Abstract
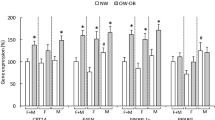
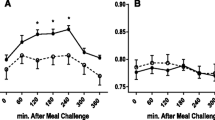
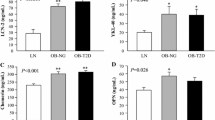
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) have a great potential for nutrition and obesity studies. PBMC reflect the nutritional response of key organs involved in energy homeostasis maintenance, which is altered in the obese state. Here, we aimed to determine the usefulness of PBMC as a source of early markers of obesity. To that purpose, we analysed whether PBMC could reflect the insensitivity to changes in feeding conditions associated with obesity during the development of this pathology. Expression of key genes central to energy metabolism was measured by Q-PCR in PBMC samples of normoweight (control) and cafeteria-fed (obese) rats in feeding, fasting and refeeding conditions. Samples were obtained monthly from 2 (beginning of cafeteria diet-feeding) to 6 months of age. In general terms, expression of genes related to fatty acid synthesis (Fasn, Srebp1) and adipogenesis (Pparg) decreased with fasting and increased with refeeding. Conversely, the expression of a key gene regulating beta-oxidation (Cpt1a) and the gene for an orexigenic neuropeptide (Npy)—in accordance with their metabolic role—increased with fasting and decreased with refeeding. This expression pattern disappeared in obese rats, in which insensitivity to feeding conditions was observed after only 1 month of cafeteria diet-feeding. Thus, during development, PBMC accurately reflect nutritional regulation of energy homeostasic genes and the insensitivity to feeding associated with obesity, even in the earlier stages with a low degree of overweight. For this reason, this set of blood cells could constitute a potential source of biomarkers of early homeostatic imbalance which would be useful in nutrition studies that could help prevent the occurrence of obesity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aljada A, Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Abdo T, Tripathy D, Chaudhuri A, Dandona P (2004) Increase in intranuclear nuclear factor kappaB and decrease in inhibitor kappaB in mononuclear cells after a mixed meal: evidence for a proinflammatory effect. Am J Clin Nutr 79:682–690
Bokarewa M, Nagaev I, Dahlberg L, Smith U, Tarkowski A (2005) Resistin, an adipokine with potent proinflammatory properties. J Immunol 174:5789–5795
Bouwens M, Afman LA, Muller M (2007) Fasting induces changes in peripheral blood mononuclear cell gene expression profiles related to increases in fatty acid beta-oxidation: functional role of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor alpha in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Am J Clin Nutr 86:1515–1523
Bouwens M, Afman LA, Müller M (2008) Activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells reveals an individual gene expression profile response. BMC Genomics 9:262
Bouwens M, van de Rest O, Dellschaft N, Bromhaar MG, de Groot LC, Geleijnse JM, Müller M, Afman LA (2009) Fish-oil supplementation induces antiinflammatory gene expression profiles in human blood mononuclear cells. Am J Clin Nutr 90:415–424
Brisbois TD, Farmer AP, McCargar LJ (2012) Early markers of adult obesity: a review. Obes Rev 13:347–367
Burczynski ME, Dorner AJ (2006) Transcriptional profiling of peripheral blood cells in clinical pharmacogenomic studies. Pharmacogenomics 7:187–202
Caimari A, Oliver P, Keijer J, Palou A (2010) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a model to study the response of energy homeostasis-related genes to acute changes in feeding conditions. OMICS 14:129–141
Caimari A, Oliver P, Palou A (2008) Impairment of nutritional regulation of adipose triglyceride lipase expression with age. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:1193–1200
Caimari A, Oliver P, Palou A (2007) Regulation of adiponutrin expression by feeding conditions in rats is altered in the obese state. Obesity (Silver Spring) 15:591–599
Caimari A, Oliver P, Rodenburg W, Keijer J, Palou A (2010) Feeding conditions control the expression of genes involved in sterol metabolism in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of normoweight and diet-induced (cafeteria) obese rats. J Nutr Biochem 21:1127–1133
Caimari A, Oliver P, Rodenburg W, Keijer J, Palou A (2010) Slc27a2 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells as a molecular marker for overweight development. Int J Obes (Lond) 34:831–839
Chaussabel D, Allman W, Mejias A, Chung W, Bennett L, Ramilo O, Pascual V, Palucka AK, Banchereau J (2005) Analysis of significance patterns identifies ubiquitous and disease-specific gene-expression signatures in patient peripheral blood leukocytes. Ann NY Acad Sci 1062:146–154
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Goyenechea E, Martínez JA (2008) Sirtuin gene expression in human mononuclear cells is modulated by caloric restriction. Eur J Clin Invest 38:672–678
Crujeiras AB, Parra D, Milagro FI, Goyenechea E, Larrarte E, Margareto J, Martínez JA (2008) Differential expression of oxidative stress and inflammation related genes in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in response to a low-calorie diet: a nutrigenomics study. OMICS 12:251–261
de Mello VD, Kolehmainen M, Schwab U, Mager U, Laaksonen DE, Pulkkinen L, Niskanen L, Gylling H, Atalay M, Rauramaa R, Uusitupa M (2008) Effect of weight loss on cytokine messenger RNA expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of obese subjects with the metabolic syndrome. Metabolism 57:192–199
Dhillo WS (2007) Appetite regulation: an overview. Thyroid 17:433–445
Ghanim H, Aljada A, Hofmeyer D, Syed T, Mohanty P, Dandona P (2004) Circulating mononuclear cells in the obese are in a proinflammatory state. Circulation 110:1564–1571
Goyenechea E, Parra D, Crujeiras AB, Abete I, Martínez JA (2009) A nutrigenomic inflammation-related PBMC-based approach to predict the weight-loss regain in obese subjects. Ann Nutr Metab 54:43–51
Horton JD, Goldstein JL, Brown MS (2002) SREBPs: activators of the complete program of cholesterol and fatty acid synthesis in the liver. J Clin Invest 109:1125–1131
Korner J, Woods SC, Woodworth KA (2009) Regulation of energy homeostasis and health consequences in obesity. Am J Med 122:S12–S18
Liew CC, Ma J, Tang HC, Zheng R, Dempsey AA (2006) The peripheral blood transcriptome dynamically reflects system wide biology: a potential diagnostic tool. J Lab Clin Med 147:126–132
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25:402–408
Maas K, Chan S, Parker J, Slater A, Moore J, Olsen N, Aune TM (2002) Cutting edge: molecular portrait of human autoimmune disease. J Immunol 169:5–9
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Mizuno TM, Makimura H, Silverstein J, Roberts JL, Lopingco T, Mobbs CV (1999) Fasting regulates hypothalamic neuropeptide Y, agouti-related peptide, and proopiomelanocortin in diabetic mice independent of changes in leptin or insulin. Endocrinology 140:4551–4557
Mohanty P, Ghanim H, Hamouda W, Aljada A, Garg R, Dandona P (2002) Both lipid and protein intakes stimulate increased generation of reactive oxygen species by polymorphonuclear leukocytes and mononuclear cells. Am J Clin Nutr 75:767–772
Napoleone E, DI Santo A, Amore C, Baccante G, di Febbo C, Porreca E, de Gaetano G, Donati MB, Lorenzet R (2007) Leptin induces tissue factor expression in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a possible link between obesity and cardiovascular risk? J Thromb Haemost 5:1462–1468
O'Rourke RW, Kay T, Lyle EA, Traxler SA, Deveney CW, Jobe BA, Roberts CT, Marks D, Rosenbaum JT (2006) Alterations in peripheral blood lymphocyte cytokine expression in obesity. Clin Exp Immunol 146:39–46
Olsen N, Sokka T, Seehorn CL, Kraft B, Maas K, Moore J, Aune TM (2004) A gene expression signature for recent onset rheumatoid arthritis in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1387–1392
Palou M, Priego T, Sanchez J, Villegas E, Rodriguez AM, Palou A, Pico C (2008) Sequential changes in the expression of genes involved in lipid metabolism in adipose tissue and liver in response to fasting. Pflugers Arch 456:825–836
Patel L, Buckels AC, Kinghorn IJ, Murdock PR, Holbrook JD, Plumpton C, Macphee CH, Smith SA (2003) Resistin is expressed in human macrophages and directly regulated by PPAR gamma activators. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 300:472–476
Pico C, Sanchez J, Oliver P, Palou A (2002) Leptin production by the stomach is up-regulated in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats. Obes Res 10:932–938
Radler U, Stangl H, Lechner S, Lienbacher G, Krepp R, Zeller E, Brachinger M, Eller-Berndl D, Fischer A, Anzur C, Schoerg G, Mascher D, Laschan C, Anderwald C, Lohninger A (2011) A combination of (ω-3) polyunsaturated fatty acids, polyphenols and L-carnitine reduces the plasma lipid levels and increases the expression of genes involved in fatty acid oxidation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells and HepG2 cells. Ann Nutr Metab 58:133–140
Roth GS, Tzankoff SP, Elahi D (1981) Effects of age on control of lipolysis during fasting. J Gerontol 36:391–397
Samara A, Marie B, Pfister M, Visvikis-Siest S (2008) Leptin expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) is related with blood pressure variability. Clin Chim Acta 395:47–50
Sampey BP, Vanhoose AM, Winfield HM, Freemerman AJ, Muehlbauer MJ, Fueger PT, Newgard CB, Makowski L (2011) Cafeteria diet is a robust model of human metabolic syndrome with liver and adipose inflammation: comparison to high-fat diet. Obesity (Silver Spring) 19:1109–1117
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Spiegelman BM (1995) Regulation of adipocyte gene expression and differentiation by peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma. Curr Opin Genet Dev 5:571–576
Tsiotra PC, Tsigos C, Yfanti E, Anastasiou E, Vikentiou M, Psarra K, Papasteriades C, Raptis SA (2007) Visfatin, TNF-alpha and IL-6 mRNA expression is increased in mononuclear cells from type 2 diabetic women. Horm Metab Res 39:758–763
van Erk MJ, Blom WA, van Ommen B, Hendriks HF (2006) High-protein and high-carbohydrate breakfasts differentially change the transcriptome of human blood cells. Am J Clin Nutr 84:1233–1241
Vidal-Puig A, Jimenez-Liñan M, Lowell BB, Hamann A, Hu E, Spiegelman B, Flier JS, Moller DE (1996) Regulation of PPAR gamma gene expression by nutrition and obesity in rodents. J Clin Invest 97:2553–2561
Visvikis-Siest S, Marteau JB, Samara A, Berrahmoune H, Marie B, Pfister M (2007) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs): a possible model for studying cardiovascular biology systems. Clin Chem Lab Med 45:1154–1168
Yu BP, Bertrand HA, Masoro EJ (1980) Nutrition-aging influence of catecholamine-promoted lipolysis. Metabolism 29:438–444
Zang Y, Wang T, Xie W, Wang-Fischer YL, Getty L, Han J, Corkey BE, Guo W (2005) Regulation of acetyl CoA carboxylase and carnitine palmitoyl transferase-1 in rat adipocytes. Obes Res 13:1530–1539
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Instituto de Salud Carlos III, Centro de Investigación Biomédica en Red Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición, CIBERobn. This work was also supported by the Spanish Government (Ministry of Education and Science, AGL 2009-11277/ALI) and the European Union (BIOCLAIMS FP7-244995). Our laboratory is a member of the European Research Network of Excellence NuGO (The European Nutrigenomics Organization, EU Contract: FOOD-CT-2004-506360 NUGO).
Ethical standards
The experiments followed in this study were reviewed and approved by the Bioethical Committee of the University of the Balearic Islands.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, P., Reynés, B., Caimari, A. et al. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells: a potential source of homeostatic imbalance markers associated with obesity development. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 465, 459–468 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1246-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-013-1246-8