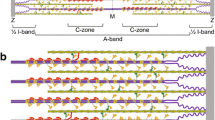
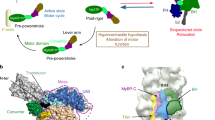
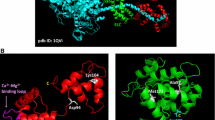
Abstract
Cardiac myosin-binding protein C (cMyBP-C) research has been characterized by two waves. Initial interest was piqued by its discovery in 1973 as a contaminant of myosin preparations from skeletal muscle. The second wave started in 1995 by the discovery that mutations in the gene encoding cMyBP-C cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM). In this review, we will address what is known of cMyBP-C's role as a regulator of contraction as well as its role in HCM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antos CL, McKinsey TA, Frey N, Kutschke W, McAnally J, Shelton JM, Richardson JA, Hill JA, Olson EN (2002) Activated glycogen synthase-3β suppresses cardiac hypertrophy in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 99:907–912. doi:10.1073/pnas.231619298
Arteaga GM, Palmiter KA, Leiden JM, Solaro RJ (2000) Attenuation of length dependence of calcium activation in myofilaments of transgenic mouse hearts expressing slow skeletal troponin I. J Physiol 526:541–549. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2000.t01-1-00541.x
Badorff C, Ruetten H, Mueller S, Stahmer M, Gehring D, Jung F, Ihling C, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2002) Fas receptor signaling inhibits glycogen synthase kinase 3β and induces cardiac hypertrophy following pressure overload. J Clin Inv 109:373–381
Bardswell SC, Cuello F, Kentish JC, Avkiran M (2012) cMyBP-C as a promiscuous substrate: phosphorylation by non-PKA kinases and its potential significance. J Mus Res Cell Mot 33:53–60
Barefield D, Sadayappan S (2010) Phosphorylation and function of cardiac myosin binding protein-C in health and disease. J Mol Cell Cardiol 48:866–875
Bhuiyan MS, Gulick J, Osinska H, Gupta M, Robbins J (2012) Determination of the critical residues responsible for cardiac myosin binding protein C's interactions. J Mol Cell Cardiol 53:838–847
Bonne G, Carrier L, Bercovici J, Cruaud C, Richard P, Hainque B, Gautel M, Labeit S, James M, Beckmann J (1995) Cardiac myosin binding protein-C gene splice acceptor site mutation is associated with familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet 11:438–440
Cazorla O, Szilagyi S, Vignier N, Salazar G, Kramer E, Vassort G, Carrier L, Lacampagne A (2006) Length and protein kinase A modulations of myocytes in cardiac myosin binding protein C-deficient mice. Cardiovas Res 69:370–380. doi:10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.11.009
Chen PP, Patel JR, Rybakova IN, Walker JW, Moss RL (2010) Protein kinase A-induced myofilament desensitization to Ca2+ as a result of phosphorylation of cardiac myosin-binding protein C. J Gen Physiol 136:615–627. doi:10.1085/jgp.201010448
Cohen P (1979) The hormonal control of glycogen metabolism in mammalian muscle by multivalent phosphorylation. Biochem Socie trans 7:459–480
Embi N, Rylatt DB, Cohen P (1980) Glycogen synthase kinase-3 from rabbit skeletal muscle. Eur J Biochem 107:519–527
England PJ (1975) Correlation between contraction and phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin in perfused rat heart. FEBS lett 50:57–60
Freiburg A, Gautel M (1996) A molecular map of the interactions between titin and myosin-binding protein C. Implications for sarcomeric assembly in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Eur J Biochem 235:317–323
Gautel M, Zuffardi O, Freiburg A, Labeit S (1995) Phosphorylation switches specific for the cardiac isoform of myosin binding protein-C: a modulator of cardiac contraction? EMBO J 14:1952–1960
Gilbert R, Kelly MG, Mikawa T, Fischman DA (1996) The carboxyl terminus of myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C, C-protein) specifies incorporation into the A-band of striated muscle. J Cell Sci 109:101–111
Goodwin JF (1970) Congestive and hypertrophic cardiomyopathies. Lancet 295:731–739
Gruen M, Gautel M (1999) Mutations in β-myosin S2 that cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (FHC) abolish the interaction with the regulatory domain of myosin-binding protein-C. J Mol Biol 286:933–949
Gruen M, Prinz H, Gautel M (1999) cAPK-phosphorylation controls the interaction of the regulatory domain of cardiac myosin binding protein C with myosin-S2 in an on-off fashion. FEBS lett 453:254–259
Haq S, Choukroun G, Kang ZB, Ranu H, Matsui T, Rosenzweig A, Molkentin JD, Alessandrini A, Woodgett J, Hajjar R, Michael A, Force T (2000) Glycogen synthase kinase-3β is a negative regulator of cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. J Cell Biol 151:117–130. doi:10.1083/jcb.151.1.117
Haq S, Choukroun G, Lim H, Tymitz KM, del Monte F, Gwathmey J, Grazette L, Michael A, Hajjar R, Force T, Molkentin JD (2001) Differential activation of signal transduction pathways in human hearts with hypertrophy versus advanced heart failure. Circulation 103:670–677. doi:10.1161/01.cir.103.5.670
Harris SP, Lyons RG, Bezold KL (2011) In the thick of it: HCM-causing mutations in myosin binding proteins of the thick filament. Circ Res 108:751–764. doi:10.1161/circresaha.110.231670
Konhilas JP, Irving TC, Wolska BM, Jweied EE, Martin AF, Solaro RJ, de Tombe PP (2003) Troponin I in the murine myocardium: influence on length-dependent activation and interfilament spacing. J Physiol 547:951–961. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.038117
Kooij V, Holewinski RJ, Murphy AM, Van Eyk JE (2013) Characterization of the cardiac myosin binding protein-C phosphoproteome in healthy and failing human hearts. J Mol Cell Cardiol 60:116–120
Kooij V, Saes M, Jaquet K, Zaremba R, Foster DB, Murphy AM, dos Remedios C, van der Velden J, Stienen GJM (2010) Effect of troponin I Ser23/24 phosphorylation on Ca2+-sensitivity in human myocardium depends on the phosphorylation background. J Mol Cell Cardio 48:954–963
Kuster DWD, Bawazeer AC, Zaremba R, Goebel M, Boontje NM, Velden J (2012) Cardiac myosin binding protein C phosphorylation in cardiac disease. J Mus Res Cell Mot 33:43–52
Kuster DWD, Mulders J, ten Cate FJ, Michels M, dos Remedios CG, da Costa Martins PA, van der Velden J,Oudejans CB (2013) MicroRNA transcriptome profiling in cardiac tissue of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patients with MYBPC3 mutations. J Mol Cell Cardiol 65C:59–66. doi:10.1016/j.yjmcc.2013.09.012
Kuster DWD, Sequeira V, Najafi A, Boontje N, Wijnker PJM, Witjas-Paalberends R, Marston S, dos Remedios CG, Carrier L, Demmers JAA, Redwood CS, Sadayappan S, van der Velden J (2013) GSK3β Phosphorylates newly identified site in the Pro-Ala rich region of cardiac myosin binding protein C and alters cross-bridge cycling kinetics in human. Circ Res 112:633–639. doi:10.1161/circresaha.112.275602
Lim MS, Walsh MP (1986) Phosphorylation of skeletal and cardiac muscle C-proteins by the catalytic subunit of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Cell Biol 64:622–630
Luther PK, Winkler H, Taylor K, Zoghbi ME, Craig R, Padrón R, Squire JM, Liu J (2011) Direct visualization of myosin-binding protein C bridging myosin and actin filaments in intact muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 108:11423–11428
Maron BJ, Gardin JM, Flack JM, Gidding SS, Kurosaki TT, Bild DE (1995) Prevalence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a general population of young adults: echocardiographic analysis of 4111 subjects in the CARDIA study. Circulation 92:785–789
Marston S, Copeland ON, Jacques A, Livesey K, Tsang V, McKenna WJ, Jalilzadeh S, Carballo S, Redwood C, Watkins H (2009) Evidence from human myectomy samples that MYBPC3 mutations cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy through haploinsufficiency. Circ Res 105:219–222
Miyamoto CA, Fischman DA, Reinach FC (1999) The interface between MyBP-C and myosin: site-directed mutagenesis of the CX myosin-binding domain of MyBP-C. J Mus Res Cell Mot 20:703–716
Moos C, Mason CM, Besterman JM, Feng INM, Dubin JH (1978) The binding of skeletal muscle C-protein to F-actin, and its relation to the interaction of actin with myosin subfragment-1. J Mol Biol 124:571–586
Morisco C, Zebrowski D, Condorelli G, Tsichlis P, Vatner SF, Sadoshima J (2000) The Akt-glycogen synthase kinase 3β pathway regulates transcription of atrial natriuretic factor induced by β-adrenergic receptor stimulation in cardiac myocytes. J Bio Chem 275:14466–14475. doi:10.1074/jbc.275.19.14466
Mun JY, Gulick J, Robbins J, Woodhead J, Lehman W, Craig R (2011) Electron microscopy and 3D reconstruction of F-actin decorated with cardiac myosin-binding protein C. J Mol Biol 410:214–225
Offer G, Moos C, Starr R (1973) A new protein of the thick filaments of vertebrate skeletal myofibrils: extraction, purification and characterization. J Mol Biol 74:653–676
Orlova A, Galkin VE, Jeffries CMJ, Egelman EH, Trewhella J (2011) The N-terminal domains of myosin binding protein C can bind polymorphically to F-actin. J Mol Biol 412:379–386
Pfuhl M, Gautel M (2012) Structure, interactions and function of the N-terminus of cardiac myosin binding protein C (MyBP-C): who does what, with what, and to whom? J Mus Res Cell Mot 33:83–94
Previs MJ, Previs SB, Gulick J, Robbins J, Warshaw DM (2012) Molecular mechanics of cardiac myosin-binding protein C in native thick filaments. Science 337:1215–1218. doi:10.1126/science.1223602
Ratti J, Rostkova E, Gautel M, Pfuhl M (2011) Structure and interactions of myosin-binding protein C domain C0: cardiac-specific regulation of myosin at its neck? J Biol Chem 286:12650–12658
Ray KP, England PJ (1976) Phosphorylation of the inhibitory subunit of troponin and its effect on the calcium dependence of cardiac myofibril adenosine triphosphatase. FEBS lett 70:11–16
Reddy YS (1976) Phosphorylation of cardiac regulatory proteins by cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. Am J Physiol 231:1330–1336
Richard P, Charron P, Carrier L, Ledeuil C, Cheav T, Pichereau C, Benaiche A, Isnard R, Dubourg O, Burban M, Gueffet J-P, Millaire A, Desnos M, Schwartz K, Hainque B, Komajda M, Project EHF (2003) Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: distribution of disease genes, spectrum of mutations, and implications for a molecular diagnosis strategy. Circulation 107:2227–2232
Rottbauer W, Gautel M, Zehelein J, Labeit S, Franz WM, Fischer C, Vollrath B, Mall G, Dietz R, Kübler W, Katus HA (1997) Novel splice donor site mutation in the cardiac myosin-binding protein-C gene in familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Characterization of cardiac transcript and protein. J Clin Inv 100:475–482
Sadayappan S, Gulick J, Osinska H, Martin LA, Hahn HS, Dorn GW, Klevitsky R, Seidman CE, Seidman JG, Robbins J (2005) Cardiac myosin-binding protein-C phosphorylation and cardiac function. Circ Res 97:1156–1163. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000190605.79013.4d
Sadayappan S, Tombe PP (2012) Cardiac myosin binding protein-C: redefining its structure and function. Biophys Rev 4:93–106
Santos S, Marques V, Pires M, Silveira L, Oliveira H, Lanca V, Brito D, Madeira H, Esteves JF, Freitas A, Carreira I, Gaspar I, Monteiro C,Fernandes A (2012) High resolution melting: improvements in the genetic diagnosis of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy in a Portuguese cohort. BMC Med Gen 13 (13)
Sequeira V, Wijnker PJM, Nijenkamp LLAM, Kuster DWD, Najafi A, Witjas-Paalberends ER, Regan JA, Boontje N, ten Cate FJ, Germans T, Carrier L, Sadayappan S, van Slegtenhorst MA, Zaremba R, Foster DB, Murphy AM, Poggesi C, dos Remedios C, Stienen GJM, Ho CY, Michels M, van der Velden J (2013) Perturbed length-dependent activation in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with missense sarcomeric gene mutations. Circ Res 112:1491–1505. doi:10.1161/circresaha.111.300436
Shaffer JF, Harris SP (2009) Species-specific differences in the Pro-Ala rich region of cardiac myosin binding protein-C. J Musc Res Cell Mot 30:303–306
Shaffer JF, Kensler RW, Harris SP (2009) The myosin-binding protein C motif binds to F-actin in a phosphorylation-sensitive manner. J Biol Chem 284:12318–12327. doi:10.1074/jbc.M808850200
Solaro RJ, Moir AJG, Perry SV (1976) Phosphorylation of troponin I and the inotropic effect of adrenaline in the perfused rabbit heart. Nature 262:615–617
Starr R, Offer G (1978) The interaction of C-protein with heavy meromyosin and subfragment-2. Biochem J 171:813–816
Stelzer JE, Dunning SB, Moss RL (2006) Ablation of cardiac myosin-binding protein-C accelerates stretch activation in murine skinned myocardium. Circ Res 98:1212–1218
Stelzer JE, Fitzsimons DP, Moss RL (2006) Ablation of myosin-binding protein-C accelerates force development in mouse myocardium. Biophys J 90:4119–4127
Stelzer JE, Patel JR, Moss RL (2006) Protein kinase A-mediated acceleration of the stretch activation response in murine skinned myocardium is eliminated by ablation of cMyBP-C. Circ Res 99:884–890. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000245191.34690.66
Sutherland C (2011) What are the bona fide GSK3 substrates? Int J Alzh Disea 2011:23. doi:10.4061/2011/505607
Tardiff J (2005) Sarcomeric proteins and familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: linking mutations in structural proteins to complex cardiovascular phenotypes. Heart Fail Rev 10:237–248
Teare D (1958) Asymmetrical hypertrophy of the heart in young adults. Br Heart J 20 (1)
Tong CW, Stelzer JE, Greaser ML, Powers PA, Moss RL (2008) Acceleration of crossbridge kinetics by protein kinase A phosphorylation of cardiac myosin binding protein C modulates cardiac function. Circ Res 103:974–982
van Dijk SJ, Dooijes D, dos Remedios C, Michels M, Lamers JMJ, Winegrad S, Schlossarek S, Carrier L, ten Cate FJ, Stienen GJM, van der Velden J (2009) Cardiac myosin-binding protein C mutations and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: haploinsufficiency, deranged phosphorylation and cardiomyocyte dysfunction. Circulation 119:1473–1483
van Dijk SJ, Paalberends ER, Najafi A, Michels M, Sadayappan S, Carrier L, Boontje NM, Kuster DWD, van Slegtenhorst M, Dooijes D, dos Remedios C, ten Cate FJ, Stienen GJM, van der Velden J (2012) Contractile dysfunction irrespective of the mutant protein in human hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with normal systolic function. Circ Heart Fail 5:36–46
Watkins H, Conner D, Thierfelder L, Jarcho JA, MacRae C, McKenna WJ, Maron BJ, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (1995) Mutations in the cardiac myosin binding protein-C gene on chromosome 11 cause familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Nat Genet 11:434–437
Whitten AE, Jeffries CM, Harris SP, Trewhella J (2008) Cardiac myosin-binding protein C decorates F-actin: implications for cardiac function. Proc Natl Acad Sci (USA) 105:18360–18365. doi:10.1073/pnas.0808903105
Woodgett J (1990) Molecular cloning and expression of glycogen synthase kinase-3/factor A. EMBO J 9:2431–2438
Woodgett J (1991) cDNA cloning and properties of glycogen synthase kinase-3. Methods Enzymol 200:564–577
Xu Q, Dewey S, Nguyen S, Gomes AV (2010) Malignant and benign mutations in familial cardiomyopathies: insights into mutations linked to complex cardiovascular phenotypes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 48:899–909
Yamamoto K, Moos C (1983) The C-proteins of rabbit red, white, and cardiac muscles. J Biol Chem 258:8395–8401
Yamasaki R, Wu Y, McNabb M, Greaser M, Labeit S, Granzier H (2002) Protein kinase A phosphorylates titin's cardiac-specific N2B domain and reduces passive tension in rat cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 90:1181–1188. doi:10.1161/01.res.0000021115.24712.99
Yang Q, Sanbe A, Osinska H, Hewett TE, Klevitsky R, Robbins J (1998) A mouse model of myosin binding protein C human familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. J Clin Inv 102:1292–1300
Yang Q, Sanbe A, Osinska H, Hewett TE, Klevitsky R, Robbins J (1999) In vivo modeling of myosin binding protein C familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 85:841–847. doi:10.1161/01.res.85.9.841
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the seventh framework program of the European Union (“BIG-HEART,” grant agreement 241577) and the Netherlands organization for scientific research (NWO; VIDI grant 917.11.344).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sequeira, V., Witjas-Paalberends, E.R., Kuster, D.W.D. et al. Cardiac myosin-binding protein C: hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutations and structure–function relationships. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 201–206 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1400-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1400-3