Abstract
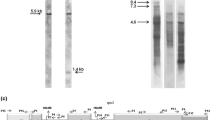
Some species of the holoparasitic flowering plant genus Cuscuta, like C. reflexa, have retained a plastid genome that encodes photosynthesis-related gene products as well as the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase (PEP). In contrast, other species like C. gronovii and C. subinclusa have lost the rpo genes coding for the PEP subunits while photosynthetic genes have been retained. In order to ensure expression of the photosynthesis-related genes in the absence of PEP, a number of adaptations within the plastid genome were required that enable gene transcription mediated exclusively by the nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase (NEP). In this study we analyzed promoter sequence conservation and transcription start sites of a typical PEP gene of non-parasitic plants, rbcL, which codes for the large subunit of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase. We show that despite high sequence conservation of the coding region of rbcL among different Cuscuta species and tobacco, the 5′ non-coding regions of C. gronovii and C. subinclusa have suffered extensive deletions encompassing the PEP promoter that is present in C. reflexa and tobacco. Primer-extension analyses enabled the identification of transcripts initiated at NEP promoter motifs in C. gronovii and C. subinclusa that are not detectable in the 5′ non-coding region of C. reflexa.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- atpB :
-
Gene coding for the β-subunit of the plastid ATPase
- NEP :
-
Nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase
- PEP :
-
Plastid-encoded plastid RNA polymerase
- rbcL :
-
Gene coding for the large subunit of Rubisco
- Rubisco :
-
Ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase
References
Allison LA, Simon LD, Maliga P (1996) Deletion of rpoB reveals a second distinct transcription system in plastids of higher plants. EMBO J 15:2802–2809
Bligny M, Courtois F, Thaminy S, Chang C-C, Lagrange T, Baruh-Wolff J, Stern D, Lerbs-Mache S (2000) Regulation of plastid rDNA transcription by interaction of CDF2 with two different RNA polymerases. EMBO J 19:1851–1860
Chang CC, Sheen J, Bligny M, Niwa Y, Lerbs-Mache S, Stern DB (1999) Functional analysis of two maize cDNAs encoding T7-like RNA polymerases. Plant Cell 11:911–926
deSantis-Maciossek G, Kofer W, Bock A, Schoch S, Maier RM, Wanner G, Rüdiger W, Koop HU, Herrmann RG (1999) Targeted disruption of the plastid RNA polymerase genes rpoA, B and C1: molecular biology, biochemistry and ultrastructure. Plant J 18:477–489
Falk J, Schmidt A, Krupinska K (1993) Characterization of plastid DNA transcription in ribosome deficient plastids of heat-bleached barley leaves. J Plant Physiol 141:176–181
Haberhausen G, Zetsche K (1994) Functional loss of all ndh genes in an otherwise relatively unaltered plastid genome of the holoparasitic flowering plant Cuscuta reflexa. Plant Mol Biol 24:217–222
Haberhausen G, Valentin K, Zetsche K (1992) Organisation and sequence of photosynthetic genes from the plastid genome of the holoparasitic flowering plant Cuscuta reflexa. Mol Gen Genet 232:154–161
Hajdukiewicz PTJ, Allison LA, Maliga P (1997) The two RNA polymerases encoded by the nuclear and the plastid compartments transcribe distinct groups of genes in tobacco plastids. EMBO J 16:4041–4048
Hedtke B, Börner T, Weihe A (1997) Mitochondrial and chloroplast phage-type RNA polymerases in Arabidopsis. Science 277:809–811
Hess W, Börner T (1999) Organellar RNA polymerases of higher plants. Int Rev Cytol 190:1–59
Hess W, Prombona A, Fiedler B, Subramanian A, Börner T (1993) Chloroplast rps15 and the rpoB/C1/C2 gene cluster are strongly transcribed in ribosome-deficient plastids: evidence for a functioning non-chloroplast-encoded RNA polymerase. EMBO J 12:563–571
Hibberd JM, Bungard RA, Press MC, Jeschke WD, Scholes JD, Quick WP (1998) Localization of photosynthetic metabolism in the parasitic angiosperm Cuscuta reflexa. Planta 205:506–513
Hübschmann T, Börner T (1998) Characterization of transcript initiation sites in ribosome-deficient barley plastids. Plant Mol Biol 36:493–496
Igloi T, Kössel H (1992) The transcriptional apparatus of chloroplasts. Crit Rev Plant Sci 10:525–558
Kapoor S, Suzuki J, Sugiura M (1997) Identification and functional significance of a new class of non-consensus-type plastid promoters. Plant J 11:327–337
Krause K, Maier RM, Kofer W, Krupinska K, Herrmann RG (2000) Disruption of plastid-encoded RNA polymerase genes in tobacco: expression of only a distinct set of genes is not based on selective transcription of the plastid chromosome. Mol Gen Genet 263:1022–1030
Krause K, Berg S, Krupinska K (2003) Plastid transcription in the holoparasitic plant genus Cuscuta: parallel loss of the rrn16 PEP-promoter and of the rpoA and rpoB genes coding for the plastid-encoded RNA polymerase. Planta 216:815–823
Legen J, Kemp S, Krause K, Profanter B, Herrmann R, Maier R (2002) Comparative analysis of plastid transcription profiles of entire plastid chromosomes from tobacco attributed to wild-type and PEP-deficient transcription machineries. Plant J 31:171–188
Liere K, Maliga P (1999) In vitro characterization of the tobacco rpoB promoter reveals a core sequence motif conserved between phage-type plastid and plant mitochondrial promoter. EMBO J 18:249–257
Liere K, Maliga P (2001) Plastid RNA polymerases in higher plants. Regulation of photo-synthesis. In: Aro E-M, Anderson B (eds) Kluwer, Rotterdam, pp 29–39
Lusson N, Delavault PM, Thalouarn PA (1998) The rbcL gene from the nonphotosynthetic parasite Lathraea clandestina is not transcribed by a plastid-encoded RNA polymerase. Curr Genet 34:210–215
Maliga P (1998) Two plastid RNA polymerases of higher plants: an evolving story. Trends Plant Sci 3:4–6
Miyagi T, Kapoor S, Sugita M, Sugiura M (1998) Transcript analysis of the tobacco plastid operon rps2/atpI/H/F/A reveals the existence of a non-consensus type II (NCII) promoter upstream of the atpI coding sequence. Mol Gen Genet 257:299–307
Morden CW, Wolfe KH, dePamphilis CW, Palmer JD (1991) Plastid translation and transcription genes in a non-photosynthetic plant: intact, missing and pseudo genes. EMBO J 10:3281–3288
Mullet JE, Orozco EM, Chua N-H (1985) Multiple transcripts for higher plant rbcL and atpB genes and localization of the transcription initiation site of the rbcL gene. Plant Mol Biol 4:35–54
Orozco EM Jr, Chen LJ, Eiler RJ (1990) The divergently transcribed rbcL and atpB genes of tobacco plastid DNA are separated by nineteen base pairs. Curr Genet 17:65–71
Shinozaki K, Sugiura M (1982) The nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast gene for the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase-oxygenase. Gene 20:91–102
Silhavy D, Maliga P (1998) Mapping of promoters for the nucleus-encoded plastid RNA polymerase (NEP) in the iojap maize mutant. Curr Genet 33:340–344
Thalouarn P, Theodet C, Russo N, Delavault P (1994) The reduced plastid genome of a non-photosynthetic angiosperm Orobanche hederae has retained the rbcL gene. Plant Physiol Biochem 32:233–242
van der Kooij TAW, Krause K, Dörr I, Krupinska K (2000) Molecular, functional and ultrastructural characterisation of plastids from six species of the parasitic flowering plant genus Cuscuta. Planta 210:701–707
Vera A, Sugiura M (1992) Combination of in vitro capping and ribonuclease protection improves the detection of transcription start sites in chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol 19:309–311
Wakasugi T, Sugita M, Tsudzuki T, Sugiura M (1998) Updated map of tobacco chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol Rep 16:231–241
Weihe A, Börner T (1999) Transcription and the architecture of promoters in chloroplasts. Trends Plant Sci 4:169–170
Wolfe KH, Morden CW, Palmer JD (1992) Function and evolution of a minimal plastid genome from a non-photosynthetic parasitic plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:10648–10652
Xie G, Allison LA (2002) Sequences upstream of the YRTA core region are essential for transcription of the tobacco atpB NEP promoter in chloroplasts in vivo. Curr Genet 41:176–182
Acknowledgement
S. Berg received a PhD grant from the Friedrich-Naumann foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, S., Krause, K. & Krupinska, K. The rbcL genes of two Cuscuta species, C. gronovii and C. subinclusa, are transcribed by the nuclear-encoded plastid RNA polymerase (NEP). Planta 219, 541–546 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1260-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1260-3