Abstract
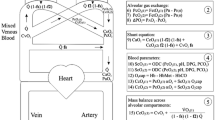
To evaluate whether nitric oxide (NO) is an appropriate test gas for assessing pulmonary gas exchange, we determined the rates of disappearance from the alveolar space (λ) of NO and singly and doubly 18O-labelled carbon dioxide (C16O18O, C18O2) by performing single-breath manoeuvres on seven artificially ventilated rabbits. By exploiting unique features of both isotopic species and by analysing pulmonary gas transport and λ values with a commonly used model, we found that diffusion forms 98±6% (mean ± SD) of the overall resistance to alveolar-capillary NO transfer. This means that measurements of pulmonary NO uptake reveal the entire diffusive properties of the alveolar-capillary membrane, because the extremely fast binding of NO to haemoglobin negates the ”reactive” component within red blood cells of pulmonary capillaries.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 8 May 1998 / Received after revision: 12 August 1998 / Accepted: 17 August 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Heller, H., Schuster, KD. Nitric oxide used to test pulmonary gas exchange in rabbits. Pflügers Arch 437, 94–97 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050752
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050752