, Van de Peer Y, Boerjan W (2003) Genome-wide characterization of the lignification toolbox in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 133:1051–1071
Rasul S, Dubreuil-Maurizi C, Lamotte O, Koen E, Poinssot B, Alcaraz G, Wendehenne D, Jeandroz S (2012) Nitric oxide production mediates oligogalacturonide-triggered immunity and resistance to Botrytis cinerea in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant, Cell Environ 35:1483–1499
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Navarro L, Bari R, Jones JD (2007) Pathological hormone imbalances. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:372–379
Robert-Seilaniantz A, Grant M, Jones JD (2011) Hormone crosstalk in plant disease and defense: more than just jasmonate-salicylate antagonism. Annu Rev Phytopathol 49:317–343
Rockel P, Strube F, Rockel A, Wildt J, Kaiser WM (2002) Regulation of nitric oxide (NO) production by plant nitrate reductase in vivo and in vitro. J Exp Bot 53:103–110
Spoel SH, Dong X (2008) Making sense of hormone crosstalk during plant immune responses. Cell Host Microbe 3:348–351
Spoel SH, Loake GJ (2011) Redox-based protein modifications: the missing link in plant immune signalling. Curr Opin Plant Biol 14:358–364
Tada Y, Spoel SH, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Mou Z, Song J, Wang C, Zuo J, Dong X (2008) Plant immunity requires conformational changes [corrected] of NPR1 via S-nitrosylation and thioredoxins. Science 321:952–956
van Loon LC, Geraats BP, Linthorst HJ (2006) Ethylene as a modulator of disease resistance in plants. Trends Plant Sci 11:184–191
Vorwerk S, Somerville S, Somerville C (2004) The role of plant cell wall polysaccharide composition in disease resistance. Trends Plant Sci 9:203–209
Wang D, Pajerowska-Mukhtar K, Culler AH, Dong X (2007) Salicylic acid inhibits pathogen growth in plants through repression of the auxin signaling pathway. Curr Biol 17:1784–1790
Wang YQ, Feechan A, Yun BW, Shafiei R, Hofmann A, Taylor P, Xue P, Yang FQ, Xie ZS, Pallas JA, Chu CC, Loake GJ (2009) S-nitrosylation of AtSABP3 antagonizes the expression of plant immunity. J Biol Chem 284:2131–2137
Wilkinson JQ, Crawford NM (1991) Identification of the Arabidopsis CHL3 gene as the nitrate reductase structural gene NIA2. Plant Cell 3:461–471
Woodward AW, Bartel B (2005) Auxin: regulation, action, and interaction. Ann Bot 95:707–735
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq, grant no. 473090/2011-2). S.C.V. and G.T.D. were supported by a student fellowship and H.C.O. by a research fellowship from Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP). I.S. and M.G.A.V. are supported by a research fellowship from CNPq.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vitor, S.C., Duarte, G.T., Saviani, E.E. et al. Nitrate reductase is required for the transcriptional modulation and bactericidal activity of nitric oxide during the defense response of Arabidopsis thaliana against Pseudomonas syringae . Planta 238, 475–486 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1906-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-013-1906-0