Abstract
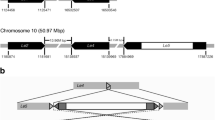
The lemma and palea (lemma/palea), which form the husk of barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) seeds, constitutively express high levels of defense-related genes, relative to leaves [Abebe et al. (2004) Crop Sci 44:942–950]. One of these genes, Lem2, is expressed mainly in the lemma/palea and coleoptile and is strongly upregulated by salicylic acid (SA) and its functional analog 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid . Induction by SA was rapid, occurring within 4 h of treatment. However, Lem2 is not responsive to methyl jasmonate (MeJA) or wounding and is downregulated by drought, dehydration, and abscisic acid. These results suggest that Lem2 is involved in systemic acquired resistance. Sequence analysis showed that LEM2 is a jacalin-related lectin (JRL)-like protein with two domains. Consistent with northern and western blot data, transient expression analyses using Lem2::gfp constructs showed strong expression in lemmas and a trace expression in leaves. Successive 5′ deletions of the 1,414 bp upstream region gradually weakened promoter strength, as measured by real-time PCR. Promoter deletion studies also revealed that the −75/+70 region (containing the TATA box, 5′ UTR, and a SA-response element) determines tissue specificity and that the distal promoter region simply enhances expression. Southern analysis indicated that Morex barley has at least three copies of the Lem2 gene arranged in tandem on chromosome 5(1H) Bin 02, near the short arm telomere. Lem2 is not present in the barley cultivars Steptoe, Harrington, Golden Promise, and Q21861.









Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABA:
-
Abscisic acid
- ABRE:
-
Abscisic acid response element
- ERE:
-
Ethylene response element
- HSE:
-
Heat shock element
- Gal:
-
Galactose
- Glc:
-
Glucose
- HR:
-
Hypersensitive response
- INA:
-
2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic acid
- JA:
-
Jasmonate
- JRL:
-
Jacalin-related lectin
- Man:
-
Mannose
- MeJA:
-
Methyl-jasmonate
- PAGE:
-
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis
- PR:
-
Pathogenesis-related
- RACE:
-
Rapid amplification of cDNA ends
- SA:
-
Salicylic acid
- SAR:
-
Systemic acquired resistance
References
Abebe T, Skadsen RW, Kaeppler HF (2004) Cloning and identification of highly expressed genes in barley lemma and palea. Crop Sci 44:942–950
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Bannai H, Tamada Y, Maruyama O, Nakai K, Miyano S (2002) Extensive feature detection of N-terminal protein sorting signals. Bioinformatics 18:298–305
Chirgwin JM, Prybyla A, MacDonald RJ, Rutter WJ (1979) Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry 18:5294–5299
Chisholm ST, Parra MA, Anderberg RJ, Carrington JC (2001) Arabidopsis RTM1 and RTM2 genes function in phloem to restrict long-distance movement of tobacco etch virus. Plant Physiol 127:1667–1675
Chiu W-L, Niwa Y, Zeng W, Hirano T, Kobayashi H, Sheen J (1996) Engineered GFP as a vital reporter in plants. Curr Biol 6:325–330
Christensen AH, Quail PH (1996) Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Res 5:213–218
Claes B, Dekeyser R, Villaroel R, Van den Bulcke M, Bauw G, Van Montagu M, Caplan A (1990) Characterization of a rice gene showing organ-specific expression in response to salt stress and drought. Plant Cell 2:19–27
Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
De Souza Filho GA, Ferreira BS, Dias GM, Queiroz SK, Branco AT, Bressan-Smith RE, Oliveira JG, Garcia AB (2003) Accumulation of SALT protein in rice plants as a response to environmental stresses. Plant Sci 164:623–628
Feys BJ, Parker JE (2000) Interplay of signaling pathways in plant disease resistance. Trends Genet 16:449–455
Friedrich L, Lawton K, Ruess W, Masner P et al (1996) A benzothiadiazole derivate induces systemic acquired resistance in tobacco. Plant J 10:61–70
Gaffney T, Friedrich L, Vernooij B, Negrotto D, Nye G, Uknes S, Ward E, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1993) Requirement of salicylic acid for the induction of systemic acquired resistance. Science 261:754–756
Garcia AB, Engler JA, Claes B, Villarroel R, Van Montagu M, Gerats T, Caplan A (1998) The expression of the salt-responsive gene salT from rice is regulated by hormonal and developmental cues. Planta 207:172–180
Geer LY, Domrachev M, Lipman DJ, Bryant SH (2002) CDART: protein homology by domain architecture. Genome Res 12:1619–1623
Geshi N, Brandt A (1998) Two jasmonate-inducible MBPs from Brassica napus L. seedlings with homology to jacalin. Planta 204:295–304
Gorlach J, Volrath S, Knauf-Beiter G, Hengy G, Beckhove U, Kogel KH, Oostendorp M, Staub T, Ward E, Kessman H, Ryals J (1996) Benzothiadiazole, a novel class of inducers of systemic acquired resistance, activates gene expression and disease resistance in wheat. Plant Cell 8:629–643
Gupta V, Willits MG, Glazebrook J (2000) Arabidopsis thaliana EDS4 contributes to salicylic acid (SA)-dependent expression of defense responses: evidence for inhibition of jasmonic acid signalling by SA. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:503–511
Hammond-Kosack KE, Jones JDG (1996) Resistance gene-dependent plant defense responses. Plant Cell 8:1773–1791
Hammond-Kosack K, Jones JDG (2000) Response to plant pathogens. In: Buchanan BB, Gruissem W, Jones RL (eds) Biochemistry and molecular biology of plants. American Society of Plant Physiologists, Rockville, pp 1102–1156
Heath MC (2000) Hypersensitive response-related death. Plant Mol Biol 44:321–334
Horvath DM, Huang DJ, Chua N-H (1998) Four classes of salicylate-induced tobacco genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:895–905
Kaeppler H, Menon G, Skadsen R, Nuutila A, Carlson A (2000) Transgenic oat plants via visual selection of cells expressing green fluorescent protein. Plant Cell Rep 19:661–666
Kim ST, Kim SG, Hwang DH, Kang SY, Koo SC, Cho MJ, Kang KY (2004) Expression of a salt-induced protein (SALT) in suspension-cultured cells and leaves of rice following exposure to fungal elicitor and phytohormones. Plant Cell Rep 23(4):256–262
Kunkel BN, Brooks DM (2002) Crosstalk between signaling pathways in pathogen defense. Curr Opin Plant Biol 5:325–331
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Lawton K, Friedrich L, Hunt M, Weymann K, Delaney T, Kessmann H, Staub T, Ryals J (1996) Benzothiadiazole induces disease resistance in Arabidopsis by activation of the systemic acquired resistance signal transduction pathway. Plant J 10:71–82
Lee J, Parthier B, Löbler M (1996) Jasmonate signalling can be uncoupled from abscisic acid signalling in barley: identification of jasmonate-regulated transcripts which are not induced by abscisic acid. Planta 199:625–632
Lescot M, Dèhais P, Thijs J, Marchal K, Moreau Y, Van de Peer Y, Rouzé P, Rombauts S (2002) PlantCARE, a database of plant cis-acting regulatory elements and a portal to tools for in silico analysis of promoter sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 30:325–327
Lin X, Kaul S, Rounsley SD et al (1999) Sequence and analysis of chromosome 2 of the plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 402:761–768
Mann K, Farias CM, DelSol FG, Santos CF, Grangeiro TB, Nagano CS, Cavada BS, Calvete JJ (2001) The amino-acid sequence of the glucose/mannose-specific lectin isolated from Parkia platycephala seeds reveals three tandemly arranged jacalin-related domains. Eur J Biochem 268:4414–4422
Murray HG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Murray SL, Thomson C, Chini A, Read ND, Loake GJ (2002) Characterisation of a novel defense-related Arabidopsis mutant, cir1, isolated by luciferase imaging. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:557–566
Nakamura S, Ikegami A, Matsumura Y, Nakanishi T, Nomura K (2002) Molecular cloning and expression of the mannose/glucose specific lectin from Castanea crenata cotyledons. J Biochem (Tokyo) 131:241–246
Niki T, Mitsuhara I, Seo S, Ohtsubo N, Ohashi Y (1998) Antagonistic effect of salicylic acid and jasmonic acid on the expression of pathogenesis-related (PR) protein genes in wounded mature tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 39:500–507
Norman-Setterblad C, Vidal S, Palva ET (2000) Interacting signal pathways control defense gene expression in Arabidopsis in response to cell wall-degrading enzymes from Erwinia carotovora. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:430–438
Penninckx IAMA, Eggermont K, Terras FRG, Thomma BPHJ, Samblanx GWD, Buchala A, Metraux J-P, Manners JM, Broekaert WF (1996) Pathogen-induced systemic activation of a plant defensin gene in Arabidopsis follows a salicylic acid-independent pathway. Plant Cell 8:2309–2323
Peumans WJ, Van Damme EJM (1995) Lectins as plant defense proteins. Plant Physiol 109:347–352
Peumans WJ, Winter HC, Bemer V, Van Leuven F, Goldstein IJ, Truffa-Bachi P, Van Damme EJM (1997) Isolation of a novel plant lectin with an unusual specificity from Calystegia sepium. Glycoconjugate J 14:259–265
Peumans WJ, Hause B, Van Damme EJ (2000) The galactose-binding and mannose-binding jacalin-related lectins are located in different sub-cellular compartments. FEBS Lett 477:186–192
Preston CA, Lewandowski C, Enyedi AJ, Baldwin IT (1999) Tobacco mosaic virus inoculation inhibits wound-induced jasmonic acid-mediated responses within but not between plants. Planta 209:87–95
Qin XF, Holuigue L, Horvath DM, Chua N-H (1994) Immediate early transcription activation by salicylic acid via the cauliflower mosaic virus as-1 element. Plant Cell 6:863–874
Reymond P, Weber H, Damond M, Farmer EE (2000) Differential gene expression in response to mechanical wounding and insect feeding in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 12:707–719
Rosa JC, De Oliveira PSL, Garratt R, Beltramini L, Resing K, Roque-Barreira M-C, Greene LJ (1999) KM+, a mannose-binding lectin from Artocarpus integrifolia: amino acid sequence, predicted tertiary structure, carbohydrate recognition, and analysis of the beta-prism fold. Protein Sci 8:13–24
Rouster J, Van Mechelen J, Cameron-Mills V (1998) The untranslated leader sequence of the barley lipoxygenase 1 (Lox1) gene confers embryo-specific expression. Plant J 15:435–440
Roy A, Banerjee S, Majumder P, Das S (2002) Efficiency of mannose-binding plant lectins in controlling a Hemopteran insect, the red cotton bug. J Agric Food Chem 50:6775–6779
Ryals JA, Neuenschwander UH, Willits MG, Molina A, Steiner H-Y, Hunt MD (1996) Systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 8:1809–1819
Sasaki T, Matsumoto T, Yamamoto K et al (2002) The genome sequence and structure of rice chromosome 1. Nature 420:312–316
Schweizer P, Buchala A, Métraux J-P (1997) Gene-expression patterns and levels of jasmonic acid in rice treated with the resistance inducer 2,6-dichloroisonicotinic acid. Plant Physiol 115:61–70
Skaden RW, Schulze-Lefert P, Herbst JM (1995) Molecular cloning, characterization and expression analysis of two catalase isozyme genes in barley. Plant Mol Biol 29:1005–1014
Skadsen RW, Sathish P, Kaeppler HF (2000) Expression of thaumatin-like permatin PR-5 genes switches from the ovary wall to the aleurone in developing barley and oat seeds. Plant Sci 156:11–22
Skadsen RW, Sathish P, Federico ML, Abebe T, Fu J, Kaeppler HF (2002) Cloning of the promoter for a novel barley gene, Lem1, and its organ-specific promotion of gfp expression in lemma and palea. Plant Mol Biol 49:545–555
Stomp AM (1992) GUS protocol: using the GUS gene reporter of gene expression. Academic Press, New York, pp 103–112
Thaler JS, Karban R, Ullman DE, Boege K, Bostock RM (2002) Cross-talk between jasmonate and salicylate plant defense pathways: effects on several plant parasites. Oecologia 131:227–235
Thomma BP, Penninckx IA, Broekaert WF,Cammue BP (2001) The complexity of disease signaling in Arabidopsis. Curr Opin Immunol 13:63–68
Uknes S, Dincher S, Friedrich L, Negrotto D, Williams S, Thompson-Taylor H, Potter S, Ward E, Ryals J (1993) Regulation of pathogenesis-related protein-1a gene expression in tobacco. Plant Cell 5:159–169
Van Damme EJ, Barre A, Verhaert P, Rougé P, Peumans WJ (1996) Molecular cloning of the mitogenic mannose/maltose-specific rhizome lectin from Calystegia sepium. FEBS Lett 397:352–356
Van Damme EJM, Peumans WJ, Barre A, Rougé P (1998) Plant lectins: a composite of several distinct families of structurally and evolutionary related proteins with diverse biological roles. Crit Rev Plant Sci 17:575–692
Van Damme EJ, Barre A, Mazard AM, Verhaert P, Horman A, Debray H, Rouge P, Peumans WJ (1999a) Characterization and molecular cloning of the lectin from Helianthus tuberosus. Eur J Biochem 259:135–142
Van Damme EJM, Charels D, Roy S, Tierens K, Barre A, Martins JC, Rougé P, Van Leuven F, Does M, Peumans WJ (1999b) A Gene encoding a hevein-like protein from elderberry fruits is homologous to PR-4 and class V chitinase genes. Plant Physiol 119:1547–1556
Van Damme EJM, Hause B, Hu J, Barre A, Rougé P, Proost P, Peumans WJ (2002) Two distinct jacalin-related lectins with a different specificity and subcellular location are major vegetative storage proteins in the bark of the black mulberry tree. Plant Physiol 130:757–769
Vernooij B, Friedrich L, Ahl-Goy P, Staub T, Kessmann H, Ryals J (1995) 2,6-Dichloroisonicotinic acid-induced resistance to pathogens without the accumulation of salicylic acid. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 8:228–234
Walling LL (2000) The myrad plant responses to herbivores. J Plant Growth Regul 19:195–216
Wan Y, Lemaux P (1994) Generation of large numbers of independently transformed fertile barley plants. Plant Physiol 104:37–48
Ward ER, Uknes SJ, Williams SC, Dincher SS, Wiederhold DL, Alexander DC, Ahl-Goy P, Metraux J-P, Ryals JA (1991) Coordinate gene activity in response to agents that induce systemic acquired resistance. Plant Cell 3:1085–1094
Williams CE, Collier CC, Nemacheck JA, Liang C, Cambron SE (2002) A lectin-like wheat gene responds systemically to attempted feeding by avirulent first-instar Hessian fly larvae. J Chem Ecol 28:1411–1428
Xiang C, Miao ZH, Lam E (1996) Coordinated activation of as-1 type elements and a tobacco gluthatione S-transferase gene by auxins, salicylic acid, methyl-jasmonate and hydrogen peroxide. Plant Mol Biol 32:415–426
Xu Q, Liu Y, Wang X, Gu H, Chen Z (1998) Purification and characterization of a novel anti-fungal protein from Gastrodia elata. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:899–905
Yu Y, Tomkins JP, Waugh R, Frisch DA, Kudrna D, Kleinhofs A, Brueggeman RS, Muehlbauer GJ, Wise RP, Wing RA (2000) A bacterial artificial chromosome library for barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) and the identification of clones containing putative resistance genes. Theor Appl Genet 101:1093–1099
Zhang W, Peumans WJ, Barre A, Astoul CH, Rovira P, Rouge P, Proost P, Truffa-Bachi P, Jalali AA, Van Damme EJ (2000) Isolation and characterization of a jacalin-related mannose-binding lectin from salt-stressed rice (Oryza sativa) plants. Planta 210:970–978
Acknowledgements
We thank John Herbst, Laura Oesterle, Janelle Young, Sarah Olsen, and Josh Ladwig for their technical assistance. We thank Maria Laura Federico for assistance with real-time PCR. We also thank Andris Kleinhofs for mapping Lem2 and providing Lem2-containing BAC clones. This work was supported by the North American Barley Genome Mapping Project, the American Malting Barley Association, and the United States Department of Agriculture, CRIS number 3655-21430-006-00D.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mention of trade names or commercial products in this article is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U. S. Department of Agriculture
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abebe, T., Skadsen, R.W. & Kaeppler, H.F. A proximal upstream sequence controls tissue-specific expression of Lem2, a salicylate-inducible barley lectin-like gene. Planta 221, 170–183 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1429-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1429-9