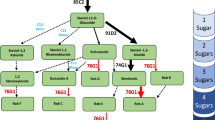
Abstract
Acetylajmalan esterase (AAE) plays an essential role in the late stage of ajmaline biosynthesis. Based on the partial peptide sequences of AAE isolated and purified from Rauvolfia cell suspensions, a full-length AAE cDNA clone was isolated. The amino acid sequence of AAE has the highest level of identity of 40% to putative lipases known from the Arabidopsis thaliana genome project. Based on the primary structure AAE is a new member of the GDSL lipase superfamily. The expression in Escherichia coli failed although a wide range of conditions were tested. With a novel virus-based plant expression system, it was possible to express AAE functionally in leaves of Nicotiana benthamiana Domin. An extraordinarily high enzyme activity was detected in the Nicotiana tissue, which exceeded that in Rauvolfia serpentina (L.) Benth. ex Kurz cell suspension cultures about 20-fold. This expression allowed molecular analysis of AAE for the first time and increased the number of functionally expressed alkaloid genes from Rauvolfia now to eight, and the number of ajmaline pathway-specific cDNAs to a total of six.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GFP:
-
Green fluorescent protein
- MSH:
-
2-Mercaptoethanol
- PMSF:
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
References
Barleben L, Ma X, Koepke J, Peng G, Michel H, Stöckigt J (2005) Expression, purification, crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of strictosidine glucosidase, an enzyme initiating biosynthetic pathways to a unique diversity of indole alkaloid skeletons. Biochim Biophys Acta 1747:89–92
Bayer A, Ma X, Stöckigt J (2004) Acetyltransfer in natural product biosynthesis—functional cloning and molecular analysis of vinorine synthase. Bioorg Med Chem 12:2787–2795
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cummins I, Edwards R (2004) Purification and cloning of an esterase from the weed black-grass (Alopecurus myosuroides), which bioactivates aryloxyphenoxypropionate herbicides. Plant J 39:894–904
Dogru E, Warzecha H, Seibel F, Haebel S, Lottspeich F, Stöckigt J (2000) The gene encoding polyneuridine aldehyde esterase of monoterpenoid indole alkaloid biosynthesis in plants is an ortholog of the α/β hydrolase super family. Eur J Biochem 267:1397–1406
Eckerskorn C, Lottspeich F (1989) Internal amino acid sequence analysis of proteins separated by gel electrophoresis after tryptic digestion in polyacrylamide matrix. Chromatographia 28:92–94
Eckerskorn C, Mewes W, Goretzky HC, Lottspeich F (1988) A new siliconized glass fiber as support for protein-chemical analysis of electroblotted proteins. Eur J Biochem 176:509–519
Gao S, von Schumann G, Stöckigt J (2002) A newly-detected reductase from Rauvolfia closes a gap in the biosynthesis of the antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline. Planta Med 68:906–911
Hampp N, Zenk MH (1988) Homogeneous strictosidine synthase from cell suspension cultures of Rauvolfia serpentina. Phytochemistry 27:3811–3815
Hemscheidt T, Zenk MH (1980) Glucosidases involved in indole alkaloid biosynthesis of Catharanthus cell cultures. FEBS Lett 101:187–191
Koepke J, Ma X, Fritzsch G, Michel H, Stöckigt J (2005) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray analysis of strictosidine synthase and its complex with the substrate tryptamine. Acta Crystallogr Sect D Biol Crystallogr 61:690–693
Kutchan TM (1993) Strictosidine: from alkaloid to enzyme to gene. Phytochemistry 32:493–506
Linsmaier EM, Skoog F (1965) Organic growth factor requirements of tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 18:100–127
Ma X, Koepke J, Fritzsch G, Diem R, Kutchan TM, Michel H, Stöckigt J (2004a) Crystallization and preliminary X-ray crystallographic analysis of strictosidine synthase from Rauvolfia – the first member of a novel enzyme family. Biochim Biophys Acta 1702:121–124
Ma X, Koepke J, Bayer A, Linhard V, Fritzsch G, Zhang B, Michel H, Stöckigt J (2004b) Vinorine synthase from Rauvolfia – the first example of crystallization and preliminary X-ray diffraction analysis of an enzyme of the BAHD superfamily. Biochim Biophys Acta 1701:129–132
Ma X, Koepke J, Panjikar S, Fritzsch G, Stöckigt J (2005) Crystal structure of vinorine synthase, the first representative of the BAHD superfamily. J Biol Chem 280:13576–13583
Marillonnet S, Giritch A, Gils M, Kandzia R, Klimyuk V, Gleba Y (2004) In planta engineering of viral RNA replicons: efficient assembly by recombination of DNA modules delivered by Agrobacterium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6852–6857
Mattern-Dogru E, Ma X, Hartmann J, Decker H, Stöckigt J (2002) Potential active-site residues in polyneuridine aldehyde esterase, a central enzyme of indole alkaloid biosynthesis, by modelling and site-directed mutagenesis. Eur J Biochem 269:2889–2896
Polz L, Schübel H, Stöckigt J (1987) Characterization of 2β-(R)-17- 0-acetylajmalan: acetylesterase – a specific enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of the Rauwolfia alkaloid ajmaline. Z Naturforsch 42c:333–342
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 3rd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor
Sato F, Hashimoto T, Hachiya A, Tamura K, Choi KB, Morishige T, Fujimoto H, Yamada Y (2001) Metabolic engineering of plant alkaloid biosynthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:367–372
von Schumann G, Gao S, Stöckigt J (2002) Vomilenine reductase—a novel enzyme catalyzing a crucial step in the biosynthesis of the therapeutically applied antiarrhythmic alkaloid ajmaline. Bioorg Med Chem 10:1913–1918
Stöckigt J (1995) Biosynthesis in Rauwolfia serpentina—modern aspects of an old medicinal plant. In: Cordell GA (ed) The alkaloids, vol 47. Academic, San Diego, pp 115–172
Treimer JF, Zenk MH (1979) Purification and properties of strictosidine synthase, the key enzyme in indole alkaloid formation. Eur J Biochem 101:225–233
Vazquez-Flota FA, De Luca V (1998) Jasmonate modulates development- and light-regulated alkaloid biosynthesis in Catharanthus roseus. Phytochemistry 49:395–402
Walker K, Croteau R (2001) Taxol biosynthetic genes. Phytochemistry 58:1–7
Weid M, Ziegler J, Kutchan TM (2004) The roles of latex and the vascular bundle in morphine biosynthesis in the opium poppy, Papaver somniferum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:13957–13962
Zenk MH (1995) Chasing the enzymes of alkaloid biosynthesis. In: Golding BT, Griffin RJ, Maskill H (eds) Organic reactivity: Physical and biological aspects. The Royal Society of Chemistry, Newcastle upon Tyne, pp 89–109
Zenk MH, Stöckigt J (1977) Strictosidine (Isovincoside): the key intermediate in the biosynthesis of monoterpenoid indole alkaloids. J Chem Soc Chem Commun 269:646–648
Acknowledgements
E. Genady and J. Woll thank the Botschaft der Arabischen Republik Ägypten and the Landesgraduiertenförderung (Rheinland-Pfalz, Germany) for a grant. Dr. G. v. Schumann is acknowledged for excellent assistance in enzyme purification. We also thank Prof. F. Lottspeich, R. Mentele (Martinsried, Germany) for performing partial protein sequencing, Prof. Y. Gleba, Dr. V. Klimyuk (Halle, Germany) and Prof. T. Kutchan (Halle, Germany) for helpful suggestions and linguistic help. This research was supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Bonn, Bad-Godesberg, Germany), Fonds der Chemischen Industrie (Frankfurt/Main, Germany) and Bundesministerium für Bildung und Wissenschaft (Berlin, Germany).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence reported in this article has been submitted to the GenBank/EBI under GenBank Accession no. AY762990
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ruppert, M., Woll, J., Giritch, A. et al. Functional expression of an ajmaline pathway-specific esterase from Rauvolfia in a novel plant-virus expression system. Planta 222, 888–898 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0031-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-005-0031-0