Abstract
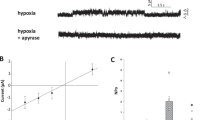
K influx and efflux (both ouabain- and bumetanide-resistant) in haemoglobin S-containing red cells (sickle cells) were markedly stimulated by urea (> 0.25 M). Stimulation was rapid and reversible. Volume-sensitive KCl cotransport in both HbA or HbS red cells is thought to be O2-dependent but we show here that urea-stimulated K fluxes in sickle cells were largely insensitive to O2 tension. Urea-stimulated K fluxes were not inhibited by lowering the external Ca concentration (with EGTA) but were abolished by Cl-substitution (with MeSO4 or NO3) or pretreatment of cells with the protein phosphatase inhibitor, calyculin A (0.1 μM). Results are consistent with a stimulatory action of urea on the KCl cotransporter, independent of oxygen tension, mediated via the phosphorylation cascade which regulates the transporter. The importance of this effect to the physiology and pathology of sickle cells is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 7 November 1997 / Received after revision and accepted: 2 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Culliford, S., Ellory, J., Gibson, J. et al. Effects of urea and oxygen tension on K flux in sickle cells. Pflügers Arch 435, 740–742 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050576
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050576