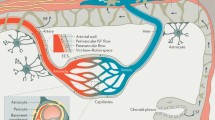
Abstract
The peripheral (PNS) and central nervous system (CNS) are delicate structures, highly sensitive to homeostatic changes—and crucial for basic vital functions. Thus, a selection of barriers ensures the protection of the nervous system from noxious blood-borne or surrounding stimuli. In this chapter, anatomy and functioning of the blood–nerve (BNB), the blood–brain (BBB), and the blood–spinal cord barriers (BSCB) are presented and the key tight junction (TJ) proteins described: claudin-1, claudin-3, claudin-5, claudin-11, claudin-12, claudin-19, occludin, Zona occludens-1 (ZO-1), and tricellulin are by now identified as relevant for nerval barriers. Different diseases can lead to or be accompanied by neural barrier disruption, and impairment of these barriers worsens pathology. Peripheral nerve injury and inflammatory polyneuropathy cause an increased permeability of BNB as well as BSCB, while, e.g., diseases of the CNS such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, spinal cord injury, or Alzheimer’s disease can progress and worsen through barrier dysfunction. Moreover, the complex role and regulation of the BBB after ischemic stroke is described. On the other side, PNS and CNS barriers hamper the delivery of drugs in diseases when the barrier is intact, e.g., in certain neurodegenerative diseases or inflammatory pain. Understanding of the barrier - regulating processes has already lead to the discovery of new molecules as drug enhancers. In summary, the knowledge of all of these mechanisms might ultimately lead to the invention of drugs to control barrier function to help ameliorating or curing neurological diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Sadi R, Khatib K, Guo S, Ye D, Youssef M, Ma T (2011) Occludin regulates macromolecule flux across the intestinal epithelial tight junction barrier. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 300:G1054–G1064
Alanne MH, Pummi K, Heape AM, Grenman R, Peltonen J, Peltonen S (2009) Tight junction proteins in human Schwann cell autotypic junctions. J Histochem Cytochem 57:523–529
Argaw AT, Gurfein BT, Zhang Y, Zameer A, John GR (2009) VEGF-mediated disruption of endothelial CLN-5 promotes blood-brain barrier breakdown. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:1977–1982
Aslam M, Kalluri SR, Cepok S, Kraus V, Buck D, Srivastava R, Hemmer B (2010) The antibody response to oligodendrocyte specific protein in multiple sclerosis. J Neuroimmunol 221:81–86
Banks WA (2016) From blood-brain barrier to blood-brain interface: new opportunities for CNS drug delivery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15:275–292
Bartanusz V, Jezova D, Alajajian B, Digicaylioglu M (2011) The blood-spinal cord barrier: morphology and clinical implications. Ann Neurol 70:194–206
Blasig IE, Winkler L, Lassowski B, Mueller SL, Zuleger N, Krause E, Krause G, Gast K, Kolbe M, Piontek J (2006) On the self-association potential of transmembrane tight junction proteins. Cell Mol Life Sci 63:505–514
Brkic M, Balusu S, Van Wonterghem E, Gorle N, Benilova I, Kremer A, Van Hove I, Moons L, De Strooper B, Kanazir S, Libert C, Vandenbroucke RE (2015) Amyloid beta oligomers disrupt blood-CSF barrier integrity by activating matrix metalloproteinases. J Neurosci 35:12766–12778
Brown RC, Mark KS, Egleton RD, Huber JD, Burroughs AR, Davis TP (2003) Protection against hypoxia-induced increase in blood-brain barrier permeability: role of tight junction proteins and NFkappaB. J Cell Sci 116:693–700
Brown RC, Mark KS, Egleton RD, Davis TP (2004) Protection against hypoxia-induced blood-brain barrier disruption: changes in intracellular calcium. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C1045–C1052
Bunge MB, Wood PM, Tynan LB, Bates ML, Sanes JR (1989) Perineurium originates from fibroblasts: demonstration in vitro with a retroviral marker. Science 243:229–231
Carrano A, Hoozemans JJ, van der Vies SM, van Horssen J, de Vries HE, Rozemuller AJ (2012) Neuroinflammation and blood-brain barrier changes in capillary amyloid angiopathy. Neurodegener Dis 10:329–331
Cording J, Gunther R, Vigolo E, Tscheik C, Winkler L, Schlattner I, Lorenz D, Haseloff RF, Schmidt-Ott KM, Wolburg H, Blasig IE (2015) Redox regulation of cell contacts by tricellulin and occludin: redox-sensitive cysteine sites in tricellulin regulate both tri- and bicellular junctions in tissue barriers as shown in hypoxia and ischemia. Antioxid Redox Signal 23:1035–1049
Dabrowski S, Staat C, Zwanziger D, Sauer RS, Bellmann C, Gunther R, Krause E, Haseloff RF, Rittner H, Blasig I (2015) Redox-sensitive structure and function of the first extracellular loop of the cell-cell contact protein claudin-1—lessons from molecular structure to animal. Antioxid Redox Signal 22:1–14
Denninger AR, Breglio A, Maheras KJ, LeDuc G, Cristiglio V, Deme B, Gow A, Kirschner DA (2015) Claudin-11 tight junctions in myelin are a barrier to diffusion and lack strong adhesive properties. Biophys J 109:1387–1397
Devaux J, Gow A (2008) Tight junctions potentiate the insulative properties of small CNS myelinated axons. J Cell Biol 183:909–921
Donnenfeld H, Kascsak RJ, Bartfeld H (1984) Deposits of IgG and C3 in the spinal cord and motor cortex of ALS patients. J Neuroimmunol 6:51–57
Echeverry S, Shi XQ, Rivest S, Zhang J (2011) Peripheral nerve injury alters blood-spinal cord barrier functional and molecular integrity through a selective inflammatory pathway. J Neurosci 31:10819–10828
Elahy M, Jackaman C, Mamo JC, Lam V, Dhaliwal SS, Giles C, Nelson D, Takechi R (2015) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction developed during normal aging is associated with inflammation and loss of tight junctions but not with leukocyte recruitment. Immun Ageing 12:2
Errede M, Girolamo F, Ferrara G, Strippoli M, Morando S, Boldrin V, Rizzi M, Uccelli A, Perris R, Bendotti C, Salmona M, Roncali L, Virgintino D (2012) Blood-brain barrier alterations in the cerebral cortex in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 71:840–854
Fischer S, Wiesnet M, Marti HH, Renz D, Schaper W (2004) Simultaneous activation of several second messengers in hypoxia-induced hyperpermeability of brain derived endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 198:359–369
Fujita H, Sugimoto K, Inatomi S, Maeda T, Osanai M, Uchiyama Y, Yamamoto Y, Wada T, Kojima T, Yokozaki H, Yamashita T, Kato S, Sawada N, Chiba H (2008) Tight junction proteins claudin-2 and -12 are critical for vitamin D-dependent Ca2+ absorption between enterocytes. Mol Biol Cell 19:1912–1921
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1993) Occludin: a novel integral membrane protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 123:1777–1788
Furuse M, Itoh M, Hirase T, Nagafuchi A, Yonemura S, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (1994) Direct association of occludin with ZO-1 and its possible involvement in the localization of occludin at tight junctions. J Cell Biol 127:1617–1626
Furuse M, Fujita K, Hiiragi T, Fujimoto K, Tsukita S (1998) Claudin-1 and -2: novel integral membrane proteins localizing at tight junctions with no sequence similarity to occludin. J Cell Biol 141:1539–1550
Furuse M, Hata M, Furuse K, Yoshida Y, Haratake A, Sugitani Y, Noda T, Kubo A, Tsukita S (2002) Claudin-based tight junctions are crucial for the mammalian epidermal barrier; a lesson from claudin-1-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 156:1099–1111
Garbuzova-Davis S, Hernandez-Ontiveros DG, Rodrigues MC, Haller E, Frisina-Deyo A, Mirtyl S, Sallot S, Saporta S, Borlongan CV, Sanberg PR (2012) Impaired blood-brain/spinal cord barrier in ALS patients. Brain Res 1469:114–128
Gow A, Southwood CM, Li JS, Pariali M, Riordan GP, Brodie SE, Danias J, Bronstein JM, Kachar B, Lazzarini RA (1999) CNS myelin and sertoli cell tight junction strands are absent in Osp/claudin-11 null mice. Cell 99:649–659
Greene C, Campbell M (2016) Tight junction modulation of the blood brain barrier: CNS delivery of small molecules. Tissue Barriers 4:e1138017
Grossmann J (2002) Molecular mechanisms of “detachment-induced apoptosis—Anoikis”. Apoptosis 7:247–260
Gunzel D, Yu AS (2013) Claudins and the modulation of tight junction permeability. Physiol Rev 93:525–569
Guo J, Wang L, Zhang Y, Wu J, Arpag S, Hu B, Imhof BA, Tian X, Carter BD, Suter U, Li J (2014) Abnormal junctions and permeability of myelin in PMP22-deficient nerves. Ann Neurol 75:255–265
Hackel D, Brack A, Fromm M, Rittner HL (2012) Modulation of tight junction proteins in the perineurium for regional pain control. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1257:199–206
Haseloff RF, Dithmer S, Winkler L, Wolburg H, Blasig IE (2015) Transmembrane proteins of the tight junctions at the blood-brain barrier: structural and functional aspects. Semin Cell Dev Biol 38:16–25
Heo JH, Han SW, Lee SK (2005) Free radicals as triggers of brain edema formation after stroke. Free Radic Biol Med 39:51–70
Hirakawa H, Okajima S, Nagaoka T, Takamatsu T, Oyamada M (2003) Loss and recovery of the blood-nerve barrier in the rat sciatic nerve after crush injury are associated with expression of intercellular junctional proteins. Exp Cell Res 284:196–210
Hosomi N, Ban CR, Naya T, Takahashi T, Guo P, Song XY, Kohno M (2005) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha neutralization reduced cerebral edema through inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase production after transient focal cerebral ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 25:959–967
Hou J, Renigunta A, Konrad M, Gomes AS, Schneeberger EE, Paul DL, Waldegger S, Goodenough DA (2008) Claudin-16 and claudin-19 interact and form a cation-selective tight junction complex. J Clin Invest 118:619–628
Huang ZG, Xue D, Preston E, Karbalai H, Buchan AM (1999) Biphasic opening of the blood-brain barrier following transient focal ischemia: effects of hypothermia. Can J Neurol Sci 26:298–304
Ikenouchi J, Furuse M, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Tsukita S, Tsukita S (2005) Tricellulin constitutes a novel barrier at tricellular contacts of epithelial cells. J Cell Biol 171:939–945
Ikenouchi J, Sasaki H, Tsukita S, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2008) Loss of occludin affects tricellular localization of tricellulin. Mol Biol Cell 19:4687–4693
Itoh M, Furuse M, Morita K, Kubota K, Saitou M, Tsukita S (1999) Direct binding of three tight junction-associated MAGUKs, ZO-1, ZO-2, and ZO-3, with the COOH termini of claudins. J Cell Biol 147:1351–1363
Iwamoto N, Higashi T, Furuse M (2014) Localization of angulin-1/LSR and tricellulin at tricellular contacts of brain and retinal endothelial cells in vivo. Cell Struct Funct 39:1–8
Kago T, Takagi N, Date I, Takenaga Y, Takagi K, Takeo S (2006) Cerebral ischemia enhances tyrosine phosphorylation of occludin in brain capillaries. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:1197–1203
Kamitani T, Sakaguchi H, Tamura A, Miyashita T, Yamazaki Y, Tokumasu R, Inamoto R, Matsubara A, Mori N, Hisa Y, Tsukita S (2015) Deletion of tricellulin causes progressive hearing loss associated with degeneration of Cochlear hair cells. Sci Rep 5:18402
Kanda T, Yamawaki M, Mizusawa H (2003) Sera from Guillain-Barre patients enhance leakage in blood-nerve barrier model. Neurology 60:301–306
Kanda T, Numata Y, Mizusawa H (2004) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: decreased claudin-5 and relocated ZO-1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:765–769
Kang Z, Wang C, Zepp J, Wu L, Sun K, Zhao J, Chandrasekharan U, DiCorleto PE, Trapp BD, Ransohoff RM, Li X (2013) Act1 mediates IL-17-induced EAE pathogenesis selectively in NG2+ glial cells. Nat Neurosci 16:1401–1408
Kashiwamura Y, Sano Y, Abe M, Shimizu F, Haruki H, Maeda T, Kawai M, Kanda T (2011) Hydrocortisone enhances the function of the blood-nerve barrier through the up-regulation of claudin-5. Neurochem Res 36:849–855
Katsuno T, Umeda K, Matsui T, Hata M, Tamura A, Itoh M, Takeuchi K, Fujimori T, Nabeshima Y, Noda T, Tsukita S (2008) Deficiency of zonula occludens-1 causes embryonic lethal phenotype associated with defected yolk sac angiogenesis and apoptosis of embryonic cells. Mol Biol Cell 19:2465–2475
Kaushansky N, Hemo R, Eisenstein M, Ben-Nun A (2007) OSP/claudin-11-induced EAE in mice is mediated by pathogenic T cells primarily governed by OSP192Y residue of major encephalitogenic region OSP179-207. Eur J Immunol 37:2018–2031
Kebir H, Kreymborg K, Ifergan I, Dodelet-Devillers A, Cayrol R, Bernard M, Giuliani F, Arbour N, Becher B, Prat A (2007) Human TH17 lymphocytes promote blood-brain barrier disruption and central nervous system inflammation. Nat Med 13:1173–1175
Kikuchi S, Ninomiya T, Tatsumi H, Sawada N, Kojima T (2010) Tricellulin is expressed in autotypic tight junctions of peripheral myelinating Schwann cells. J Histochem Cytochem 58:1067–1073
Kooij G, Kopplin K, Blasig R, Stuiver M, Koning N, Goverse G, van der Pol SM, van Het Hof B, Gollasch M, Drexhage JA, Reijerkerk A, Meij IC, Mebius R, Willnow TE, Muller D, Blasig IE, de Vries HE (2014) Disturbed function of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier aggravates neuro-inflammation. Acta Neuropathol 128:267–277
Kook SY, Hong HS, Moon M, Ha CM, Chang S, Mook-Jung I (2012) Abeta(1)(−)(4)(2)-RAGE interaction disrupts tight junctions of the blood-brain barrier via Ca(2)(+)-calcineurin signaling. J Neurosci 32:8845–8854
Koto T, Takubo K, Ishida S, Shinoda H, Inoue M, Tsubota K, Okada Y, Ikeda E (2007) Hypoxia disrupts the barrier function of neural blood vessels through changes in the expression of claudin-5 in endothelial cells. Am J Pathol 170:1389–1397
Kristensson K, Olsson Y (1971) The perineurium as a diffusion barrier to protein tracers. Differences between mature and immature animals. Acta Neuropathol 17:127–138
Krug SM, Amasheh S, Richter JF, Milatz S, Gunzel D, Westphal JK, Huber O, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2009) Tricellulin forms a barrier to macromolecules in tricellular tight junctions without affecting ion permeability. Mol Biol Cell 20:3713–3724
Krug SM, Amasheh M, Dittmann I, Christoffel I, Fromm M, Amasheh S (2013) Sodium caprate as an enhancer of macromolecule permeation across tricellular tight junctions of intestinal cells. Biomaterials 34:275–282
Krug SM, Schulzke JD, Fromm M (2014) Tight junction, selective permeability, and related diseases. Semin Cell Dev Biol 36:166–176
Kucenas S, Takada N, Park HC, Woodruff E, Broadie K, Appel B (2008) CNS-derived glia ensheath peripheral nerves and mediate motor root development. Nat Neurosci 11:143–151
Kuroiwa T, Ting P, Martinez H, Klatzo I (1985) The biphasic opening of the blood-brain barrier to proteins following temporary middle cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neuropathol 68:122–129
Lanz TV, Becker S, Osswald M, Bittner S, Schuhmann MK, Opitz CA, Gaikwad S, Wiestler B, Litzenburger UM, Sahm F, Ott M, Iwantscheff S, Grabitz C, Mittelbronn M, von Deimling A, Winkler F, Meuth SG, Wick W, Platten M (2013) Protein kinase Cbeta as a therapeutic target stabilizing blood-brain barrier disruption in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:14735–14740
Larsen JM, Martin DR, Byrne ME (2014) Recent advances in delivery through the blood-brain barrier. Curr Top Med Chem 14:1148–1160
Lee JY, Kim HS, Choi HY, Oh TH, Yune TY (2012) Fluoxetine inhibits matrix metalloprotease activation and prevents disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier after spinal cord injury. Brain 135:2375–2389
Lee JY, Choi HY, Ahn HJ, Ju BG, Yune TY (2014) Matrix metalloproteinase-3 promotes early blood-spinal cord barrier disruption and hemorrhage and impairs long-term neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. Am J Pathol 184:2985–3000
Lee JY, Choi HY, Na WH, Ju BG, Yune TY (2015) 17beta-estradiol inhibits MMP-9 and SUR1/TrpM4 expression and activation and thereby attenuates BSCB disruption/hemorrhage after spinal cord injury in male rats. Endocrinology 156:1838–1850
Liebner S, Corada M, Bangsow T, Babbage J, Taddei A, Czupalla CJ, Reis M, Felici A, Wolburg H, Fruttiger M, Taketo MM, von Melchner H, Plate KH, Gerhardt H, Dejana E (2008) Wnt/beta-catenin signaling controls development of the blood-brain barrier. J Cell Biol 183:409–417
Lopez-Ramirez MA, Wu D, Pryce G, Simpson JE, Reijerkerk A, King-Robson J, Kay O, de Vries HE, Hirst MC, Sharrack B, Baker D, Male DK, Michael GJ, Romero IA (2014) MicroRNA-155 negatively affects blood-brain barrier function during neuroinflammation. FASEB J 28:2551–2565
Manole E, Ceafalan LC, Oproiu AM, Popa-Wagner A, Popescu BO (2015) Claudin-1 and occludin expression in demyelinating peripheral neuropathies. Romanian J Morphol Embryol 56:1097–1102
Meister S, Storck SE, Hameister E, Behl C, Weggen S, Clement AM, Pietrzik CU (2015) Expression of the ALS-causing variant hSOD1(G93A) leads to an impaired integrity and altered regulation of claudin-5 expression in an in vitro blood-spinal cord barrier model. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 35:1112–1121
Miyamoto T, Morita K, Takemoto D, Takeuchi K, Kitano Y, Miyakawa T, Nakayama K, Okamura Y, Sasaki H, Miyachi Y, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2005) Tight junctions in Schwann cells of peripheral myelinated axons: a lesson from claudin-19-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 169:527–538
Moreau N, Mauborgne A, Bourgoin S, Couraud PO, Romero IA, Weksler BB, Villanueva L, Pohl M, Boucher Y (2016) Early alterations of hedgehog signaling pathway in vascular endothelial cells after peripheral nerve injury elicit blood-nerve barrier disruption, nerve inflammation, and neuropathic pain development. Pain 157:827–839
Morita K, Sasaki H, Furuse M, Tsukita S (1999) Endothelial claudin: claudin-5/TMVCF constitutes tight junction strands in endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 147:185–194
Nayak G, Lee SI, Yousaf R, Edelmann SE, Trincot C, Van Itallie CM, Sinha GP, Rafeeq M, Jones SM, Belyantseva IA, Anderson JM, Forge A, Frolenkov GI, Riazuddin S (2013) Tricellulin deficiency affects tight junction architecture and cochlear hair cells. J Clin Invest 123:4036–4049
Ni C, Wang C, Zhang J, Qu L, Liu X, Lu Y, Yang W, Deng J, Lorenz D, Gao P, Meng Q, Yan X, Blasig IE, Qin Z (2014) Interferon-gamma safeguards blood-brain barrier during experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Am J Pathol 184:3308–3320
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, Seo Y, Sasaki H, Hashimoto N, Furuse M, Tsukita S (2003) Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol 161:653–660
Notterpek L, Roux KJ, Amici SA, Yazdanpour A, Rahner C, Fletcher BS (2001) Peripheral myelin protein 22 is a constituent of intercellular junctions in epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:14404–14409
Obermeier B, Daneman R, Ransohoff RM (2013) Development, maintenance and disruption of the blood-brain barrier. Nat Med 19:1584–1596
Ohtsuki S, Sato S, Yamaguchi H, Kamoi M, Asashima T, Terasaki T (2007) Exogenous expression of claudin-5 induces barrier properties in cultured rat brain capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Physiol 210:81–86
Pan W, Banks WA, Kastin AJ (1997) Permeability of the blood-brain and blood-spinal cord barriers to interferons. J Neuroimmunol 76:105–111
Parmantier E, Lynn B, Lawson D, Turmaine M, Namini SS, Chakrabarti L, McMahon AP, Jessen KR, Mirsky R (1999) Schwann cell-derived desert hedgehog controls the development of peripheral nerve sheaths. Neuron 23:713–724
Pfeiffer F, Schafer J, Lyck R, Makrides V, Brunner S, Schaeren-Wiemers N, Deutsch U, Engelhardt B (2011) Claudin-1 induced sealing of blood-brain barrier tight junctions ameliorates chronic experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol 122:601–614
Podjaski C, Alvarez JI, Bourbonniere L, Larouche S, Terouz S, Bin JM, Lecuyer MA, Saint-Laurent O, Larochelle C, Darlington PJ, Arbour N, Antel JP, Kennedy TE, Prat A (2015) Netrin 1 regulates blood-brain barrier function and neuroinflammation. Brain 138:1598–1612
Poliak S, Matlis S, Ullmer C, Scherer SS, Peles E (2002) Distinct claudins and associated PDZ proteins form different autotypic tight junctions in myelinating Schwann cells. J Cell Biol 159:361–372
Prockop LD, Naidu KA, Binard JE, Ransohoff J (1995) Selective permeability of [3H]-D-mannitol and [14C]-carboxyl-inulin across the blood-brain barrier and blood-spinal cord barrier in the rabbit. J Spinal Cord Med 18:221–226
Pummi KP, Heape AM, Grenman RA, Peltonen JT, Peltonen SA (2004) Tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudins in developing and adult human perineurium. J Histochem Cytochem 52:1037–1046
Rajasekharan S, Kennedy TE (2009) The netrin protein family. Genome Biol 10:239
Rao RK, Basuroy S, Rao VU, Karnaky KJ Jr, Gupta A (2002) Tyrosine phosphorylation and dissociation of occludin-ZO-1 and E-cadherin-beta-catenin complexes from the cytoskeleton by oxidative stress. Biochem J 368:471–481
Rittner HL, Hackel D, Yamdeu RS, Mousa SA, Stein C, Schafer M, Brack A (2009) Antinociception by neutrophil-derived opioid peptides in noninflamed tissue—role of hypertonicity and the perineurium. Brain Behav Immun 23:548–557
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Takano H, Noda T, and Tsukita S. complex Phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell 11: 4131–4142, 2000.
Samak G, Aggarwal S, Rao RK (2011) ERK is involved in EGF-mediated protection of tight junctions, but not adherens junctions, in acetaldehyde-treated Caco-2 cell monolayers. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 301:G50–G59
Sandoval KE, Witt KA (2008) Blood-brain barrier tight junction permeability and ischemic stroke. Neurobiol Dis 32:200–219
Sauer RS, Krug SM, Hackel D, Staat C, Konasin N, Yang S, Niedermirtl B, Bosten J, Gunther R, Dabrowski S, Doppler K, Sommer C, Blasig IE, Brack A, Rittner HL (2014) Safety, efficacy, and molecular mechanism of claudin-1-specific peptides to enhance blood-nerve-barrier permeability. J Control Release 185:88–98
Severson EA, Kwon M, Hilgarth RS, Parkos CA, Nusrat A (2010) Glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK-3) influences epithelial barrier function by regulating occludin, claudin-1 and E-cadherin expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:592–597
Shimizu F, Sawai S, Sano Y, Beppu M, Misawa S, Nishihara H, Koga M, Kuwabara S, Kanda T (2014) Severity and patterns of blood-nerve barrier breakdown in patients with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyradiculoneuropathy: correlations with clinical subtypes. PLoS One 9:e104205
Sirotkin H, Morrow B, Saint-Jore B, Puech A, Das Gupta R, Patanjali SR, Skoultchi A, Weissman SM, Kucherlapati R (1997) Identification, characterization, and precise mapping of a human gene encoding a novel membrane-spanning protein from the 22q11 region deleted in velo-cardio-facial syndrome. Genomics 42:245–251
Storck SE, Meister S, Nahrath J, Meissner JN, Schubert N, Di Spiezio A, Baches S, Vandenbroucke RE, Bouter Y, Prikulis I, Korth C, Weggen S, Heimann A, Schwaninger M, Bayer TA, Pietrzik CU (2016) Endothelial LRP1 transports amyloid-beta(1-42) across the blood-brain barrier. J Clin Invest 126:123–136
Su P, Zhao F, Cao Z, Zhang J, Aschner M, Luo W (2015) Mir-203-mediated tricellulin mediates lead-induced in vitro loss of blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier (BCB) function. Toxicol in Vitro 29:1185–1194
Uceyler N, Necula G, Wagemann E, Toyka KV, Sommer C (2016) Endoneurial edema in sural nerve may indicate recent onset inflammatory neuropathy. Muscle Nerve 53:705–710
Umeda K, Ikenouchi J, Katahira-Tayama S, Furuse K, Sasaki H, Nakayama M, Matsui T, Tsukita S, Furuse M (2006) ZO-1 and ZO-2 independently determine where claudins are polymerized in tight-junction strand formation. Cell 126:741–754
van Paassen BW, van der Kooi AJ, van Spaendonck-Zwarts KY, Verhamme C, Baas F, de Visser M (2014) PMP22 related neuropathies: Charcot-Marie-tooth disease type 1A and hereditary neuropathy with liability to pressure palsies. Orphanet J Rare Dis 9:38
Wen J, Qian S, Yang Q, Deng L, Mo Y, Yu Y (2014) Overexpression of netrin-1 increases the expression of tight junction-associated proteins, claudin-5, occludin, and ZO-1, following traumatic brain injury in rats. Exp Ther Med 8:881–886
Winkler EA, Sengillo JD, Sagare AP, Zhao Z, Ma Q, Zuniga E, Wang Y, Zhong Z, Sullivan JS, Griffin JH, Cleveland DW, Zlokovic BV (2014) Blood-spinal cord barrier disruption contributes to early motor-neuron degeneration in ALS-model mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:E1035–E1042
Wu Q, Zhang YJ, Gao JY, Li XM, Kong H, Zhang YP, Xiao M, Shields CB, Hu G (2014) Aquaporin-4 mitigates retrograde degeneration of rubrospinal neurons by facilitating edema clearance and glial scar formation after spinal cord injury in mice. Mol Neurobiol 49:1327–1337
Yang M, Rainone A, Shi XQ, Fournier S, Zhang J (2014) A new animal model of spontaneous autoimmune peripheral polyneuropathy: implications for Guillain-Barre syndrome. Acta Neuropathol Commun 2:5
Yang S, Krug SM, Heitmann J, Hu L, Reinhold AK, Sauer S, Bosten J, Sommer C, Fromm M, Brack A, Rittner HL (2016) Analgesic drug delivery via recombinant tissue plasminogen activator and microRNA-183-triggered opening of the blood-nerve barrier. Biomaterials 82:20–33
Zhao Z, Nelson AR, Betsholtz C, Zlokovic BV (2015) Establishment and dysfunction of the blood-brain barrier. Cell 163:1064–1078
Zhong Z, Deane R, Ali Z, Parisi M, Shapovalov Y, O’Banion MK, Stojanovic K, Sagare A, Boillee S, Cleveland DW, Zlokovic BV (2008) ALS-causing SOD1 mutants generate vascular changes prior to motor neuron degeneration. Nat Neurosci 11:420–422
Zhou Q, Costinean S, Croce CM, Brasier AR, Merwat S, Larson SA, Basra S, Verne GN (2015) MicroRNA 29 targets nuclear factor-kappaB-repressing factor and claudin 1 to increase intestinal permeability. Gastroenterology 148:158–169
Zhou Y, Ye L, Zheng B, Zhu S, Shi H, Zhang H, Wang Z, Wei X, Chen D, Li X, Xu H, Xiao J (2016) Phenylbutyrate prevents disruption of blood-spinal cord barrier by inhibiting endoplasmic reticulum stress after spinal cord injury. Am J Transl Res 8:1864–1875
Zwanziger D, Hackel D, Staat C, Bocker A, Brack A, Beyermann M, Rittner H, Blasig IE (2012) A peptidomimetic tight junction modulator to improve regional analgesia. Mol Pharm 9:1785–1794
Acknowledgement
The Interdisciplinary Centre for Clinical Research (IZKF) of the Medical Faculty of the University of Wuerzburg supported the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reinhold, A., Rittner, H. Barrier function in the peripheral and central nervous system—a review. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 469, 123–134 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1920-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1920-8