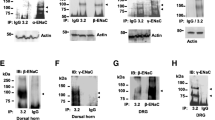
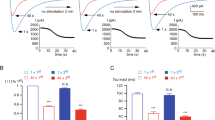
Abstract
This study describes the interaction between CaV3.2 calcium channels and the receptor for activated C kinase 1 (Rack-1), a scaffold protein which has recently been implicated in neuropathic pain. The coexpression of CaV3.2 and Rack-1 in tsA-201 cells led to a reduction in the magnitude of whole-cell CaV3.2 currents and CaV3.2 channel expression at the plasma membrane. Co-immunoprecipitations from transfected cells show the formation of a molecular protein complex between Cav3.2 channels and Rack-1. We determined that the interaction of Rack-1 occurs at the intracellular II–III loop and the C-terminus of the channel. Finally, the coexpression of PKCβII abolished the effect of Rack-1 on current densities. Altogether, our findings show that Rack-1 regulates CaV3.2-mediated calcium entry in a PKC-dependent manner.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data used in our study is available from the authors on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable
Change history
21 October 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02633-z
Abbreviations
- Rack-1:
-
Receptor for activated C kinase 1
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- DECA:
-
Dequalinium chloride
- NMDAR:
-
N-Methyl-d-aspartate receptors
- GABAAR:
-
Gamma-aminobutyric-acid A receptor
References
Adams DR, Ron D, Kiely PA (2011) RACK1, a multifaceted scaffolding protein: structure and function. Cell Commun Signal 9:22. https://doi.org/10.1186/1478-811X-9-22
Ashique AM, Kharazia V, Yaka R, Phamluong K, Peterson AS, Ron D (2006) Localization of the scaffolding protein RACK1 in the developing and adult mouse brain. Brain Res 1069:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2005.11.018
Basbaum AI, Bautista DM, Scherrer G, Julius D (2009) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of pain. Cell 139:267–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.09.028
Blesneac I, Chemin J, Bidaud I, Huc-Brandt S, Vandermoere F, Lory P (2015) Phosphorylation of the Cav3.2 T-type calcium channel directly regulates its gating properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112:13705–13710. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1511740112
Bourinet E, Altier C, Hildebrand ME, Trang T, Salter MW, Zamponi GW (2014) Calcium-permeable ion channels in pain signaling. Physiol Rev 94:81–140. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00023.2013
Brandon NJ, Jovanovic JN, Smart TG, Moss SJ (2002) Receptor for activated C kinase-1 facilitates protein kinase C-dependent phosphorylation and functional modulation of GABAA receptors with the activation of G-protein-coupled receptors. J Neurosci 22(6353–6361):20026649
Brandon NJ, Uren JM, Kittler JT, Wang H, Olsen R, Parker PJ, Moss SJ (1999) Subunit-specific association of protein kinase C and the receptor for activated C kinase with GABA type A receptors. J Neurosci 19:9228–9234
Candelas M, Reynders A, Arango-Lievano M, Neumayer C, Fruquiere A, Demes E, Hamid J, Lemmers C, Bernat C, Monteil A, Compan V, Laffray S, Inquimbert P, Le Feuvre Y, Zamponi GW, Moqrich A, Bourinet E, Mery PF (2019) Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels shape electrical firing in mouse Lamina II neurons. Sci Rep 9:3112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-39703-3
Colloca L, Ludman T, Bouhassira D, Baron R, Dickenson AH, Yarnitsky D, Freeman R, Truini A, Attal N, Finnerup NB, Eccleston C, Kalso E, Bennett DL, Dworkin RH, Raja SN (2017) Neuropathic pain. Nat Rev Dis Primers 3:17002. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2017.2
Cox EA, Bennin D, Doan AT, O’Toole T, Huttenlocher A (2003) RACK1 regulates integrin-mediated adhesion, protrusion, and chemotactic cell migration via its Src-binding site. Mol Biol Cell 14:658–669. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e02-03-0142
Ficelova V, Souza IA, Cmarko L, Gandini MA, Stringer RN, Zamponi GW, Weiss N (2020) Functional identification of potential non-canonical N-glycosylation sites within Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels. Mol Brain 13:149. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-020-00697-z
Gaifullina AS, Lazniewska J, Gerasimova EV, Burkhanova GF, Rzhepetskyy Y, Tomin A, Rivas-Ramirez P, Huang J, Cmarko L, Zamponi GW, Sitdikova GF, Weiss N (2019) A potential role for T-type calcium channels in homocysteinemia-induced peripheral neuropathy. Pain 160:2798–2810. https://doi.org/10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001669
Gandini MA, Sandoval A, Felix R (2014) Whole-cell patch-clamp recording of recombinant voltage-sensitive Ca2+ channels heterologously expressed in HEK-293 cells. Cold Spring Harb Protoc 2014:396–401. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot073213
Gandini MA, Souza IA, Ferron L, Innes AM, Zamponi GW (2021) The de novo CACNA1A pathogenic variant Y1384C associated with hemiplegic migraine, early onset cerebellar atrophy and developmental delay leads to a loss of Cav2.1 channel function. Mol Brain 14:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13041-021-00745-2
Garcia-Caballero A, Gadotti VM, Stemkowski P, Weiss N, Souza IA, Hodgkinson V, Bladen C, Chen L, Hamid J, Pizzoccaro A, Deage M, Francois A, Bourinet E, Zamponi GW (2014) The deubiquitinating enzyme USP5 modulates neuropathic and inflammatory pain by enhancing Cav3.2 channel activity. Neuron 83:1144–1158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2014.07.036
Gomez K, Calderon-Rivera A, Sandoval A, Gonzalez-Ramirez R, Vargas-Parada A, Ojeda-Alonso J, Granados-Soto V, Delgado-Lezama R, Felix R (2020) Cdk5-dependent phosphorylation of CaV3.2 T-type channels: possible role in nerve ligation-induced neuropathic allodynia and the compound action potential in primary afferent C fibers. J Neurosci 40:283–296. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0181-19.2019
Isacson CK, Lu Q, Karas RH, Cox DH (2007) RACK1 is a BKCa channel binding protein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 292:C1459-1466. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00322.2006
Jagodic MM, Pathirathna S, Joksovic PM, Lee W, Nelson MT, Naik AK, Su P, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM (2008) Upregulation of the T-type calcium current in small rat sensory neurons after chronic constrictive injury of the sciatic nerve. J Neurophysiol 99:3151–3156. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.01031.2007
Lazniewska J, Rzhepetskyy Y, Zhang FX, Zamponi GW, Weiss N (2016) Cooperative roles of glucose and asparagine-linked glycosylation in T-type calcium channel expression. Pflugers Arch 468:1837–1851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1881-y
Lu R, Fan B, Yin D, Li Y, Wang B, Zhu S, Chen Y, Xu Z (2019) Receptor for activated C kinase 1 mediates the chronic constriction injury-induced neuropathic pain in the rats’ peripheral and central nervous system. Neurosci Lett 712:134477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2019.134477
Messinger RB, Naik AK, Jagodic MM, Nelson MT, Lee WY, Choe WJ, Orestes P, Latham JR, Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2009) In vivo silencing of the Ca(V)3.2 T-type calcium channels in sensory neurons alleviates hyperalgesia in rats with streptozocin-induced diabetic neuropathy. Pain 145:184–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pain.2009.06.012
Millan MJ (1999) The induction of pain: an integrative review. Prog Neurobiol 57:1–164. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0301-0082(98)00048-3
Mischak H, Pierce JH, Goodnight J, Kazanietz MG, Blumberg PM, Mushinski JF (1993) Phorbol ester-induced myeloid differentiation is mediated by protein kinase C-alpha and -delta and not by protein kinase C-beta II, -epsilon, -zeta, and -eta. J Biol Chem 268:20110–20115
Orestes P, Osuru HP, McIntire WE, Jacus MO, Salajegheh R, Jagodic MM, Choe W, Lee J, Lee SS, Rose KE, Poiro N, Digruccio MR, Krishnan K, Covey DF, Lee JH, Barrett PQ, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Todorovic SM (2013) Reversal of neuropathic pain in diabetes by targeting glycosylation of Ca(V)3.2 T-type calcium channels. Diabetes 62:3828–3838. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-0813
Rangel A, Sanchez-Armass S, Meza U (2010) Protein kinase C-mediated inhibition of recombinant T-type Cav3.2 channels by neurokinin 1 receptors. Mol Pharmacol 77:202–210. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.109.058727
Ron D, Chen CH, Caldwell J, Jamieson L, Orr E, Mochly-Rosen D (1994) Cloning of an intracellular receptor for protein kinase C: a homolog of the beta subunit of G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:839–843. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.3.839
Ron D, Jiang Z, Yao L, Vagts A, Diamond I, Gordon A (1999) Coordinated movement of RACK1 with activated betaIIPKC. J Biol Chem 274:27039–27046. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.38.27039
Rotenberg SA, Sun XG (1998) Photoinduced inactivation of protein kinase C by dequalinium identifies the RACK-1-binding domain as a recognition site. J Biol Chem 273:2390–2395. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.4.2390
Scanzi J, Accarie A, Muller E, Pereira B, Aissouni Y, Goutte M, Joubert-Zakeyh J, Picard E, Boudieu L, Mallet C, Gelot A, Ardid D, Carvalho FA, Dapoigny M (2016) Colonic overexpression of the T-type calcium channel Cav 3.2 in a mouse model of visceral hypersensitivity and in irritable bowel syndrome patients. Neurogastroenterol Motil 28:1632–1640. https://doi.org/10.1111/nmo.12860
Snutch TP, Zamponi GW (2018) Recent advances in the development of T-type calcium channel blockers for pain intervention. Br J Pharmacol 175:2375–2383. https://doi.org/10.1111/bph.13906
Stebbins EG, Mochly-Rosen D (2001) Binding specificity for RACK1 resides in the V5 region of beta II protein kinase C. J Biol Chem 276:29644–29650. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M101044200
Talley EM, Cribbs LL, Lee JH, Daud A, Perez-Reyes E, Bayliss DA (1999) Differential distribution of three members of a gene family encoding low voltage-activated (T-type) calcium channels. J Neurosci 19:1895–1911
Todorovic SM, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2011) T-type voltage-gated calcium channels as targets for the development of novel pain therapies. Br J Pharmacol 163:484–495. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01256.x
Waxman SG, Zamponi GW (2014) Regulating excitability of peripheral afferents: emerging ion channel targets. Nat Neurosci 17:153–163. https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.3602
Weiss N, Black SA, Bladen C, Chen L, Zamponi GW (2013) Surface expression and function of Cav3.2 T-type calcium channels are controlled by asparagine-linked glycosylation. Pflugers Arch 465:1159–1170. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1259-3
Weiss N, Hameed S, Fernandez-Fernandez JM, Fablet K, Karmazinova M, Poillot C, Proft J, Chen L, Bidaud I, Monteil A, Huc-Brandt S, Lacinova L, Lory P, Zamponi GW, De Waard M (2012) A Ca(v)3.2/syntaxin-1A signaling complex controls T-type channel activity and low-threshold exocytosis. J Biol Chem 287:2810–2818. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.290882
Woolf CJ, American College of Physicians, American Physiological Society (2004) Pain: moving from symptom control toward mechanism-specific pharmacologic management. Ann Intern Med 140:441–451. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-140-8-200404200-00010
Woolf CJ, Salter MW (2000) Neuronal plasticity: increasing the gain in pain. Science 288:1765–1769. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.288.5472.1765
Yaka R, He DY, Phamluong K, Ron D (2003) Pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide (PACAP(1–38)) enhances N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor function and brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression via RACK1. J Biol Chem 278:9630–9638. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M209141200
Yaka R, Phamluong K, Ron D (2003) Scaffolding of Fyn kinase to the NMDA receptor determines brain region sensitivity to ethanol. J Neurosci 23:3623–3632
Yaka R, Thornton C, Vagts AJ, Phamluong K, Bonci A, Ron D (2002) NMDA receptor function is regulated by the inhibitory scaffolding protein, RACK1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:5710–5715. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.062046299
Yang J, Wang Q, Zheng W, Tuli J, Li Q, Wu Y, Hussein S, Dai XQ, Shafiei S, Li XG, Shen PY, Tu JC, Chen XZ (2012) Receptor for activated C kinase 1 (RACK1) inhibits function of transient receptor potential (TRP)-type channel Pkd2L1 through physical interaction. J Biol Chem 287:6551–6561. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.305854
Zhu X, Liu Y, Huang H, Zhang Y, Huang S, Zhou W, Bian X, Shen S, Cao S (2018) PKCbetaII-induced upregulation of PGP9.5 and VEGF in postoperative persistent pain in rats. J Pain Res 11:2095–2106. https://doi.org/10.2147/JPR.S144852
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Lina Chen for her technical support. We thank Dr. Anna Huttenlocher for the pEGFP-N1-RACK1 plasmid and Dr. Frederic Mushinski for the MTH PKC beta II plasmid. We also thank Dr. Norbert Weiss for providing the GFP channel fusion constructs and Dr. Said M’Dahoma for early participation in this project.
Funding
This work was supported by a Foundation Grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (CIHR) to GWZ. MAG held a postdoctoral fellowship from CIHR. GWZ is a Canada Research Chair.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MAG designed the study and drafted the manuscript. GWZ supervised the study and co-wrote the manuscript. MAG, IAS, EG, and AK performed the experiments and data analysis. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Not applicable
Consent to participate
Not applicable
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the special issue on Nociception in Pflügers Archiv—European Journal of Physiology
The original online version of this article was revised: Originally, the article has been published online with spelling error in author name. Abhishek Kullar should be change to Abhishek Khullar.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandini, M.A., Souza, I.A., Khullar, A. et al. Regulation of CaV3.2 channels by the receptor for activated C kinase 1 (Rack-1). Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 474, 447–454 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02631-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02631-1