Abstract
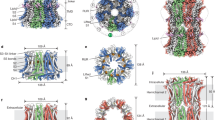
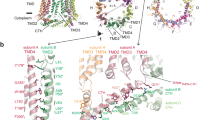
Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1), formerly known as FAM26C, was recently identified as a physiologically important plasma membrane ion channel. CALHM1 and its Caenorhabditis elegans homolog, CLHM-1, are regulated by membrane voltage and extracellular Ca2+ concentration ([Ca2+]o). In the presence of physiological [Ca2+]o (∼1.5 mM), CALHM1 and CLHM-1 are closed at resting membrane potentials but can be opened by strong depolarizations. Reducing [Ca2+]o increases channel open probability, enabling channel activation at negative membrane potentials. Together, voltage and Ca2+ o allosterically regulate CALHM channel gating. Through convergent evolution, CALHM has structural features that are reminiscent of connexins and pannexins/innexins/LRRC8 (volume-regulated anion channel (VRAC)) gene families, including four transmembrane helices with cytoplasmic amino and carboxyl termini. A CALHM1 channel is a hexamer of CALHM1 monomers with a functional pore diameter of ∼14 Å. CALHM channels discriminate poorly among cations and anions, with signaling molecules including Ca2+ and ATP able to permeate through its pore. CALHM1 is expressed in the brain where it plays an important role in cortical neuron excitability induced by low [Ca2+]o and in type II taste bud cells in the tongue that sense sweet, bitter, and umami tastes where it functions as an essential ATP release channel to mediate nonsynaptic neurotransmitter release. CLHM-1 is expressed in C. elegans sensory neurons and body wall muscles, and its genetic deletion causes locomotion defects. Thus, CALHM is a voltage- and Ca2+ o-gated ion channel, permeable to large cations and anions, that plays important roles in physiology.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beblo DA, Veenstra RD (1997) Monovalent cation permeation through the connexin40 gap junction channel. Cs, Rb, K, Na, Li, TEA, TMA, TBA, and effects of anions Br, Cl, F, acetate, aspartate, glutamate, and NO3. J Gen Physiol 109:509–522
Beecham GW, Schnetz-Boutaud N, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA (2009) CALHM1 polymorphism is not associated with late-onset Alzheimer disease. Ann Hum Genet 73:379–381
Bertram L, Schjeide BM, Hooli B, Mullin K, Hiltunen M, Soininen H, Ingelsson M, Lannfelt L, Blacker D, Tanzi RE (2008) No association between CALHM1 and Alzheimer’s disease risk. Cell 135:993–994, author reply 994-6
Chandrashekar J, Kuhn C, Oka Y, Yarmolinsky DA, Hummler E, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2010) The cells and peripheral representation of sodium taste in mice. Nature 464:297–301
Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2010) The cell biology of taste. J Cell Biol 190:285–296
Cotrina ML, Lin JH, Lopez-Garcia JC, Naus CC, Nedergaard M (2000) ATP-mediated glia signaling. J Neurosci 20:2835–2844
Cotrina ML, Lin JH, Nedergaard M (1998) Cytoskeletal assembly and ATP release regulate astrocytic calcium signaling. J Neurosci 18:8794–8804
Dreses-Werringloer U, Lambert JC, Vingtdeux V, Zhao H, Vais H, Siebert A, Jain A, Koppel J, Rovelet-Lecrux A, Hannequin D, Pasquier F, Galimberti D, Scarpini E, Mann D, Lendon C, Campion D, Amouyel P, Davies P, Foskett JK, Campagne F, Marambaud P (2008) A polymorphism in CALHM1 influences Ca2+ homeostasis, Abeta levels, and Alzheimer’s disease risk. Cell 133:1149–1161
Dreses-Werringloer U, Vingtdeux V, Zhao H, Chandakkar P, Davies P, Marambaud P (2013) CALHM1 controls the Ca2+-dependent MEK, ERK, RSK and MSK signaling cascade in neurons. J Cell Sci 126:1199–1206
Finger TE, Danilova V, Barrows J, Bartel DL, Vigers AJ, Stone L, Hellekant G, Kinnamon SC (2005) ATP signaling is crucial for communication from taste buds to gustatory nerves. Science 310:1495–1499
Gallego-Sandin S, Alonso MT, Garcia-Sancho J (2011) Calcium homoeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) reduces the calcium content of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and triggers ER stress. Biochem J 437:469–475
Harris AL, Contreras JE (2014) Motifs in the permeation pathway of connexin channels mediate voltage and Ca2+ sensing. Front Physiol 5:113
Hisatsune C, Yasumatsu K, Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Ogawa N, Kuroda Y, Yoshida R, Ninomiya Y, Mikoshiba K (2007) Abnormal taste perception in mice lacking the type 3 inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor. J Biol Chem 282:37225–37231
Hou X, Pedi L, Diver MM, Long SB (2012) Crystal structure of the calcium release-activated calcium channel Orai. Science 338:1308–1313
Huang YJ, Maruyama Y, Dvoryanchikov G, Pereira E, Chaudhari N, Roper SD (2007) The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse taste buds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:6436–6441
Kinnamon SC, Finger TE (2013) A taste for ATP: neurotransmission in taste buds. Front Cell Neurosci 7:264
Lambert JC, Sleegers K, Gonzalez-Perez A, Ingelsson M, Beecham GW, Hiltunen M, Combarros O, Bullido MJ, Brouwers N, Bettens K, Berr C, Pasquier F, Richard F, Dekosky ST, Hannequin D, Haines JL, Tognoni G, Fievet N, Dartigues JF, Tzourio C, Engelborghs S, Arosio B, Coto E, De Deyn P, Del Zompo M, Mateo I, Boada M, Antunez C, Lopez-Arrieta J, Epelbaum J, Schjeide BM, Frank-Garcia A, Giedraitis V, Helisalmi S, Porcellini E, Pilotto A, Forti P, Ferri R, Delepine M, Zelenika D, Lathrop M, Scarpini E, Siciliano G, Solfrizzi V, Sorbi S, Spalletta G, Ravaglia G, Valdivieso F, Vepsalainen S, Alvarez V, Bosco P, Mancuso M, Panza F, Nacmias B, Bossu P, Hanon O, Piccardi P, Annoni G, Mann D, Marambaud P, Seripa D, Galimberti D, Tanzi RE, Bertram L, Lendon C, Lannfelt L, Licastro F, Campion D, Pericak-Vance MA, Soininen H, Van Broeckhoven C, Alperovitch A, Ruiz A, Kamboh MI, Amouyel P (2010) The CALHM1 P86L polymorphism is a genetic modifier of age at onset in Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis study. J Alzheimers Dis 22:247–255
Locovei S, Bao L, Dahl G (2006) Pannexin 1 in erythrocytes: function without a gap. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:7655–7659
Lopez W, Gonzalez J, Liu Y, Harris AL, Contreras JE (2013) Insights on the mechanisms of Ca2+ regulation of connexin26 hemichannels revealed by human pathogenic mutations (D50N/Y). J Gen Physiol 142:23–35
Ma Z, Siebert AP, Cheung KH, Lee RJ, Johnson B, Cohen AS, Vingtdeux V, Marambaud P, Foskett JK (2012) Calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) is the pore-forming subunit of an ion channel that mediates extracellular Ca2+ regulation of neuronal excitability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:E1963–E1971
Maeda S, Nakagawa S, Suga M, Yamashita E, Oshima A, Fujiyoshi Y, Tsukihara T (2009) Structure of the connexin 26 gap junction channel at 3.5 A resolution. Nature 458:597–602
Matsumoto I, Ohmoto M, Abe K (2013) Functional diversification of taste cells in vertebrates. Semin Cell Dev Biol 24:210–214
Matsumoto I, Ohmoto M, Narukawa M, Yoshihara Y, Abe K (2011) Skn-1a (Pou2f3) specifies taste receptor cell lineage. Nat Neurosci 14:685–687
McNally BA, Yamashita M, Engh A, Prakriya M (2009) Structural determinants of ion permeation in CRAC channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22516–22521
Minster RL, Demirci FY, DeKosky ST, Kamboh MI (2009) No association between CALHM1 variation and risk of Alzheimer disease. Hum Mutat 30:E566–E569
Moreno-Ortega AJ, Buendia I, Mouhid L, Egea J, Lucea S, Ruiz-Nuno A, Lopez MG, Cano-Abad MF (2015) CALHM1 and its polymorphism P86L differentially control Ca homeostasis, mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling, and cell vulnerability upon exposure to amyloid beta. Aging Cell. doi:10.1111/acel.12403
Moyer BD, Hevezi P, Gao N, Lu M, Kalabat D, Soto H, Echeverri F, Laita B, Yeh SA, Zoller M, Zlotnik A (2009) Expression of genes encoding multi-transmembrane proteins in specific primate taste cell populations. PLoS One 4, e7682
Oh S, Rivkin S, Tang Q, Verselis VK, Bargiello TA (2004) Determinants of gating polarity of a connexin 32 hemichannel. Biophys J 87:912–928
Puljung MC, Berthoud VM, Beyer EC, Hanck DA (2004) Polyvalent cations constitute the voltage gating particle in human connexin37 hemichannels. J Gen Physiol 124:587–603
Purnick PE, Oh S, Abrams CK, Verselis VK, Bargiello TA (2000) Reversal of the gating polarity of gap junctions by negative charge substitutions in the N-terminus of connexin 32. Biophys J 79:2403–2415
Qiu Z, Dubin AE, Mathur J, Tu B, Reddy K, Miraglia LJ, Reinhardt J, Orth AP, Patapoutian A (2014) SWELL1, a plasma membrane protein, is an essential component of volume-regulated anion channel. Cell 157:447–458
Ripps H, Qian H, Zakevicius J (2004) Properties of connexin26 hemichannels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Cell Mol Neurobiol 24:647–665
Romanov RA, Kolesnikov SS (2006) Electrophysiologically identified subpopulations of taste bud cells. Neurosci Lett 395:249–254
Rubio-Moscardo F, Seto-Salvia N, Pera M, Bosch-Morato M, Plata C, Belbin O, Gene G, Dols-Icardo O, Ingelsson M, Helisalmi S, Soininen H, Hiltunen M, Giedraitis V, Lannfelt L, Frank A, Bullido MJ, Combarros O, Sanchez-Juan P, Boada M, Tarraga L, Pastor P, Perez-Tur J, Baquero M, Molinuevo JL, Sanchez-Valle R, Fuentes-Prior P, Fortea J, Blesa R, Munoz FJ, Lleo A, Valverde MA, Clarimon J (2013) Rare variants in calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) found in early onset Alzheimer’s disease patients alter calcium homeostasis. PLoS One 8, e74203
Sanchez HA, Villone K, Srinivas M, Verselis VK (2013) The D50N mutation and syndromic deafness: altered Cx26 hemichannel properties caused by effects on the pore and intersubunit interactions. J Gen Physiol 142:3–22
Siebert AP, Ma Z, Grevet JD, Demuro A, Parker I, Foskett JK (2013) Structural and functional similarities of calcium homeostasis modulator 1 (CALHM1) ion channel with connexins, pannexins, and innexins. J Biol Chem 288:6140–6153
Tanis JE, Ma Z, Krajacic P, He L, Foskett JK, Lamitina T (2013) CLHM-1 is a functionally conserved and conditionally toxic Ca2+-permeable ion channel in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Neurosci 33:12275–12286
Taruno A, Matsumoto I, Ma Z, Marambaud P, Foskett JK (2013) How do taste cells lacking synapses mediate neurotransmission? CALHM1, a voltage-gated ATP channel. Bioessays 35:1111–1118
Taruno A, Vingtdeux V, Ohmoto M, Ma Z, Dvoryanchikov G, Li A, Adrien L, Zhao H, Leung S, Abernethy M, Koppel J, Davies P, Civan MM, Chaudhari N, Matsumoto I, Hellekant G, Tordoff MG, Marambaud P, Foskett JK (2013) CALHM1 ion channel mediates purinergic neurotransmission of sweet, bitter and umami tastes. Nature 495:223–226
Tordoff MG, Aleman TR, Ellis HT, Ohmoto M, Matsumoto I, Shestopalov VI, Mitchell CH, Foskett JK, Poole RL (2015) Normal taste acceptance and preference of PANX1 knockout mice. Chem Senses 40:453–459
Vandenbeuch A, Anderson CB, Kinnamon SC (2015) Mice lacking pannexin 1 release ATP and respond normally to all taste qualities. Chem Senses 40:461–467
Verselis VK, Ginter CS, Bargiello TA (1994) Opposite voltage gating polarities of two closely related connexins. Nature 368:348–351
Vingtdeux V, Chandakkar P, Zhao H, Blanc L, Ruiz S, Marambaud P (2015) CALHM1 ion channel elicits amyloid-beta clearance by insulin-degrading enzyme in cell lines and in vivo in the mouse brain. J Cell Sci 128:2330–2338
Vingtdeux V, Tanis JE, Chandakkar P, Zhao H, Dreses-Werringloer U, Campagne F, Foskett JK, Marambaud P (2014) Effect of the CALHM1 G330D and R154H human variants on the control of cytosolic Ca2+ and Abeta levels. PLoS One 9, e112484
Voss FK, Ullrich F, Munch J, Lazarow K, Lutter D, Mah N, Andrade-Navarro MA, von Kries JP, Stauber T, Jentsch TJ (2014) Identification of LRRC8 heteromers as an essential component of the volume-regulated anion channel VRAC. Science 344:634–638
Wang HZ, Veenstra RD (1997) Monovalent ion selectivity sequences of the rat connexin43 gap junction channel. J Gen Physiol 109:491–507
Wang J, Dahl G (2010) SCAM analysis of Panx1 suggests a peculiar pore structure. J Gen Physiol 136:515–527
Yamashita M, Navarro-Borelly L, McNally BA, Prakriya M (2007) Orai1 mutations alter ion permeation and Ca2+-dependent fast inactivation of CRAC channels: evidence for coupling of permeation and gating. J Gen Physiol 130:525–540
Yarmolinsky DA, Zuker CS, Ryba NJ (2009) Common sense about taste: from mammals to insects. Cell 139:234–244
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health (NIH) Grants R01DC012538 (J.K.F. and Z.M.) and R03DC014328 (J.E.T.), an American Heart Postdoctoral fellowship 12POST11940054 (J.E.T.), JSPS KAKENHI Grants (25893201 and 26713008) (A.T.), The Salt Science Research Foundation (1429 and 1542) (A.T.), Society for Research on Umami Taste, Nestlé Nutrition Council, Japan (A.T.), and Kyoto Prefectural Public University Corporation (A.T.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Z., Tanis, J.E., Taruno, A. et al. Calcium homeostasis modulator (CALHM) ion channels. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 468, 395–403 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1757-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-015-1757-6