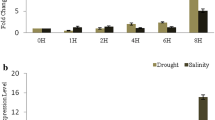
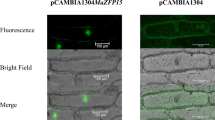
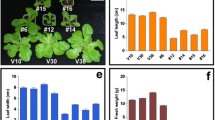
Abstract
Capsicum annuum RING Zinc Finger Protein 1 (CaRZFP1) gene is a novel C3HC4-type RING zinc finger protein gene which was previously isolated from a cDNA library for hot pepper plants treated of heat-shock. The CaRZFP1 was inducible to diverse environmental stresses in hot pepper plants. We introduced the CaRZFP1 into the Wisconsin 38 cultivar of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) by Agrobacterium mediated transformation under the control of the CaMV 35S promoter. Expression of the transgene in the transformed tobacco plants was demonstrated by RNA blot analyses. There appeared no adverse effect of over-expression of the transgene on overall growth and development of transformants. The genetic analysis of tested T1 lines showed that the transgene segregated in a Mendelian fashion. Transgenic tobacco lines that expressed the CaRZFP1 gene were compared with several different empty vector lines and they exhibited enhanced growth; they have larger primary root, more lateral root, larger hypocotyls and bigger leaf size, resulting in heavier fresh weight. Enhanced growth of transgenic lines accompanied with longer vegetative growth that resulted in bigger plants with higher number of leaves. Microarray analysis revealed the up-regulation of some growth related genes in the transgenic plants which were verified by specific oligomer RNA blot analyses. These results indicate that CaRZFP1 activates and up-regulates some growth related proteins and thereby effectively promoting plant growth.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AGP:
-
Arabinogalactan protein
- FtsZ:
-
Filamentous temperature-sensitive Z
- GRP:
-
Glycine rich protein
- LHCP:
-
Light harvesting complex protein
- PRP:
-
Proline rich protein
- TAIR:
-
The Arabidopsis Information Resource
References
Alexandrov NN, Troukhan ME, Brover VV, Tatarinova T, Flavell RB, Feldmann KA (2006) Features of Arabidopsis gene and genome discovered using full-length cDNAs. Plant Mol Biol 60:71–87
Armengaud P, Breitling R, Amtmann A (2004) The potassium-dependent transcriptome of Arabidopsis reveals a prominent role of jasmonic acid in nutrient signaling. Plant Physiol 136:2556–2576
Arumugam TU, Davies E, Morita EH, Abe S (2007) Sequence, expression and tissue localization of a gene encoding a makorin RING zinc-finger protein in germinating rice (Oryza sativa L. ssp. Japonica) seeds. Plant Physiol Biochem 45:767–780
Bernhardt C, Tierney ML (2000) Expression of AtPRP3, a proline-rich structural cell wall protein from Arabidopsis, is regulated by Cell-Type-specific developmental pathways involved in root hair formation. Plant Physiol 122:705–714
Deng XW, Matsui M, Wei N, Wagner D, Chu AM, Feldmann KA, Quail PH (1992) COP1, and Arabidopsis regulatory gene, encodes a protein with both a zinc-binding motif and a G homologous domain. Cell 71:791–801
Ding L, Zhu JK (1997) A role for arabinogalactan-proteins in root epidermal cell expansion. Planta 203:289–294
Freemont PS, Hanson IM, Trowsdale J (1991) A novel cysteine-rich sequence motif. Cell 64:483–484
Freemont PS (2000) RING for destruction? Curr Biol 10:84–87
Haas BJ, Volfovsky N, Town CD, Troukhan M, Alexandrov N, Feldmann KA, Flavell RB, White O, Salzberg SL (2002) Full-length messenger RNA sequences greatly improve genome annotation. Genome Biol 3:1–12
Horsch RB, Fry JE, Hoffmann NL, Eichholtz D, Rogers SG, Fraley RT (1985) A simple and general method for transferring genes into plants. Science 227:1229–1231
Isabel S, Leblanc E, Boissinot M, Boudreau DK, Grondin M, Picard FJ, Martel EA, Parham NJ, Chain PS, Bader DE, Mulvey MR, Bryden L, Roy PH, Ouellette M, Bergeron MG (2008) Divergence among genes encoding the elongation factor Tu of Yersinia species. J Bacteriol (Epub ahead of print)
Joazeiro CA, Wing SS, Huang H, Leverson JD, Hunter T, Liu YC (1999) The tyrosin kinase negative regulator c-Cbl as a RING-type E2-dependent ubiquitin-protein ligase. Science 286:309–312
Knox JP, Linstead PJ, Peart J, Cooper C, Roberts K (1991) Developmentally regulated epitopes of cell surface arabinogalactan proteins and their relation to root tissue pattern formation. Plant J 1:317–326
Ko JH, Seung HY, Kyung HH (2006) Upregulation of an Arabidopsis RING-H2 gene, XERICO confers drought tolerance through increased abscisic acid biosynthesis. Plant J 47:343–355
Mazumder B, Sampath P, Seshadri V, Maitra RK, DiCorleto PE, Fox PL (2003) Regulated release of L13a from the 60S ribosomal subunit as a mechanism of transcript-specific translational control. Cell 115:187–198
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Planta 157:385–391
Park MH, Suzuki Y, Chono M, Knox JP, Yamaguchi I (2003) CsAGP1, a gibberellin-responsive gene from cucumber hypocotyls, encodes a classical arabinogalactan protein and is involved in stem elongation. Plant Physiol 131:1450–1459
Peng J, Richards DE, Moritz T, Cano-Delgado A, Harberd NP (1999) Extragenic Suppressors of the Arabidopsis gai mutation alter the dose-response relationship of diverse gibberellin responses. Plant Physiol 119:1199–1208
Pennell RI, Roberts K (1990) Sexual development in the pea is presaged by altered expression of arabinogalactan protein. Nature 344:547–549
Raab S, Hoth S (2007) A mutation in the AtPRP4 splicing factor gene suppresses seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant Biol (Stuttg) 9:447–452
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Press, New York
Sasaki T, Matsumoto T, Yamamoto K, Sakata K, Baba T, Katayose Y, Wu J, Niimura Y, Cheng Z, Nagamura Y, Antonio BA, Kanamori H, Hosokawa S, Masukawa M, Arikawa K, Chiden Y, Hayashi M, Okamoto M, Ando T, Aoki H, Arita K, Hamada M, Harada C, Hijishita S, Honda M, Ichikawa Y, Idonuma A, Iijima M, Ikeda M, Ikeno M, Ito S, Ito T, Ito Y, Ito Y, Iwabuchi A, Kamiya K, Karasawa W, Katagiri S, Kikuta A, Kobayashi N, Kono I, Machita K, Maehara T, Mizuno H, Mizubayashi T, Mukai Y, Nagasaki H, Nakashima M, Nakama Y, Nakamichi Y, Nakamura M, Namiki N, Negishi M, Ohta I, Ono N, Saji S, Sakai K, Shibata M, Shimokawa T, Shomura A, Song J, Takazaki Y, Terasawa K, Tsuji K, Waki K, Yamagata H, Yamane H, Yoshiki S, Yoshihara R, Yukawa K, Zhong H, Iwama H, Endo T, Ito H, Hahn JH, Kim HI, Eun MY, Yano M, Jiang J, Gojobori T (2002) The genome sequence and structure of rice chromosome 1. Nature 420:312–316
Saurin AJ, Borden KLB, Boddy MN, Freemont PS (1996) Does this have a familiar RING? Trends Biochem Sci 21:208–214
Schulz B, Kolukisaoglu HU (2006) Genomics of plant ABC transporters: the alphabet of photosynthetic life forms or just holes in membranes? FEBS Lett 580:1010–1016
Schumann U, Prestele J, O’Geen H, Brueggeman R, Wanner G, Giet C (2007) Requirement of the C3HC4 zinc RING finger of the Arabidopsis PEX10 for photorespiration and leaf peroxisome contact with chloroplasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:1069–1074
Seifert GJ, Roberts K (2007) The biology of arabinogalactan proteins. Annu Rev Plant Biol 58:137–161
Seong ES, Choi D, Cho HS, Lim CK, Cho HJ, Wang MH (2007) Characterization of a stress-responsive ankyrin repeat-containing zinc finger protein of Capsicum annuum (CaKR1). J Biochem Mol Biol 40:952–958
Serpe MD, Nothnagel EA (1994) Effects of Yariv phenylglycosides on Rosa cell suspension: evidence for the involvement of arabinogalactan-proteins in cell proliferation. Planta 193:542–550
Serrano M, Guzman P (2004) Isolation and gene expression analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana mutants with constitutive expression of ATL2, an early elicitor-response RING-H2 zinc-finger gene. Genetics 167:919–929
Shi H, Kim Y, Guo Y, Stevenson B, Zhu JK (2003) The Arabidopsis SOS5 locus encodes a putative cell surface adhesion protein and is required for normal cell expansion. Plant Cell 15:19–32
Spitzer C, Schellmann S, Sabovljevic A, Shahriari M, Keshavaiah C, Bechtold N, Herzog M, Müller S, Hanisch FG, Hülskamp M (2006) The Arabidopsis elch mutant reveals functions of an ESCRT component in cytokinesis. Development 133:4679–4689
Srinivasan R, Mishra M, Wu L, Yin Z, Balasubramanian MK (2008) The bacterial cell division protein FtsZ assembles into cytoplasmic rings in fission yeast. Genes Dev 22:1741–1746
Suh MC, Hong CB, Kim SS, Sim WS (1994) Transgenic tobacco plants with Bacillus thuringiensis δ-endotoxin gene resistant to Korean born tobacco budworms. Mol Cells 4:211–719
Torii KU, McNellis TW, Deng XW (1998) Functional dissection of Arabidopsis COP1 reveals specific roles of its three structural modules in light control of seedling development. EMBO J 17:5577–5587
Vij S, Tyagi AK (2006) Genome-wide analysis of the associated protein (SAP) gene family containing A20/AN1 zinc-finger(s) in rice and their phylogenetic relationship with Arabidopsis. Mol Gen Genomics 276:171–565
Willats WGT, Knox JP (1996) A-role for arabinogalactan-proteins in plant cell expansions: evidence from studies on the interaction of β-glucosyl Yariv reagent with seedlings of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 9:919–925
Workman C, Jensen LJ, Jarmer H, Berka R, Gautier L, Nielser HB, Saxild HH, Nielsen C, Brunak S, Knudsen S (2002) A new non-linear normalization method for reducing variability in DNA microarray experiments. Genome biol 3:1–16
Wu H, Wong E, Ogdahi J, Cheung AY (2000) A pollen tube growth-promoting arabinogalactan protein from Nicotiana alata is similar to the tobacco TTS protein. Plant J 22:165–176
Xu R, Li QQ (2003) A RING-H2 zinc-finger protein gene RIE1 is essential for seed development in Arabidopsis. Plant Mol Biol 53:37–50
Yang J, Sardar HS, McGovern KR, Zhang Y, Showalter AM (2007) A lysine-rich arabinogalactan protein in Arabidopsis is essential for plant growth and development, including cell division and expansion. Plant J 49:629–640
Yoo CM, Wen J, Motes CM, Sparks JA, Blancaflor EB (2008) A class one ADP-ribosylation factor GTPase-activating protein is critical for maintaining directional root hair growth in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Physiol 147:1659–1674
Yu HJ, Hogan P, Sundaresan V (2005) Analysis of the female gametophyte transcriptome of Arabidopsis by comparative expression profiling. Plant Physiol 139:1853–1869
Yuan J, Kight A, Goforth RL, Moore M, Peterson EC, Sakon J, Henry R (2002) ATP stimulates signal recognition particle (SRP)/FtsY-supported protein integration in chloroplasts. J Biol Chem 277:32400–32404
Zeba N, Ashrafuzzaman M, Hong CB (2006) Molecular characterization of the Capsicum annuum RING Zinc Finger Protein 1 (CaRZFP1) gene induced by abiotic stresses. J Plant Biol 49:484–490
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants to Choo Bong Hong from the Crop Functional Genomics Center of the twenty-first century Frontier Research Program (code# CG1434) funded by the Ministry of Science and Technology of Korea and from the Priority Research Institute supported by the Korean Research Foundation (grant no. 2005-005-J16002). Naheed Zeba and Mohammad Isbat were partially supported by BK21 Research Fellowships from the Ministry of Education and Human Resources Development, Korea. Transformation, in vitro regeneration, and cultivation of tobacco plants were provided by Kab Lim Lee and Mi Jin Lee of Planta Co., Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
N. Zeba and M. Isbat contributed equally to the work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zeba, N., Isbat, M., Kwon, NJ. et al. Heat-inducible C3HC4 type RING zinc finger protein gene from Capsicum annuum enhances growth of transgenic tobacco. Planta 229, 861–871 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0884-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-008-0884-0