Abstract
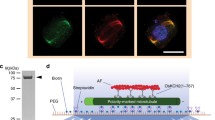
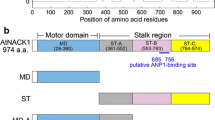
During plant cytokinesis, kinesin-related motor proteins are believed to play critical roles in microtubule organization and vesicle transport in the phragmoplast. Previously, we reported that the motor AtPAKRP1 was associated with the plus end of phragmoplast microtubules in Arabidopsis thaliana [Lee Y-RJ, Liu B (2000) Curr Biol 10:797–800]. In this paper, we report a full-length cDNA from the same organism, which encodes a polypeptide 74% identical to AtPAKRP1. This AtPAKRP1-like protein—AtPAKRP1L—and AtPAKRP1 share similar domain structures along the polypeptides. Peptide antibodies were raised and purified to distinguish the two polypeptides in vitro and in vivo. When monospecific anti-AtPAKRP1 and anti-AtPAKRP1L antibodies were used in immunofluorescence, they both decorated the plus end of phragmoplast microtubules at all stages of phragmoplast development. Their localization patterns were indistinguishable from each other. By using bacterially expressed fusion proteins of motor-less versions of both polypeptides, it was revealed that AtPAKRP1 and AtPAKRP1L were able to interact with themselves and with each other. Using T-DNA insertional mutants, it was also demonstrated that AtPAKRP1 and AtPAKRP1L were not required for each other’s localization. Our results therefore indicate that AtPAKRP1 and AtPAKRP1L are both expressed in the same cells, and likely have identical functions in the phragmoplast by forming either homodimers or heterodimers.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AtPAKRP1 :
-
Arabidopsis thaliana phragmoplast-associated kinesin-related protein 1
- AtPAKRP1L :
-
A. thaliana phragmoplast-associated kinesin-related protein 1-like
- GST :
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- KRP :
-
Kinesin-related protein
- 6×His :
-
Six-histidine tag
References
Asada T, Kuriyama R, Shibaoka H (1997) TKRP125, a kinesin-related protein involved in the centrosome-independent organization of the cytokinetic apparatus in tobacco BY-2 cells. J Cell Sci 110:179–189
Barroso C, Chan J, Allan V, Doonan J, Hussey P, Lloyd C (2000) Two kinesin-related proteins associated with the cold-stable cytoskeleton of carrot cells: characterization of a novel kinesin, DcKRP120–2. Plant J 24:859–868
Bowser J, Reddy ASN (1997) Localization of a kinesin-like calmodulin-binding protein in dividing cells of Arabidopsis and tobacco. Plant J 12:1429–1437
Chen C, Marcus A, Li W, Hu Y, Calzada J, Grossniklaus U, Cyr R, Ma H (2002) The Arabidopsis ATK1 gene is required for spindle morphogenesis in male meiosis. Development 129:2401–2409
Galjart N, Perez F (2003) A plus-end raft to control microtubule dynamics and function. Curr Opin Cell Biol 15:48–53
Guan KL, Dixon JE (1991) Eukaryotic proteins expressed in Escherichia coli: an improved thrombin cleavage and purification procedure of fusion proteins with glutathione S-transferase. Anal Biochem 192:262–267
Ishikawa M, Soyano T, Nishihama R, Machida Y (2002) The NPK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase contains a functional nuclear localization signal at the binding site for the NACK1 kinesin-like protein. Plant J 32:789–798
Krysan P, Young J, Sussman M (1999) T-DNA as an insertional mutagen in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 11:2283–2290
Krysan P, Jester P, Gottwald J, Sussman M (2002) An Arabidopsis mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase gene family encodes essential positive regulators of cytokinesis. Plant Cell 14:1109–1120
Lee YRJ, Liu B (2000) Identification of a phragmoplast-associated kinesin-related protein in higher plants. Curr Biol 10:797–800
Lee YRJ, Giang HM, Liu B (2001) A novel plant kinesin-related protein specifically associates with the phragmoplast organelles. Plant Cell 13:2427–2439
Liu B, Lee YRJ (2001) Kinesin-related proteins in plant cytokinesis. J Plant Growth Regul 20:141–150
Liu B, Cyr RJ, Palevitz BA (1996) A kinesin-like protein, KatAp, in the cells of Arabidopsis and other plants. Plant Cell 8:119–132
Marcus A, Li W, Ma H, Cyr R (2003) A kinesin mutant with an atypical bipolar spindle undergoes normal mitosis. Mol Biol Cell 14:1717–1726
McElver J, Patton D, Rumbaugh M, Liu CM, Yang LJ, Meinke D (2000) The TITAN5 gene of Arabidopsis encodes a protein related to the ADP ribosylation factor family of GTP binding proteins. Plant Cell 12:1379–1392
Mitsui H, Hasezawa S, Nagata T, Takahashi H (1996) Cell cycle-dependent accumulation of a kinesin-like protein, KatB/C in synchronized tobacco BY-2 cells. Plant Mol Biol 30:177–181
Nishihama R, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Soyano T, Asada T, Machida Y (2001) The NPK1 mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase is a regulator of cell-plate formation in plant cytokinesis. Genes Dev 15:352–363
Nishihama R, Soyano T, Ishikawa M, Araki S, Tanaka H, Asada T, Irie K, Ito M, Terada M, Banno H et al (2002) Expansion of the cell plate in plant cytokinesis requires a kinesin-like protein/MAPKKK complex. Cell 109:87–99
Preuss M, Delmer D, Liu B (2003) The cotton kinesin-like calmodulin-binding protein associates with cortical microtubules in cotton fibers. Plant Physiol 132:154–160
Reddy ASN, Day IS (2001) Kinesins in the Arabidopsis genome: a comparative analysis among eukaryotes. Biomed Cent Genomics 2:2
Smirnova EA, Reddy ASN, Bowser J, Bajer AS (1998) Minus end-directed kinesin-like motor protein, KCBP, localizes to anaphase spindle poles in Haemanthus endosperm. Cell Motil Cytoskeleton 41:271–280
Smith LG (2002) Plant cytokinesis: motoring to the finish. Curr Biol 12:R206–R209
Strompen G, El Kasmi F, Richter S, Lukowitz W, Assaad FF, Jurgens G, Mayer U (2002) The Arabidopsis HINKEL gene encodes a kinesin-related protein involved in cytokinesis and is expressed in a cell cycle-dependent manner. Curr Biol 12:153–158
Vale RD, Fletterick RJ (1997) The design plan of kinesin motors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 13:745–777
Vos JW, Safadi F, Reddy ASN, Hepler PK (2000) The kinesin-like calmodulin binding protein is differentially involved in cell division. Plant Cell 12:979–990
Wittmann T, Boleti H, Antony C, Karsenti E, Vernos I (1998) Localization of the kinesin-like protein XKLP2 to spindle poles requires a leucine zipper, a microtubule-associated protein, and dynein. J Cell Biol 143:673–685
Yang C, Spielman M, Coles J, Li Y, Ghelani S, Bourdon V, Brown R, Lemmon B, Scott R, Dickinson H (2003) TETRASPORE encodes a kinesin required for male meiotic cytokinesis in Arabidopsis. Plant J 34:229–240
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the United States Department of Agriculture (grant no. CSREES/NRICGP 2001-35304-01913). We would like to thank the Kazusa DNA Institute, Arabidopsis Biological Research Center, the University of Wisconsin Biotechnology Center, and the Syngenta Terrey Mesa Research Institute for providing cDNA clones and mutant screening services.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, R., Lee, YR.J. & Liu, B. Localization of two homologous Arabidopsis kinesin-related proteins in the phragmoplast. Planta 220, 156–164 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1324-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1324-4