Abstract
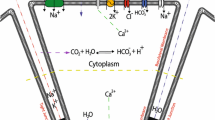
Immunofluorescence labelling and confocal microscopy were employed to examine the polarized distribution of several membrane transport proteins believed to be essential for salivary secretion in the rat submandibular gland. The Na+/K+-ATPase, Na+/H+ exchanger isoform 1 (NHE1), and the secretory Na+/K+/2Cl–cotransporter isoform were all found in the basolateral membranes of acinar and intralobular duct cells. Anion exchanger isoform 2 (AE2) was found only in the basolateral membranes of acinar cells, while AE1 was absent from glandular epithelial cells. Aquaporin 5 was detected in the apical membranes of acinar cells, while the cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator was found only in apical membranes of intralobular duct cells. NHEs 2 and 3 were found in the apical membranes of both acinar and intralobular duct cells. Our results are generally consistent with the expected distribution of most transporters based on previous physiological and pharmacological experiments. However, the apical localization of NHEs 2 and 3, and the presence of the secretory isoform of the Na+/K+/2Cl–cotransporter in intralobular duct cells were not predicted.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 10 June 1996 / Received after revision: 9 September 1996 / Accepted: 17 September 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, X., Tse, CM., Donowitz, M. et al. Polarized distribution of key membrane transport proteins in the rat submandibular gland. Pfluegers Arch 433, 260–268 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050276
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050276