Abstract
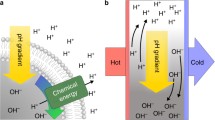
The direct measurement and quantification of proton transport in biological structures are below the detection limit of stationary pH-sensitive microelectrodes. We have thus used a more sensitive system to detect and quantify these small pH gradients: a proton-sensitive vibrating ion probe technique. This technique decreases the noise of the system to less than ±15 µV, equivalent to pH gradients below 0.0005 pH units, and can be used to measure pH gradients even in the presence of moderate buffer concentrations. At physiological pH the detection limit, analysed with artificial proton sources, is in the range of 5 pmol·s–1·cm–2. Computer simulation indicates that the spatial resolution is sufficient to localize individual proton sources less than 30 µm apart.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 16 October 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Somieski, P., Nagel, W. Measurement of pH gradients using an ion-sensitive vibrating probe technique (IP). Pflügers Arch - Eur J Physiol 442, 142–149 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000505
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240000505