Abstract
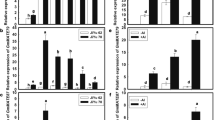
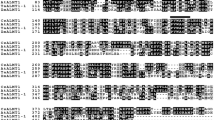
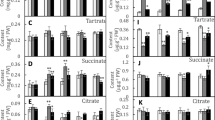
Many plant species excrete organic acids into the rhizosphere in response to aluminum stress to protect sensitive cells from aluminum rhizotoxicity. When the roots of Eucalyptus camaldulensis, a major source of pulp production, were incubated in aluminum-toxic medium, citrate released into the solution increased as a function of time. Citrate excretion was inducible by aluminum, but not by copper or sodium chloride stresses. This indicated that citrate is the major responsive organic acid released from the roots of this plant species to protect the root tips from aluminum damage. Four genes highly homologs to known citrate-transporting multidrugs and toxic compounds exclusion proteins, named EcMATE1–4, were isolated using polymerase chain reaction-based cloning techniques. Their predicted proteins included 12 membrane spanning domains, a common structural feature of citrate-transporting MATE proteins, and consisted of 502–579 amino acids with >60 % homology to orthologous genes in other plant species. One of the homologs, designated EcMATE1, was expressed in the roots more abundantly than in the shoots and in response to both Al and low pH stresses. Ectopic expression of EcMATE1 and 3 in tobacco hairy roots enhanced Al-responsive citrate excretion. Pharmacological characterization indicated that Al-responsive citrate excretion involved a protein phosphorylation/dephosphorylation process. These results indicate that citrate excretion through citrate-transporting multidrugs and toxic compounds exclusion proteins is one of the important aluminum-tolerance mechanisms in Eucalyptus camaldulensis.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Al:
-
Aluminum
- ALMT1:
-
Aluminum-activated malate transporter 1
- ART1:
-
Al-resistance transcription factor 1
- AtFRD3:
-
Arabidopsis thaliana ferric redictase defective3
- HvAACT1:
-
Hordeum vulgare aluminum-activated citrate transporter 1
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- MATE:
-
Multidrugs and toxic compounds exclusion
- MS:
-
Murashige and Skoog
- OAs:
-
Organic acids
- STOP1:
-
Sensitive to proton rhizotoxicity1
References
Anoop VM, Basu U, McCammon MT, McAlister-Henn L, Taylor GJ (2003) Modulation of citrate metabolism alters aluminum tolerance in yeast and transgenic canola overexpressing a mitochondrial citrate synthase. Plant Physiol 132:2205–2217
Campinhos E (1999) Sustainable plantations of high-yield Eucalyptus trees for production of fiber: the Aracruz case. New Forest 17:129–143
Delhaize E, Ryan PR, Randall PJ (1993) Aluminum tolerance in wheat (Triticum asestivum L.) II. Aluminum-stimulated excretion of malic acid from root apices. Plant Physiol 103:695–702
Deng W, Luo K, Li Z, Yang Y, Hu N, Wu Y (2009) Overexpression of Citrus junos mitochondrial citrate synthase gene in Nicotiana benthamiana confers aluminum tolerance. Planta 230:355–365
FAO (2001) Global data on forest plantations resources in Forest genetic resources, FAO, Rome, http://www.fao.org/docrep/004/Y2316E/y2316e0b.htm#bm11
Feikema P, Baker T (2011) Effect of soil salinity on growth of irrigated plantation Eucalyptus in south-eastern Australia. Agric Water Manage 98(7):1180–1188
Fujii M, Yokosho K, Yamaji N, Saisho D, Yamane M, Takahashi H, Sato K, Nakazono M, Ma JF (2012) Acquisition of aluminium tolerance by modification of a single gene in barley. Nat Commun 3:713
Fukuda T, Saito A, Wasaki J, Shinano T, Osaki M (2007) Metabolic alterations proposed by proteome in rice roots grown under low P and high Al concentration under low pH. Plant Sci 172:1157–1165
Furukawa J, Yamaji N, Wang H, Mitani N, Murata Y, Sato K, Katsuhara M, Takeda K, Ma JF (2007) An aluminum-activated citrate transporter in barley. Plant Cell Physiol 48:1081–1091
Greaves BL, Borralho NMG, Raymond CA (1997) Breeding objective for plantation eucalypts grown for production of kraft pulp. For Sci 43:465–472
Hampp R, Goller M, Füllgraf H (1984) Determination of compartmented metabolite pools by a combination of rapid fractionation of oat mesophyll protoplasts and enzymic cycling. Plant Physiol 75:1017–1021
Hoekenga OA, Maron LG, Pineros MA, Cancado GM, Shaff J, Kobayashi Y, Ryan PR, Dong B, Delhaize E, Sasaki T, Matsumoto H, Yamamoto Y, Koyama H, Kochian LV (2006) AtALMT1, which encodes a malate transporter, is identified as one of several genes critical for aluminum tolerance in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9738–9743
Ito K, Doi K, Tatemichi Y, Shibata M (1996) Plant regeneration of eucalypts from rotating nodule cultures. Plant Cell Rep 16:42–45
Iuchi S, Koyama H, Iuchi A, Kobayashi Y, Kitabayashi S, Kobayashi Y, Ikka T, Hirayama T, Shinozaki K, Kobayashi M (2007) Zinc finger protein STOP1 is critical for proton tolerance in Arabidopsis and coregulates a key gene in aluminum tolerance. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:9900
Kihara T, Wada T, Suzuki Y, Hara T, Koyama H (2003) Alteration of citrate metabolism in cluster roots of white lupin. Plant Cell Physiol 44:901–908
Kobayashi Y, Hoekenga OA, Itoh H, Nakashima M, Saito S, Shaff JE, Maron LG, Pineros MA, Kochian LV, Koyama H (2007) Characterization of AtALMT1 expression in aluminum-inducible malate release and its role for rhizotoxic stress tolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 145:843–852
Kochian LV, Hoekenga OA, Pineros MA (2004) How do crop plants tolerate acid soils? Mechanisms of aluminum tolerance and phosphorous efficiency. Annu Rev Plant Biol 55:459–493
Liu J, Magalhaes JV, Shaff J, Kochian LV (2009) Aluminum-activated citrate and malate transporters from the MATE and ALMT families function independently to confer Arabidopsis aluminum tolerance. Plant J 57:389–399
Ma JF, Hiradate S, Matsumoto H (1998) High aluminum resistance in buckwheat. Plant Physiol 117:753–759
Ma JF, Ryan PR, Delhaize E (2001) Aluminium tolerance in plants and the complexing role of organic acids. Trends Plant Sci 6:273–278
Magalhaes JV, Liu J, Guimaraes CT, Lana UG, Alves VM, Wang YH, Schaffert RE, Hoekenga OA, Pineros MA, Shaff JE, Klein PE, Carneiro NP, Coelho CM, Trick HN, Kochian LV (2007) A gene in the multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family confers aluminum tolerance in sorghum. Nat Genet 39:1156–1161
Maron LG, Piñeros MA, Guimarães CT, Magalhaes JV, Pleiman JK, Mao C, Shaff J, Belicuas SNJ, Kochian LV (2010) Two functionally distinct members of the MATE (multi-drug and toxic compound extrusion) family of transporters potentially underlie two major aluminum tolerance QTLs in maize. Plant J 61:728–740
Miethke M, Marahiel MA (2007) Siderophore-based iron acquisition and pathogen control. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 71:413–451
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bio assays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nakagawa T, Ishiguro S, Kimura T (2009) Gateway vectors for plant transformation. Plant biotechnol 26:275–284
Neumann G, Massonneau A, Martinoia E, Römheld V (1999) Physiological adaptations to phosphorus deficiency during proteoid root development in white lupin. Planta 208:373–382
Ohno T, Koyama H, Hara T (2003) Characterization of citrate transport through the plasma membrane in a carrot mutant cell line with enhanced citrate excretion. Plant Cell Physiol 44:156–162
Raman H, Ryan PR, Raman R, Stodart BJ, Zhang K, Martin P, Wood R, Sasaki T, Yamamoto Y, Mackay M (2008) Analysis of TaALMT1 traces the transmission of aluminum resistance in cultivated common wheat (Triticum aestivum L.). Theor Appl Genet 116:343–354
Raymond CA, Apiolaza LA (2004) Incorporating wood quality and deployment traits in Eucalyptus globulus and Eucalyptus nitens. In: Plantation forest biotechnology for the 21st century. Forest Research New Zealand, Rotorua, pp 87–99
Rogers EE, Guerinot ML (2002) FRD3, a member of the multidrug and toxin efflux family, controls iron deficiency responses in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 14:1787–1799
Rudrappa T, Czymmek KJ, Pare PW, Bais HP (2008) Root-secreted malic acid recruits beneficial soil bacteria. Plant Physiol 148:1547–1556
Sasaki T, Yamamoto Y, Ezaki B, Katsuhara M, Ahn SJ, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Matsumoto H (2004) A wheat gene encoding an aluminum-activated malate transporter. Plant J 37:645–653
Sasaki T, Ryan PR, Delhaize E, Hebb DM, Ogihara Y, Kawaura K, Noda K, Kojima T, Toyoda A, Matsumoto H (2006) Sequence upstream of the wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) ALMT1 gene and its relationship to aluminum resistance. Plant Cell Physiol 47:1343–1354
Sawaki Y, Iuchi S, Kobayashi Y, Kobayashi Y, Ikka T, Sakurai N, Fujita M, Shinozaki K, Shibata D, Kobayashi M, Koyama H (2009) STOP1 regulates multiple genes that protect Arabidopsis from proton and aluminum toxicities. Plant Physiol 150:281–294
Sparkes IA, Runions J, Kearns A, Hawes C (2006) Rapid, transient expression of fluorescent fusion proteins in tobacco plants and generation of stably transformed plants. Nat Protoc 1:2019–2025
Suzuki Y, Kawazu T, Koyama H (2004) RNA isolation from siliques, dry seeds, and other tissues of Arabidopsis thaliana. BioTechniques 37:542–544
Takita E, Koyama H, Hara T (1999) Organic acid metabolism in aluminum-phosphate utilizing cells of carrot (Daucus carota L.). Plant Cell Physiol 40:489–495
Tesfaya M, Temple SJ, Allan DL, Vance CP, Samac DA (2001) Overexpression of malate dehydrogenase in transgenic alfalfa enhances organic acid synthesis and confers tolerance to aluminum. Plant Physiol 127:1836–1844
Wagatsuma T, Jujo K, Ishikawa S, Nakashima T (1995) Aluminum-tolerant protoplasts from roots can be collected with positively charged silica microbeads: a method based on differences in surface negativity. Plant Cell Physiol 36:1493–1502
White DA, Crombie DS, Kinal J, Battaglia M, McGrath JF, Mendham DS, Walker SN (2009) Managing productivity and drought risk in Eucalyptus globulus plantations in south-western Australia. For Ecol Manage 259:33–44
Yamaji N, Huang CF, Nagao S, Yano M, Sato Y, Nagamura Y, Ma JF (2009) A zinc finger transcription factor ART1 regulates multiple genes implicated in aluminum tolerance in rice. Plant Cell Online 21:3339–3349
Yang XY, Yang JL, Zhou Y, Pineros MA, Kochian LV, Li GX, Zheng SJ (2011) A de novo synthesis citrate transporter, Vigna umbellata multidrug and toxic compound extrusion, implicates in Al-activated citrate efflux in rice bean (Vigna umbellata) root apex. Plant, Cell Environ 34:2138–2148
Zheng SJ, Ma JF, Matsumoto H (1998) High aluminum resistance in buckwheat. I. Al-induced specific secretion of oxalic acid from root apex. Plant Physiol 117:745–751
Zheng SJ, Yang JL, He YF, Yu XH, Zhang L, You JF, Shen RF, Matsumoto H (2005) Immobilization of aluminum with phosphorus in roots is associated with high aluminum resistance in buckwheat. Plant Physiol 138:297–303
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr Tsuyoshi Nakagawa (Shimane University) for providing the gateway vector, pGWB2. This work was supported by the METI (Ministry of Economy, Trade and Industry) Grant Program, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawaki, Y., Kihara-Doi, T., Kobayashi, Y. et al. Characterization of Al-responsive citrate excretion and citrate-transporting MATEs in Eucalyptus camaldulensis . Planta 237, 979–989 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1810-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-012-1810-z