Abstract.
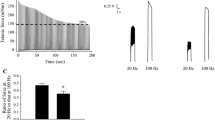
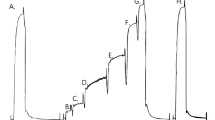
This study investigated whether a high intracellular concentration of L(+)-lactate (30 mM) affects normal excitation-contraction coupling in skeletal muscle. Electrical stimulation was used to elicit action potentials in the (sealed) transverse-tubular system of mechanically skinned muscle fibres, giving rise to twitch and tetanic force responses. As the sarcolemma was absent, lactate could be applied to the cytoplasmic environment via the bathing solution (at a constant pH of 7.1) and its effect examined independently of other metabolic changes that occur during muscle fatigue. The presence of 30 mM lactate had virtually no effect on direct activation of the contractile apparatus by Ca2+. Lactate also had no significant effect on either the rate of rise or the peak of the twitch response, with the only detectable effect being a slight (13%) slowing in its relaxation rate. As the amplitude of the twitch response (approximately 60% of maximum force) may be regarded as a sensitive indicator of the amount of Ca2+ released by an action potential, there was evidently no change in Ca2+ release in the presence of lactate. Lactate also had no significant effect on the rate of rise and peak force of the tetanic response or on its subsequent relaxation. Additional experiments, in which the sarcoplasmic reticulum was emptied of Ca2+ (in a caffeine solution) and reloaded repeatedly, showed no significant effect of 30 mM lactate on Ca2+ uptake. This study shows that the presence of L(+)-lactate does not inhibit excitation-contraction coupling in mechanically skinned fibres.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Posterino, G.S., Dutka, T.L. & Lamb, G.D. L(+)-lactate does not affect twitch and tetanic responses in mechanically skinned mammalian muscle fibres. Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 197–203 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100528
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240100528