Abstract
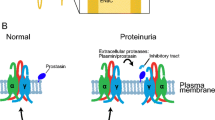
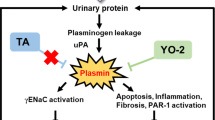
The plasminogen system is important for fibrinolysis in addition to tissue remodeling and inflammation with significance for kidney disease. The system consists of the circulating zymogen plasminogen (Plg) and the tissue- and urokinase-type plasminogen activators, tPA and uPA, expressed in the glomeruli, endothelium and tubular epithelium, respectively, and the inhibitors α2-antiplasmin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-type1, PAI-1. Plasminogen is activated by surface receptors, some with renal expression: urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR), plasminogen receptor KT (Plg-RKT), and tPA, most evident in the endothelium. Plasmin may exert effects through protease-activated receptors, PARs, expressed in the kidney. Deletion of plasminogen system component genes confers no major developmental or renal phenotypes in normal mice. In glomerular injury and renal interstitial fibrosis, deletion of various components, notably Plg, uPA, PAI, and uPAR is associated with protection suggesting a disease promoting effect of plasmin, in some cases exerted through PAR1 receptor activation. Plasminogen and uPA are aberrantly filtrated across the glomerular barrier in proteinuria, and plasminogen is activated in the tubular fluid. In the tubular fluid, plasmin may activate proteolytically the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) and inhibit the apical calcium transporter transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 5 (TRPV5), which could explain impaired sodium excretion and enhanced calcium excretion in proteinuria. Amiloride, a potassium-sparing diuretic, inhibits urokinase and plasmin activation in the tubular fluid and uPAR expression in vitro, which highlights new indications for an old drug. Protease inhibitors lowered blood pressure and antagonized fibrosis in salt-sensitive Dahl rats. Current knowledge indicates that the plasminogen system aggravates renal disease by direct and indirect hypertensive effects and is a promising target to antagonize disease progression.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- α2-AP:
-
Alpha2-antiplasmin
- plg:
-
Plasminogen
- PA:
-
Plasminogen activator
- PAI:
-
Plasminogen activator inhibitor
- PAR:
-
Protease-activated receptor
- tPA:
-
Tissue-type plasminogen activator
- uPA:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator
- uPAR:
-
Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
- suPAR:
-
Soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor
References
Almus-Jacobs F, Varki N, Sawdey MS, Loskutoff DJ (1995) Endotoxin stimulates expression of the murine urokinase receptor gene in vivo. Am J Pathol 147:688–698
Andersen H, Friis UG, Hansen PB, Svenningsen P, Henriksen JE, Jensen BL (2015) Diabetic nephropathy is associated with increased urine excretion of proteases plasmin, prostasin and urokinase and activation of amiloride-sensitive current in collecting duct cells. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:781–789. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfu402
Andersen H, Hansen PB, Bistrup C, Nielsen F, Henriksen JE, Jensen BL (2016) Significant natriuretic and antihypertensive action of the epithelial sodium channel blocker amiloride in diabetic patients with and without nephropathy. J Hypertens. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000000967
Andersen RF, Buhl KB, Jensen BL, Svenningsen P, Friis UG, Jespersen B, Rittig S (2013) Remission of nephrotic syndrome diminishes urinary plasmin content and abolishes activation of ENaC. Pediatr Nephrol 28:1227–1234. doi:10.1007/s00467-013-2439-2
Andreotti F, Davies GJ, Hackett DR, Khan MI, De Bart AC, Aber VR, Maseri A, Kluft C (1988) Major circadian fluctuations in fibrinolytic factors and possible relevance to time of onset of myocardial infarction, sudden cardiac death and stroke. Am J Cardiol 62:635–637
Andronicos NM, Chen EI, Baik N, Bai H, Parmer CM, Kiosses WB, Kamps MP, Yates JR 3rd, Parmer RJ, Miles LA (2010) Proteomics-based discovery of a novel, structurally unique, and developmentally regulated plasminogen receptor, Plg-RKT, a major regulator of cell surface plasminogen activation. Blood 115:1319–1330. doi:10.1182/blood-2008-11-188938
Appella E, Robinson EA, Ullrich SJ, Stoppelli MP, Corti A, Cassani G, Blasi F (1987) The receptor-binding sequence of urokinase. A biological function for the growth-factor module of proteases. J Biol Chem 262:4437–4440
Astrup T (1956) The biological significance of fibrinolysis. Lancet (London, England) 271:565–568
Astrup T (1958) The haemostatic balance. Thrombosis et diathesis haemorrhagica 2:347–357
Babu MS, Prabha TS, Kaul S, Al-Hazzani A, Shafi G, Roy S, Balakrishna N, Jyothy A, Munshi A (2012) Association of genetic variants of fibrinolytic system with stroke and stroke subtypes. Gene 495:76–80. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2011.12.046
Baricos WH, Cortez SL, Eldahr SS, Schnaper HW (1995) ECM degradation by cultured human mesangial cells is mediated by a PA/plasmin/MMP-2 cascade. Kidney Int 47:1039–1047. doi:10.1038/ki.1995.150
Behrendt N, Ronne E, Ploug M, Petri T, Lober D, Nielsen LS, Schleuning WD, Blasi F, Appella E, Dano K (1990) The human receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. NH2-terminal amino acid sequence and glycosylation variants. J Biol Chem 265:6453–6460
Bernik MB (1973) Increased plasminogen activator (urokinase) in tissue culture after fibrin deposition. J Clin Invest 52:823–834. doi:10.1172/jci107246
Buduneli N, Buduneli E, Ciotanar S, Atilla G, Lappin D, Kinane D (2004) Plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in gingival crevicular fluid of cyclosporin A-treated patients. J Clin Periodontol 31:556–561. doi:10.1111/j.1600-051X.2004.00517.x
Buhl KB, Friis UG, Svenningsen P, Gulaveerasingam A, Ovesen P, Frederiksen-Moller B, Jespersen B, Bistrup C, Jensen BL (2012) Urinary plasmin activates collecting duct ENaC current in preeclampsia. J Hypertension 60:1346–1351. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.112.198879
Buhl KB, Oxlund CS, Friis UG, Svenningsen P, Bistrup C, Jacobsen IA, Jensen BL (2014) Plasmin in urine from patients with type 2 diabetes and treatment-resistant hypertension activates ENaC in vitro. J Hypertens 32:1672–1677; discussion 1677. doi:10.1097/HJH.0000000000000216
Cesari M, Pahor M, Incalzi RA (2010) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1): a key factor linking fibrinolysis and age-related subclinical and clinical conditions. Cardiovasc Ther 28:e72–e91. doi:10.1111/j.1755-5922.2010.00171.x
Chen HFNM, Satoh K, Sakamoto S (1980) Urinary fibrinolysis in toxemia of pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 59:499–504
Chen HFNM, Satoh K, Sakamoto S (1980) Studies on the purification and characterization of human urinary plasminogen and plasmin. Thromb Haemost 42:1536–1547
Chen Z, Zhao R, Zhao M, Liang X, Bhattarai D, Dhiman R, Shetty S, Idell S, Ji HL (2014) Regulation of epithelial sodium channels in urokinase plasminogen activator deficiency. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 307:L609–L617. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00126.2014
Chorostowska-Wynimko J, Swiercz R, Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Wojtowicz A, Selman SH, Jankun J (2003) A novel form of the plasminogen activator inhibitor created by cysteine mutations extends its half-life: relevance to cancer and angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Ther 2:19–28
Chow KM, Szeto CC, Szeto CY, Poon P, Lai FM, Li PK (2002) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 polymorphism is associated with progressive renal dysfunction after acute rejection in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation 74:1791–1794. doi:10.1097/01.TP.0000038753.06870.E4
Collins SJ, Alexander SL, Lopez-Guisa JM, Cai X, Maruvada R, Chua SC, Zhang G, Okamura DM, Matsuo S, Eddy AA (2006) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficiency has renal benefits but some adverse systemic consequences in diabetic mice. Nephron Exp Nephrol 104:e23–e34. doi:10.1159/000093673
Couser WG, Remuzzi G, Mendis S, Tonelli M (2011) The contribution of chronic kidney disease to the global burden of major noncommunicable diseases. Kidney Int 80:1258–1270. doi:10.1038/ki.2011.368
De Taeye B, Smith LH, Vaughan DE (2005) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1: a common denominator in obesity, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:149–154. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2005.01.007
Dear AE, Medcalf RL (1998) The urokinase-type-plasminogen-activator receptor (CD87) is a pleiotropic molecule. Eur J Biochem 252:185–193
Del Rosso M, Margheri F, Serrati S, Chilla A, Laurenzana A, Fibbi G (2011) The urokinase receptor system, a key regulator at the intersection between inflammation, immunity, and coagulation. Curr Pharm Design 17:1924–1943
Deschenes G, Guigonis V, Doucet A (2004) Molecular mechanism of edema formation in nephrotic syndrome. Arch Pediatr 11:1084–1094. doi:10.1016/j.arcped.2004.03.029
Dewerchin M, Collen D, Lijnen HR (2001) Enhanced fibrinolytic potential in mice with combined homozygous deficiency of alpha2-antiplasmin and PAI-1. Thromb Haemost 86:640–646
Eddy AA, Fogo AB (2006) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in chronic kidney disease: evidence and mechanisms of action. J Am Soc Nephrol 17:2999–3012. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006050503
Edgtton KL, Gow RM, Kelly DJ, Carmeliet P, Kitching AR (2004) Plasmin is not protective in experimental renal interstitial fibrosis. Kidney Int 66:68–76. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2004.00707.x
Eide IK, Torjesen PA, Drolsum A, Babovic A, Lilledahl NP (2004) Low-renin status in therapy-resistant hypertension: a clue to efficient treatment. J Hypertens 22:2217–2226
Eitzman DT, McCoy RD, Zheng X, Fay WP, Shen T, Ginsburg D, Simon RH (1996) Bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in transgenic mice that either lack or overexpress the murine plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene. J Clin Invest 97:232–237. doi:10.1172/JCI118396
Eugen-Olsen J, Andersen O, Linneberg A, Ladelund S, Hansen TW, Langkilde A, Petersen J, Pielak T, Moller LN, Jeppesen J, Lyngbaek S, Fenger M, Olsen MH, Hildebrandt PR, Borch-Johnsen K, Jorgensen T, Haugaard SB (2010) Circulating soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor predicts cancer, cardiovascular disease, diabetes and mortality in the general population. J Intern Med 268:296–308. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2796.2010.02252.x
Fay WP, Parker AC, Condrey LR, Shapiro AD (1997) Human plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) deficiency: characterization of a large kindred with a null mutation in the PAI-1 gene. Blood 90:204–208
Feldt-Rasmussen BME, Deckert T, Giese J, Christensen NJ, Bent-Hansen L, Nielsen MD (1987) Central role for sodium in the pathogenesis of blood pressure changes independent of angiotensin, aldosterone and catecholamines in type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus. Dia- betologia 1987; 30:610–617. Diabetologia 30:610–617
Ghosh AK, Vaughan DE (2012) PAI-1 in tissue fibrosis. J Cell Physiol 227:493–507. doi:10.1002/jcp.22783
Godier A, Hunt BJ (2013) Plasminogen receptors and their role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory, autoimmune and malignant disease. J Thrombosis Haemostasis JTH 11:26–34. doi:10.1111/jth.12064
Gueler F, Rong S, Mengel M, Park JK, Kiyan J, Kirsch T, Dumler I, Haller H, Shushakova N (2008) Renal urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) receptor but not uPA deficiency strongly attenuates ischemia reperfusion injury and acute kidney allograft rejection. J Immunol 181:1179–1189
Gunzler WA, Steffens GJ, Otting F, Buse G, Flohe L (1982) Structural relationship between human high and low molecular mass urokinase. Hoppe-Seyler’s Zeitschrift fur physiologische Chemie 363:133–141
Haj-Yehia A, Nassar T, Sachais BS, Kuo A, Bdeir K, Al-Mehdi AB, Mazar A, Cines DB, Higazi AA (2000) Urokinase-derived peptides regulate vascular smooth muscle contraction in vitro and in vivo. FASEB J 14:1411–1422
Harris JJ, McCarthy HJ, Ni L, Wherlock M, Kang H, Wetzels JF, Welsh GI, Saleem MA (2013) Active proteases in nephrotic plasma lead to a podocin-dependent phosphorylation of VASP in podocytes via protease activated receptor-1. J Pathol 229:660–671. doi:10.1002/path.4149
Hasui YSJ, Sumiyoshi A, Hashida S, Ishikawa E (1988) Distribution of plasminogen activators in human kidney and male genital organs using a highly sensitive enzyme immunoassay. Thromb Res:453–459
Hayek SS, Sever S, Ko YA, Trachtman H, Awad M, Wadhwani S, Altintas MM, Wei C, Hotton AL, French AL, Sperling LS, Lerakis S, Quyyumi AA, Reiser J (2015) Soluble urokinase receptor and chronic kidney disease. N Engl J Med 373:1916–1925. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1506362
Hocherl K, Gerl M, Schweda F (2011) Proteinase-activated receptors 1 and 2 exert opposite effects on renal renin release. Hypertension 58:611–618. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.173229
Holmes WE, Pennica D, Blaber M, Rey MW, Guenzler WA, Steffens GJ, Heyneker HL (1985) Cloning and expression of the gene for pro-urokinase in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotech 3:923–929
Hoyer-Hansen G, Ronne E, Solberg H, Behrendt N, Ploug M, Lund LR, Ellis V, Dano K (1992) Urokinase plasminogen activator cleaves its cell surface receptor releasing the ligand-binding domain. J Biol Chem 267:18224–18229
Hruby Z, Wendycz D, Kopec W, Czerchawski L, Jozefowiak M, Rabczynski J (1996) Effect of antiproteolytic drugs: epsilon-aminocaproic acid (EACA) and aprotinin on experimental anti-GBM nephritis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 11:32–39
Hu JH, Touch P, Zhang J, Wei H, Liu S, Lund IK, Hoyer-Hansen G, Dichek DA (2015) Reduction of mouse atherosclerosis by urokinase inhibition or with a limited-spectrum matrix metalloproteinase inhibitor. Cardiovasc Res 105:372–382. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvv007
Huber KKJ, Binder R (1982) Rapid isolation and characterization of high molecular weight urokinase from native human urine. Thromb Haemost:197–202
Ji HL, Zhao R, Komissarov AA, Chang Y, Liu Y, Matthay MA (2015) Proteolytic regulation of epithelial sodium channels by urokinase plasminogen activator: cutting edge and cleavage sites. J Biol Chem 290:5241–5255. doi:10.1074/jbc.M114.623496
Jood K, Ladenvall P, Tjarnlund-Wolf A, Ladenvall C, Andersson M, Nilsson S, Blomstrand C, Jern C (2005) Fibrinolytic gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke. Stroke 36:2077–2081. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000183617.54752.69
Kaikita K, Fogo AB, Ma L, Schoenhard JA, Brown NJ, Vaughan DE (2001) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficiency prevents hypertension and vascular fibrosis in response to long-term nitric oxide synthase inhibition. Circulation 104:839–844
Kitching AR, Holdsworth SR, Ploplis VA, Plow EF, Collen D, Carmeliet P, Tipping PG (1997) Plasminogen and plasminogen activators protect against renal injury in crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med 185:963–968
Kobayashi N, Ueno T, Ohashi K, Yamashita H, Takahashi Y, Sakamoto K, Manabe S, Hara S, Takashima Y, Dan T, Pastan I, Miyata T, Kurihara H, Matsusaka T, Reiser J, Nagata M (2015) Podocyte injury-driven intracapillary plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 accelerates podocyte loss via uPAR-mediated beta1-integrin endocytosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 308:F614–F626. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00616.2014
Kremen M, Krishnan R, Emery I, Hu JH, Slezicki KI, Wu A, Qian K, Du L, Plawman A, Stempien-Otero A, Dichek DA (2008) Plasminogen mediates the atherogenic effects of macrophage-expressed urokinase and accelerates atherosclerosis in apoE-knockout mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:17109–17114. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808650105
Kristensen PEJ, Dane K (1991) Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator messenger RNA in the normal mouse by in situ hybridization. J Histochem Cytochem 39:341–349
Larsson L-I SL, Nielsen LS, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Kristensen R (1984) Distribution of urokinase-type plasminogen activator immunoreactivity in the mouse. J Cell Biol 98:894–903
Lijnen HR, Okada K, Matsuo O, Collen D, Dewerchin M (1999) Alpha2-antiplasmin gene deficiency in mice is associated with enhanced fibrinolytic potential without overt bleeding. Blood 93:2274–2281
Lijnen HR, Zamarron C, Blaber M, Winkler ME, Collen D (1986) Activation of plasminogen by pro-urokinase I mechanism. J Biol Chem 261:1253–1258
Liu N, Shimizu S, Ito-Ihara T, Takagi K, Kita T, Ono T (2007) Angiotensin II receptor blockade ameliorates mesangioproliferative glomerulonephritis in rats through suppression of CTGF and PAI-1, independently of the coagulation system. Nephron Exp Nephrol 105:e65–e74. doi:10.1159/000098321
Loskutoff DJ (1988) Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor and its potential influence on thrombolytic therapy. Semin Thromb Hemost 14:100–109. doi:10.1055/s-2007-1002762
Loskutoff DJ, Quigley JP (2000) PAI-1, fibrosis, and the elusive provisional fibrin matrix. J Clin Invest 106:1441–1443. doi:10.1172/JCI11765
Lund LR, Green KA, Stoop AA, Ploug M, Almholt K, Lilla J, Nielsen BS, Christensen IJ, Craik CS, Werb Z, Dano K, Romer J (2006) Plasminogen activation independent of uPA and tPA maintains wound healing in gene-deficient mice. EMBO J 25:2686–2697. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7601173
Lyon CJ, Hsueh WA (2003) Effect of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in diabetes mellitus and cardiovascular disease. Am J Med 115(Suppl 8A):62S–68S
Lyons RM, Gentry LE, Purchio AF, Moses HL (1990) Mechanism of activation of latent recombinant transforming growth factor beta 1 by plasmin. J Cell Biol 110:1361–1367
Hata M (1989) The study of plasminogen activator in renal cell carcinoma with special remarks on urokinase type plasminogen activator. Nippon Hinyokika Gakkai Zasshi:1558–1565
Malgorzewicz S, Skrzypczak-Jankun E, Jankun J (2013) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 in kidney pathology (review). Int J Mol Med 31:503–510. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2013.1234
Masuda Y, Emoto N, Nonaka H, Yagita K, Todo T, Okamura H, Yokoyama M, Hirata K (2009) Role of angiotensin and the clock system in the circadian regulation of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. Kobe J Med Sci 54:E264–E271
Menoud PA, Sappino N, Boudal-Khoshbeen M, Vassalli JD, Sappino AP (1996) The kidney is a major site of alpha(2)-antiplasmin production. J Clin Invest 97:2478–2484. doi:10.1172/jci118694
Mignatti P (1995) Extracellular matrix remodeling by metalloproteinases and plasminogen activators. Kidney Int Suppl 49:S12–S14
Nassar T, Haj-Yehia A, Akkawi S, Kuo A, Bdeir K, Mazar A, Cines DB, Higazi AA (2002) Binding of urokinase to low density lipoprotein-related receptor (LRP) regulates vascular smooth muscle cell contraction. J Biol Chem 277:40499–40504. doi:10.1074/jbc.M207172200
Navarrete M, Ho J, Krokhin O, Ezzati P, Rigatto C, Reslerova M, Rush DN, Nickerson P, Wilkins JA (2013) Proteomic characterization of serine hydrolase activity and composition in normal urine. Clin Proteomics 10:17. doi:10.1186/1559-0275-10-17
Nguyen G, Li XM, Peraldi MN, Zacharias U, Hagege J, Rondeau E, Sraer JD (1994) Receptor binding and degradation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 46:208–215
Nicholas SB, Aguiniga E, Ren Y, Kim J, Wong J, Govindarajan N, Noda M, Wang W, Kawano Y, Collins A, Hsueh WA (2005) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deficiency retards diabetic nephropathy. Kidney Int 67:1297–1307. doi:10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00207.x
Nolan C, Hall LS, Barlow GH, Tribby II (1977) Plasminogen activator from human embryonic kidney cell cultures: evidence for a proactivator. Biochimica et biophysica acta 496:384–400
Oda T, Jung YO, Kim HS, Cai X, Lopez-Guisa JM, Ikeda Y, Eddy AA (2001) PAI-1 deficiency attenuates the fibrogenic response to ureteral obstruction. Kidney Int 60:587–596. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.030002587.x
Oishi K (2009) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and the circadian clock in metabolic disorders. Clin Exp Hypertens (New York, NY : 1993) 31:208–219. doi:10.1080/10641960902822468
Okada K, Ueshima S, Kawao N, Yano M, Tamura Y, Tanaka M, Sakamoto A, Hatano M, Arima M, Miyata S, Nagai N, Tokuhisa T, Matsuo O (2013) Lack of both alpha2-antiplasmin and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 induces high IgE production. Life Sci 93:89–95. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2013.05.023
Oxlund CS, Buhl KB, Jacobsen IA, Hansen MR, Gram J, Henriksen JE, Schousboe K, Tarnow L, Jensen BL (2014) Amiloride lowers blood pressure and attenuates urine plasminogen activation in patients with treatment-resistant hypertension. J Am Soc Hypertens 8:872–881. doi:10.1016/j.jash.2014.09.019
Passero CJ, Mueller GM, Rondon-Berrios H, Tofovic SP, Hughey RP, Kleyman TR (2008) Plasmin activates epithelial Na+ channels by cleaving the gamma subunit. J Biol Chem 283:36586–36591. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805676200
Persson F, Theilade S, Eugen-Olsen J, Rossing P, Parving HH (2016) Renin angiotensin system blockade reduces urinary levels of soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Diabetes Complicat 30:1440–1442. doi:10.1016/j.jdiacomp.2016.07.003
Piedagnel R, Tiger Y, Lelongt B, Ronco PM (2006) Urokinase (u-PA) is produced by collecting duct principal cells and is post-transcriptionally regulated by SV40 large-T, arginine vasopressin, and epidermal growth factor. J Cell Physiol 206:394–401. doi:10.1002/jcp.20485
Ploug M, Ronne E, Behrendt N, Jensen AL, Blasi F, Dano K (1991) Cellular receptor for urokinase plasminogen activator. Carboxyl-terminal processing and membrane anchoring by glycosyl-phosphatidylinositol. J Biol Chem 266:1926–1933
Pohl JF, Melin-Aldana H, Sabla G, Degen JL, Bezerra JA (2001) Plasminogen deficiency leads to impaired lobular reorganization and matrix accumulation after chronic liver injury. Am J Pathol 159:2179–2186. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)63069-6
Pozzi A, Jarad G, Moeckel GW, Coffa S, Zhang X, Gewin L, Eremina V, Hudson BG, Borza DB, Harris RC, Holzman LB, Phillips CL, Fassler R, Quaggin SE, Miner JH, Zent R (2008) Beta1 integrin expression by podocytes is required to maintain glomerular structural integrity. Dev Biol 316:288–301. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.01.022
Preissner KT, Kanse SM, May AE (2000) Urokinase receptor: a molecular organizer in cellular communication. Curr Opin Cell Biol 12:621–628
Raij L, Tian R, Wong JS, He JC, Campbell KN (2016) Podocyte injury: the role of proteinuria, urinary plasminogen, and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 311:F1308–F1317. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00162.2016
Raum D, Marcus D, Alper CA, Levey R, Taylor PD, Starzl TE (1980) Synthesis of human plasminogen by the liver. Science (New York, NY) 208:1036–1037
Revelo MP, Federspiel C, Helderman H, Fogo AB (2005) Chronic allograft nephropathy: expression and localization of PAI-1 and PPAR-gamma. Nephrol Dial Transplant 20:2812–2819. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfi172
Robbins KC, Summaria L, Hsieh B, Shah RJ (1967) The peptide chains of human plasmin. Mechanism of activation of human plasminogen to plasmin. J Biol Chem 242:2333–2342
Roelofs JJ, Rowshani AT, van den Berg JG, Claessen N, Aten J, ten Berge IJ, Weening JJ, Florquin S (2003) Expression of urokinase plasminogen activator and its receptor during acute renal allograft rejection. Kidney Int 64:1845–1853. doi:10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00261.x
Roldan AL, Cubellis MV, Masucci MT, Behrendt N, Lund LR, Dano K, Appella E, Blasi F (1990) Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J 9:467–474
Rondeau E, Ochi S, Lacave R, He CJ, Medcalf R, Delarue F, Sraer JD (1989) Urokinase synthesis and binding by glomerular epithelial cells in culture. Kidney Int 36:593–600
Sachs N, Sonnenberg A (2013) Cell-matrix adhesion of podocytes in physiology and disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 9:200–210. doi:10.1038/nrneph.2012.291
Saha C, Eckert GJ, Ambrosius WT, Chun TY, Wagner MA, Zhao Q, Pratt JH (2005) Improvement in blood pressure with inhibition of the epithelial sodium channel in blacks with hypertension. Hypertension 46:481–487. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000179582.42830.1d
Sappino AP, Huarte J, Vassalli JD, Belin D (1991) Sites of synthesis of urokinase and tissue-type plasminogen activators in the murine kidney. J Clin Invest 87:962–970. doi:10.1172/JCI115104
Sawathiparnich P, Murphey LJ, Kumar S, Vaughan DE, Brown NJ (2003) Effect of combined AT1 receptor and aldosterone receptor antagonism on plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:3867–3873. doi:10.1210/jc.2003-030374
Schneider DJ, Sobel BE (2012) PAI-1 and diabetes: a journey from the bench to the bedside. Diabetes Care 35:1961–1967. doi:10.2337/dc12-0638
Shankland SJ (2006) The podocyte’s response to injury: role in proteinuria and glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 69:2131–2147. doi:10.1038/sj.ki.5000410
Shetty S, Kumar A, Johnson AR, Pueblitz S, Holiday D, Raghu G, Idell S (1996) Differential expression of the urokinase receptor in fibroblasts from normal and fibrotic human lungs. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 15:78–87. doi:10.1165/ajrcmb.15.1.8679225
Sinha A, Bajpai J, Saini S, Bhatia D, Gupta A, Puraswani M, Dinda AK, Agarwal SK, Sopory S, Pandey RM, Hari P, Bagga A (2014) Serum-soluble urokinase receptor levels do not distinguish focal segmental glomerulosclerosis from other causes of nephrotic syndrome in children. Kidney Int 85:649–658. doi:10.1038/ki.2013.546
Smith HW, Marshall CJ (2010) Regulation of cell signalling by uPAR. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:23–36. doi:10.1038/nrm2821
Sobel GW, Mohler SR, Jones NW, Dowdy A, Guest MM (1952) Urokinase: an activator of plasma profibrinolysin extracted from urine. Am J Phys 171:768–769
Sprengers ED, Kluft C (1987) Plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood 69:381–387
Staehr M, Buhl KB, Andersen RF, Svenningsen P, Nielsen F, Hinrichs GR, Bistrup C, Jensen BL (2015) Aberrant glomerular filtration of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in nephrotic syndrome leads to amiloride-sensitive plasminogen activation in urine. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 309:F235–F241. doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00138.2015
Svenningsen P, Bistrup C, Friis UG, Bertog M, Haerteis S, Krueger B, Stubbe J, Jensen ON, Thiesson HC, Uhrenholt TR, Jespersen B, Jensen BL, Korbmacher C, Skott O (2009) Plasmin in nephrotic urine activates the epithelial sodium channel. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:299–310. doi:10.1681/ASN.2008040364
Svenningsen P, Uhrenholt TR, Palarasah Y, Skjodt K, Jensen BL, Skott O (2009) Prostasin-dependent activation of epithelial Na+ channels by low plasmin concentrations. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297:R1733–R1741. doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00321.2009
Swaisgood CM, French EL, Noga C, Simon RH, Ploplis VA (2000) The development of bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis in mice deficient for components of the fibrinolytic system. Am J Pathol 157:177–187. doi:10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64529-4
Theilade S, Lyngbaek S, Hansen TW, Eugen-Olsen J, Fenger M, Rossing P, Jeppesen JL (2015) Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor levels are elevated and associated with complications in patients with type 1 diabetes. J Intern Med 277:362–371. doi:10.1111/joim.12269
Thuno M, Macho B, Eugen-Olsen J (2009) suPAR: the molecular crystal ball. Dis Markers 27:157–172. doi:10.3233/dma-2009-0657
Tudpor K, Lainez S, Kwakernaak AJ, Kovalevskaya NV, Verkaart S, van Genesen S, van der Kemp A, Navis G, Bindels RJ, Hoenderop JG (2012) Urinary plasmin inhibits TRPV5 in nephrotic-range proteinuria. J Am Soc Nephrol 23:1824–1834. doi:10.1681/ASN.2011111126
Vallet V, Chraibi A, Gaeggeler HP, Horisberger JD, Rossier BC (1997) An epithelial serine protease activates the amiloride-sensitive sodium channel. Nature 389:607–610. doi:10.1038/39329
Vassalli JD, Belin D (1987) Amiloride selectively inhibits the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. FEBS Lett 214:187–191
Vassalli JD, Sappino AP, Belin D (1991) The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest 88:1067–1072. doi:10.1172/JCI115405
Vaziri ND, Gonzales EC, Shayestehfar B, Barton CH (1994) Plasma levels and urinary excretion of fibrinolytic and protease inhibitory proteins in nephrotic syndrome. J Lab Clin Med 124:118–124
Wagner SN, Atkinson MJ, Wagner C, Hofler H, Schmitt M, Wilhelm O (1996) Sites of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression and distribution of its receptor in the normal human kidney. Histochem Cell Biol 105:53–60
Wang Y, Jones CJ, Dang J, Liang X, Olsen JE, Doe WF (1994) Human urokinase receptor expression is inhibited by amiloride and induced by tumor necrosis factor and phorbol ester in colon cancer cells. FEBS Lett 353:138–142
Wei C, El Hindi S, Li J, Fornoni A, Goes N, Sageshima J, Maiguel D, Karumanchi SA, Yap HK, Saleem M, Zhang Q, Nikolic B, Chaudhuri A, Daftarian P, Salido E, Torres A, Salifu M, Sarwal MM, Schaefer F, Morath C, Schwenger V, Zeier M, Gupta V, Roth D, Rastaldi MP, Burke G, Ruiz P, Reiser J (2011) Circulating urokinase receptor as a cause of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis. Nat Med 17:952–960. doi:10.1038/nm.2411
Wei C, Moller CC, Altintas MM, Li J, Schwarz K, Zacchigna S, Xie L, Henger A, Schmid H, Rastaldi MP, Cowan P, Kretzler M, Parrilla R, Bendayan M, Gupta V, Nikolic B, Kalluri R, Carmeliet P, Mundel P, Reiser J (2008) Modification of kidney barrier function by the urokinase receptor. Nat Med 14:55–63. doi:10.1038/nm1696
Wiklund PG, Nilsson L, Ardnor SN, Eriksson P, Johansson L, Stegmayr B, Hamsten A, Holmberg D, Asplund K (2005) Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 4G/5G polymorphism and risk of stroke: replicated findings in two nested case-control studies based on independent cohorts. Stroke 36:1661–1665. doi:10.1161/01.STR.0000174485.10277.24
Wun TC, Ossowski L, Reich E (1982) A proenzyme form of human urokinase. J Biol Chem 257:7262–7268
Xu Y, Hagege J, Mougenot B, Sraer JD, Ronne E, Rondeau E (1996) Different expression of the plasminogen activation system in renal thrombotic microangiopathy and the normal human kidney. Kidney Int 50:2011–2019
Zhang B, Xie S, Shi W, Yang Y (2012) Amiloride off-target effect inhibits podocyte urokinase receptor expression and reduces proteinuria. Nephrol Dial Transplant 27:1746–1755. doi:10.1093/ndt/gfr612
Zhang G, Kernan KA, Collins SJ, Cai X, Lopez-Guisa JM, Degen JL, Shvil Y, Eddy AA (2007) Plasmin(ogen) promotes renal interstitial fibrosis by promoting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition: role of plasmin-activated signals. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:846–859. doi:10.1681/ASN.2006080886
Zhang G, Kim H, Cai X, Lopez-Guisa JM, Alpers CE, Liu Y, Carmeliet P, Eddy AA (2003) Urokinase receptor deficiency accelerates renal fibrosis in obstructive nephropathy. J Am Soc Nephrol 14:1254–1271
Zhang L, Seiffert D, Fowler BJ, Jenkins GR, Thinnes TC, Loskutoff DJ, Parmer RJ, Miles LA (2002) Plasminogen has a broad extrahepatic distribution. Thromb Haemost 87:493–501
Zheng H, Liu X, Sharma NM, Li Y, Pliquett RU, Patel KP (2016) Urinary proteolytic activation of renal epithelial Na+ channels in chronic heart failure. Hypertension 67:197–205. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.115.05838
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Work in the authors lab is supported by The Danish Strategic Research Council/Innovationsfonden (11-115861), the Region of Southern Denmark (10-15756); The Danish Research Council for Health and Disease, The Danish Diabetes Academy funded by the Novo Nordisk Foundation, Odense University Hospital.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Svenningsen, P., Hinrichs, G.R., Zachar, R. et al. Physiology and pathophysiology of the plasminogen system in the kidney. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 469, 1415–1423 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2014-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-017-2014-y