Abstract
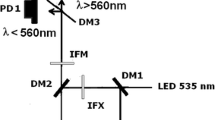
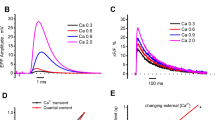
The spatiotemporal properties of the Ca2+ release process in skeletal muscle fibres were determined using a confocal spot detection system. The low-affinity, fluorescent Ca2+ indicator Oregon Green 488 BAPTA-5N (OGB-5N) was used to record localized, action potential-induced fluorescence signals from consecutive locations separated by 200 nm within a single sarcomere. Three-dimensional reconstructions of the Ca2+ transients illustrated the existence of fluorescence domains around Ca2+ release sites, which are centred at the T-tubules. By constructing isochronal plots, it was estimated that the earliest detectable full width at half-maximum (FWHM) of the Ca2+ domains was 0.77±0.08 µm and increased rapidly with time to 1.4±0.04 µm at peak (17–18 °C). A delay of 0.64±0.1 ms was observed between the onset of the fluorescence transients at the Z- and M-lines. Deconvolution of fluorescence transients gave estimates of approximately 9 and 2 µM for the peak [Ca2+] changes at the Z and M-lines, respectively. Our results are compatible with the possibility that action potential stimulation elicits Ca2+ release from a region of the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) broader than the T-SR junction.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
DiFranco, M., Novo, D. & Vergara, J.L. Characterization of the calcium release domains during excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle fibres. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 443, 508–519 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100719
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100719