Abstract
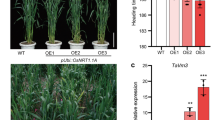
In order to characterize the functions of the sweetpotato SRF1 gene, which encodes a Dof zing finger transcriptional factor preferentially expressed in the storage roots, we isolated its full length cDNA and produced transgenic sweetpotato plants with altered SRF1 expression levels. The isolated cDNA of SRF1 encoded a polypeptide of 497 amino acids and was closely related to the cyclic Dof factors of Arabidopsis and the ascorbate oxidase binding protein of pumpkin. SRF1 was most highly expressed in storage roots, although some expression was also observed in other vegetative tissue. Transgenic plants overexpressing SRF1 showed significantly higher storage root dry matter content compared to the original cultivar Kokei No. 14 or control transgenic plants. In these plants, the starch content per fresh weight of the storage roots was also higher than that of the wild-type plants, while the glucose and fructose content drastically decreased. Among the enzymes involved in the sugar metabolism, soluble acid invertase showed a decreased activity in the transgenic plants. Gene expression analysis showed that the expression of Ibβfruct2, which encodes an isoform of vacuolar invertase, was suppressed in the transgenic plants overexpressing the SRF1 gene. These data suggest that SRF1 modulates the carbohydrate metabolism in the storage roots through negative regulation of a vacuolar invertase gene.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGPase:
-
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase
- AOBP:
-
Ascorbate oxidase binding protein
- GBSS:
-
Granule bound starch synthase
- GUS:
-
β-Glucuronidase
- RT:
-
Reverse transcription
- SBE:
-
Starch branching enzyme
- SuSy:
-
Sucrose synthase
References
Cervantes-Flores JC (2006) Development of a genetic linkage map and QTL analysis in sweetpotato. Dissertation, North Carolina State University
Dancer J, Hatzfeld WD, Stitt M (1990) Cytosolic cycles regulate the turnover of sucrose in heterotrophic cell-suspension cultures of Chenopodium rubrum L. Planta 182:223–231
Dubois M, Gilles KA, Hamilton JK, Rebers PA, Smith F (1956) Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Anal Chem 28:350–356
Geigenberger P, Regierer B, Nunes-Nesi A, Leisse A, Urbanczyk-Wochniak E, Springer F, van Dongen JT, Kossmann J, Fernie AR (2005) Inhibition of de novo pyrimidine synthesis in growing potato tubers lead to a compensatory stimulation of the pyrimidine salvage pathway and a subsequent increase in biosynthetic performance. Plant Cell 17:2077–2088
Greiner S, Rausch T, Sonnewald U, Herbers K (1999) Ectopic expression of a tobacco invertase inhibitor homolog prevents cold-induced sweetening of potato tubers. Nat Biotechnol 17:708–711
Höfgen R, Willmitzer L (1988) Storage of competent cells for Agrobacterium transformation. Nucleic Acids Res 16:9877
Huang YH, Picha DH, Kilili AW, Johnson CE (1999) Changes in invertase activities and reducing sugar content in sweetpotato stored at different temperatures. J Agric Food Chem 47:4927–4931
Huang WC, Wang AY, Wang LT, Sung HY (2003) Expression and characterization of sweet potato invertase in Pichia pastoris. J Agric Food Chem 51:1494–1499
Imaizumi T, Schultz TF, Harmon FG, Ho LA, Kay SA (2005) FKF1 F-Box protein mediates cyclic degradation of a repressor of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Science 309:293–297
Jenner HL, Winning BM, Millar AH, Tomlinson KL, Leaver CJ, Hill SA (2001) NAD malic enzyme and the control of carbohydrate metabolism in potato tubers. Plant Physiol 126:1139–1149
Klann EM, Hall B, Bennett AB (1996) Antisense acid invertase (TIV1) gene alters soluble sugar composition and size in transgenic tomato fruit. Plant Physiol 112:1321–1330
Koch K (2004) Sucrose metabolism: regulatory mechanisms and pivotal roles in sugar sensing and plant development. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7:235–246
Li XQ, Zhang D (2003) Gene expression activity and pathway selection for sucrose metabolism in developing storage root of sweet potato. Plant Cell Physiol 44:630–636
Lijavetzky D, Carbonero P, Vicente-Carbajosa J (2003) Genome-wide comparative phylogenetic analysis of the rice and Arabidopsis Dof gene families. BMC Evol Biol 3:17
McCready RM, Guggolz J, Silviera V, Owens HS (1950) Determination of starch and amylase in vegetables. Anal Chem 22:1156–1158
McKibbin RS, Muttucumaru N, Paul MJ, Powers SJ, Burrell MM, Coates S, Purcell PC, Tiessen A, Geigenberger P, Halford NG (2006) Production of high-starch, low-glucose potatoes through over-expression of the metabolic regulator SnRK1. Plant Biotechnol J 4:409–418
Mitsuhara I, Ugaki M, Hirochika H, Ohshima M, Murakami T, Gotoh Y, Katayose Y, Nakamura S, Honkura R, Nishimiya S, Ueno K, Mochizuki A, Tanimoto H, Tsugawa H, Otsuki Y, Ohashi Y (1996) Efficient promoter cassettes for enhanced expression of foreign genes in dicotyledonous and monocotyledonous plants. Plant Cell Physiol 37:49–59
Moreno-Risueno MÁ, Martínez M, Vicente-Carbajosa J, Carbonero P (2007) The family of DOF transcription factors: from green unicellular algae to vascular plants. Mol Gen Genomics 277:379–390
Nakatani M, Komeichi M (1992) Relationship between starch content and activity of starch synthase and ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase in tuberous root of sweet potato. Jpn J Crop Sci 61:463–468
Nakatani M, Tanaka M, Yoshinaga M (2002) Physiological and anatomical characterization of a late-storage root-forming mutant of sweetpotato. J Am Soc Hort Sci 127:178–183
Noda T, Kimura T, Otani M, Ideta O, Shimada T, Saito A, Suda I (2002) Physicochemical properties of amylose-free starch from transgenic sweet potato. Carbohydr Polym 49:253–260
Otani M, Shimada T, Kimura T, Saito A (1998) Transgenic plant production from embryogenic callus of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.) using Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Biotechnol 15:11–16
Regierer B, Fernie AR, Springer F, Perez-Melis A, Leisse A, Koehl K, Willmitzer L, Geigenberger P, Kossmann J (2002) Starch content and yield increase as a result of altering adenylate pools in transgenic plants. Nat Biotechnol 20:1256–1260
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbour-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Sakai K (1964) Studies on the enlargement of variations and the improvement of selection methods in sweet potato breeding. Bull Kyushu Natl Agric Exp Stn 9:247–397
Shimada T, Otani M, Hamada T, Kim SH (2006) Increase of amylase content of sweetpotato starch by RNA interference of the starch branching enzyme II gene (IbSBEII). Plant Biotechnol 23:85–90
Stark DM, Timmerman KP, Barry GF, Preiss J, Kishore GM (1992) Regulation of the amount of starch in plant tissue by ADP glucose pyrophosphorylase. Science 258:287–291
Takahata Y, Noda T, Sato T (1996) Relationship between acid invertase activity and hexose content in sweet potato storage roots. J Agric Food Chem 44:2063–2066
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
Tanaka M, Takahata Y, Nakatani M (2005) Analysis of genes developmentally regulated during storage root formation of sweet potato. J Plant Physiol 162:91–102
Tang GQ, Lüscher M, Sturm A (1999) Antisense repression of vacuolar and cell wall invertase in transgenic carrot alters early plant development and sucrose partitioning. Plant Cell 11:177–189
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Tjaden J, Möhlmann T, Kampfenkel K, Henrichs G, Neuhaus HE (1998) Altered plastidic ATP/ADP-transporter activity influences potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) tuber morphology, yield and composition of tuber starch. Plant J 16:531–540
Togari Y (1950) A study in the tuberous-root formation of sweet-potatoes. Bull Natl Agr Expt Sta (Tokyo) 68:1–96
Vandesompele J, Preter KD, Pattyn F, Poppe B, Van Roy N, De Paepe A, Speleman F (2002) Accurate normalization of real-time quantitative RT-PCR data by geometric averaging of multiple internal control genes. Genome Biol 3:research0034.1–0034.11
Wang LT, Wang AY, Hsieh CW, Chen CY, Sung HY (2005) Vacuolar invertases in sweet potato: molecular cloning characterization, and analysis of gene expression. J Agric Food Chem 53:3672–3678
Wang HW, Zhang B, Hao YJ, Huang J, Tian AG, Liao Y, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2007) The soybean Dof-type transcription factor genes, GmDof4 and GmDof11, enhance lipid content in the seeds of transgenic Arabidopsis plants. Plant J 52:716–729
Yanagisawa S (2002) The Dof family of plant transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci 7:555–560
Yanagisawa S (2004) Dof domain proteins: plant-specific transcription factors associated with diverse phenomena unique to plants. Plant Cell Physiol 45:386–391
Yanagisawa S, Sheen J (1998) Involvement of maize Dof zinc finger proteins in tissue-specific and light-regulated gene expression. Plant Cell 10:75–89
Yanagisawa S, Akiyama A, Kisaka H, Uchimiya H, Miwa T (2004) Metabolic engineering with Dof1 transcription factor in plants: improved nitrogen assimilation and growth under low-nitrogen conditions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:7833–7838
Yau YY, Simon PW (2003) A 2.5-kb insert eliminates acid soluble invertase isozyme II transcript in carrot (Daucus carota L.) roots, causing high sucrose accumulation. Plant Mol Biol 53:151–162
Yoshinaga M, Tanaka M, Nakatani M (2000) Changes in anthocyanin content and composition of developing storage root of purple-fleshed sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas (L.) Lam.). Breed Sci 50:59–64
Zrenner R, Schüler K, Sonnewald U (1996) Soluble acid invertase determines the hexose-to-sucrose ratio in cold-stored potato tubers. Planta 198:246–252
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant-in-aid from the Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry, and Fisheries (MAFF) of Japan. We thank Professor Kazufumi Yazaki at Kyoto University for kindly providing the pBI-EL2-GUS vector. We also thank Rieko Gonbori, Hirofumi Kinoshita and Masako Yoshigaki (KONARC) for their assistance with laboratory work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, M., Takahata, Y., Nakayama, H. et al. Altered carbohydrate metabolism in the storage roots of sweetpotato plants overexpressing the SRF1 gene, which encodes a Dof zinc finger transcription factor. Planta 230, 737–746 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0979-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-0979-2