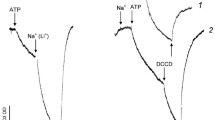
Abstract
Our previous investigations have established that Na+ translocation across the Tetraselmis viridis plasma membrane (PM) mediated by the primary ATP-driven Na+-pump, Na+-ATPase, is accompanied by H+ counter-transport [Y.V. Balnokin et al. (1999) FEBS Lett 462:402–406]. The hypothesis that the Na+-ATPase of T. viridis operates as an Na+/H+ exchanger is tested in the present work. The study of Na+ and H+ transport in PM vesicles isolated from T. viridis demonstrated that the membrane-permeant anion NO3 − caused (i) an increase in ATP-driven Na+ uptake by the vesicles, (ii) an increase in (Na++ATP)-dependent vesicle lumen alkalization resulting from H+ efflux out of the vesicles and (iii) dissipation of electrical potential, Δψ, generated across the vesicle membrane by the Na+-ATPase. The (Na++ATP)-dependent lumen alkalization was not significantly affected by valinomycin, addition of which in the presence of K+ abolished Δψ at the vesicle membrane. The fact that the Na+-ATPase-mediated alkalization of the vesicle lumen is sustained in the absence of the transmembrane Δψ is consistent with a primary role of the Na+-ATPase in driving H+ outside the vesicles. The findings allowed us to conclude that the Na+-ATPase of T. viridis directly performs an exchange of Na+ for H+. Since the Na+-ATPase generates electric potential across the vesicle membrane, the transport stoichiometry is mNa+/nH+, where m>n.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BTP :
-
Bis-Tris-Propane, 1,3-bis[tris(hydroxymethyl)methylamino]-propane
- CCCP :
-
Carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenylhydrazone
- DTT :
-
Dithiothreitol
- NCDC :
-
2-Nitro-4-carboxyphenyl N,N-diphenylcarbamate
- PMSF :
-
Phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride
- PM :
-
Plasma membrane
References
Balnokin YV, Popova L (1994) ATP-driven Na+-pump in the plasma membrane of the marine unicellular alga Platymonas viridis. FEBS Lett 343:61–64
Balnokin YV, Popova LG, Myasoyedov NA (1993) Plasma membrane ATPase of marine unicellular alga Platymonas viridis. Plant Physiol Biochem 31:159–168
Balnokin Y, Popova L, Gimmler H (1997) Further evidence for an ATP-driven sodium pump in the marine alga Tetraselmis (Platymonas) viridis. J Plant Physiol 150:264–270
Balnokin YV, Popova LG, Andreev IM (1999) Electrogenicity of the Na+-ATPase from the marine microalga Tetraselmis (Platymonas) viridis and associated H+ countertransport. FEBS Lett 462:402–406
Barbier-Brygoo H, Vinauger M, Colcombet J, Ephritikhine G, Frachisse J-M, Maurel C (2000) Anion channels in higher plants: functional characterization, molecular structure and physiological role. Biochim Biophys Acta 1465:199–218
Bashford CL, Chance B, Prince RC (1979) Oxonol dyes as monitors of membrane potential. Their behavior in photosynthetic bacteria. Biochim Biophys Acta 545:46–57
Clement NR, Gould JM (1981) Pyranine (8-hydroxy-1,3,6,-pyrenetrisulfonate) as a probe of internal aqueous hydrogen ion concentration in phospholipid vesicles. Biochemistry 20:1534–1538
Gimmler H (2000) Primary sodium plasma membrane ATPases in salt-tolerant algae: facts and fictions. J Exp Bot 51:1171–1178
Glynn IM, Karlish S (1975) The sodium pumps. Annu Rev Physiol 37:33–55
Haro R, Garciadeblas B, Rodriguez-Navarro A (1991) A novel P-type ATPase from yeast involved in sodium transport. FEBS Lett 291:189–191
Heefner DL, Harold FM (1982) ATP-driven sodium pump in Streptococcus faecalis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:2798–2802
Kaieda N, Wakagi T, Kayama N (1998) Presence of Na+-stimulated V-type ATPase in the membrane of a facultatively anaerobic and halophilic alkaliphile. FEMS Microbiol Lett 167:57–61
Krulwich TA (1983) Na+/H+ antiporters. Biochim Biophys Acta 726:245–264
Padan E, Schuldinger S (1993) Na+/H+ antiporters, molecule devices that couple Na+ and H+ circulations in cells. J Bioenerg Biomembr 25:647–669
Pagis LY, Popova LG, Andreev IM, Balnokin YV (2001) Ion specificity of Na+-transporting systems in the plasma membrane of the halotolerant alga Tetraselmis (Platymonas) viridis. Russ J Plant Physiol 48:281–286
Popova LG, Balnokin YV (1992) H+-translocating ATPase and Na+/H+ antiport activities in the plasma membrane of the marine alga Platymonas viridis. FEBS Lett 309:333–336
Popova L, Balnokin Y, Dietz K-J, Gimmler H (1999) Characterization of phosphorylated intermediates synthesized during the catalytic cycle of the sodium adenosine triphosphate as in the plasma membrane of the marine unicellular alga Tetraselmis (Platymonas) viridis. J Plant Physiol 155:302–309
Rasi-Caldogno F, Pugliarello MC, DeMichelis MI (1987) The Ca2+-transport ATPase of plant plasma membrane catalyzes a nH+/ Ca2+ exchange. Plant Physiol 83:994–1000
Shono M, Hara Y, Wada M, Fujii T (1996) A sodium pump in the plasma membrane of the marine alga Heterosigma akashiwo. Plant Cell Physiol 37:385–388
Simpson IA, Sonne O (1982) A simple, rapid and sensitive method for measuring protein concentration in subcellular membrane fractions prepared by sucrose density ultracentrifugation. Anal Biochem 119:424–427
Stein WD (1986) Transport and diffusion across cell membranes. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 477–571
Wada M, Satoh S, Kasamo K, Fujii T (1989) Presence of a sodium-activated ATPase in the plasma membrane of the marine Raphidophycean Heterosigma akashiwo. Plant Cell Physiol 30:923–928
Yu X, Carrol S, Rigaud JL, Inesi G (1993) H+ countertransport and electrogenicity of the sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ pump in the reconstituted proteoliposomes. Biophys J 64:1232–1242
Zhu J-K (2000) Genetic analysis of plant salt tolerance using Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 124:941–948
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, Grant # 01-04-49135 and Grant # 02-04-06713. We thank Dr. A. Grabov (Imperial College, London) for critical reading of the manuscript and valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balnokin, Y.V., Popova, L.G., Pagis, L.Y. et al. The Na+-translocating ATPase in the plasma membrane of the marine microalga Tetraselmis viridis catalyzes Na+/H+ exchange. Planta 219, 332–337 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1224-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-004-1224-7