Abstract
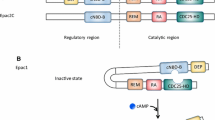
Exchange proteins directly activated by cyclic AMP (Epac) were discovered 10 years ago as new sensors for the second messenger cyclic AMP (cAMP). Epac family, including Epac1 and Epac2, are guanine nucleotide exchange factors for the Ras-like small GTPases Rap1 and Rap2 and function independently of protein kinase A. Given the importance of cAMP in the cardiovascular system, numerous molecular and cellular studies using specific Epac agonists have analyzed the role and the regulation of Epac proteins in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. The specific functions of Epac proteins may depend upon their microcellular environments as well as their expression and localization. This review discusses recent data showing the involvement of Epac in vascular cell migration, endothelial permeability, and inflammation through specific signaling pathways. In addition, we present evidence that Epac regulates the activity of various cellular compartments of the cardiac myocyte and influences calcium handling and excitation–contraction coupling. The potential role of Epac in cardiovascular disorders such as cardiac hypertrophy and remodeling is also discussed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson RH, Ly JC, Sarai RK, Lenz JF, Altangerel A, Drenckhahn D, Curry FE (2008) Epac/Rap1 pathway regulates microvascular hyperpermeability induced by PAF in rat mesentery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H1188–H1196
Aronoff DM, Carstens JK, Chen GH, Toews GB, Peters-Golden M (2006) Short communication: differences between macrophages and dendritic cells in the cyclic AMP-dependent regulation of lipopolysaccharide-induced cytokine and chemokine synthesis. J Interferon Cytokine Res 26:827–833
Baljinnyam E, Iwatsubo K, Kurotani R, Wang X, Ulucan C, Iwatsubo M, Lagunoff D, Ishikawa Y (2009) Epac increases melanoma migration by a heparan sulfate-related mechanism. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:C802–C813
Barlow CA, Rose P, Pulver-Kaste RA, Lounsbury KM (2006) Excitation-transcription coupling in smooth muscle. J Physiol 570:59–64
Basoni C, Nobles M, Grimshaw A, Desgranges C, Davies D, Perretti M, Kramer IM, Genot E (2005) Inhibitory control of TGF-beta1 on the activation of Rap1, CD11b, and transendothelial migration of leukocytes. FASEB J 19:822–824
Beavo JA, Brunton LL (2002) Cyclic nucleotide research—still expanding after half a century. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:710–718
Bers DM (2002) Cardiac excitation–contraction coupling. Nature 415:198–205
Bers DM (2008) Calcium cycling and signaling in cardiac myocytes. Annu Rev Physiol 70:23–49
Biel M, Michalakis S (2009) Cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Handb Exp Pharmacol 191:111–136
Birukova AA, Zagranichnaya T, Alekseeva E, Bokoch GM, Birukov KG (2008) Epac/Rap and PKA are novel mechanisms of ANP-induced Rac-mediated pulmonary endothelial barrier protection. J Cell Physiol 215:715–724
Birukova AA, Zagranichnaya T, Fu P, Alekseeva E, Chen W, Jacobson JR, Birukov KG (2007) Prostaglandins PGE(2) and PGI(2) promote endothelial barrier enhancement via PKA- and Epac1/Rap1-dependent Rac activation. Exp Cell Res 313:2504–2520
Bogatcheva NV, Verin AD (2008) The role of cytoskeleton in the regulation of vascular endothelial barrier function. Microvasc Res 76:202–207
Borland G, Bird RJ, Palmer TM, Yarwood SJ (2009) Activation of protein kinase Calpha by EPAC1 is required for the ERK- and CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta-dependent induction of the SOCS-3 gene by cyclic AMP in COS1 cells. J Biol Chem 284:17391–17403
Borland G, Gupta M, Magiera MM, Rundell CJ, Fuld S, Yarwood SJ (2006) Microtubule-associated protein 1B-light chain 1 enhances activation of Rap1 by exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP but not intracellular targeting. Mol Pharmacol 69:374–384
Borland G, Smith BO, Yarwood SJ (2009) EPAC proteins transduce diverse cellular actions of cAMP. Br J Pharmacol 158:70–86
Bos JL (2006) Epac proteins: multi-purpose cAMP targets. Trends Biochem Sci 31:680–686
Bos JL, Rehmann H, Wittinghofer A (2007) GEFs and GAPs: critical elements in the control of small G proteins. Cell 129:865–877
Bujak M, Frangogiannis NG (2007) The role of TGF-beta signaling in myocardial infarction and cardiac remodeling. Cardiovasc Res 74:184–195
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936
Carnegie GK, Means CK, Scott JD (2009) A-kinase anchoring proteins: from protein complexes to physiology and disease. IUBMB Life 61:394–406
Cazorla O, Lucas A, Poirier F, Lacampagne A, Lezoualc'h F (2009) The cAMP binding protein Epac regulates cardiac myofilament function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:14144–14149
Cullere X, Shaw SK, Andersson L, Hirahashi J, Luscinskas FW, Mayadas TN (2005) Regulation of vascular endothelial barrier function by Epac, a cAMP-activated exchange factor for Rap GTPase. Blood 105:1950–1955
Darrow BJ, Fast VG, Kleber AG, Beyer EC, Saffitz JE (1996) Functional and structural assessment of intercellular communication. Increased conduction velocity and enhanced connexin expression in dibutyryl cAMP-treated cultured cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 79:174–183
de Rooij J, Rehmann H, van Triest M, Cool RH, Wittinghofer A, Bos JL (2000) Mechanism of regulation of the Epac family of cAMP-dependent RapGEFs. J Biol Chem 275:20829–20836
de Rooij J, Zwartkruis FJ, Verheijen MH, Cool RH, Nijman SM, Wittinghofer A, Bos JL (1998) Epac is a Rap1 guanine-nucleotide-exchange factor directly activated by cyclic AMP. Nature 396:474–477
Derangeon M, Bourmeyster N, Plaisance I, Pinet-Charvet C, Chen Q, Duthe F, Popoff MR, Sarrouilhe D, Herve JC (2008) RhoA GTPase and F-actin dynamically regulate the permeability of Cx43-made channels in rat cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 283:30754–30765
Dodge-Kafka KL, Soughayer J, Pare GC, Carlisle Michel JJ, Langeberg LK, Kapiloff MS, Scott JD (2005) The protein kinase A anchoring protein mAKAP coordinates two integrated cAMP effector pathways. Nature 437:574–578
Doebele RC, Schulze-Hoepfner FT, Hong J, Chlenski A, Zeitlin BD, Goel K, Gomes S, Liu Y, Abe MK, Nor JE, Lingen MW, Rosner MR (2009) A novel interplay between Epac/Rap1 and MEK5/ERK5 regulates thrombospondin to control angiogenesis. Blood. PMID: 19710505 (in press)
Dudek SM, Garcia JG (2001) Cytoskeletal regulation of pulmonary vascular permeability. J Appl Physiol 91:1487–1500
Enserink JM, Christensen AE, de Rooij J, van Triest M, Schwede F, Genieser HG, Doskeland SO, Blank JL, Bos JL (2002) A novel Epac-specific cAMP analogue demonstrates independent regulation of Rap1 and ERK. Nat Cell Biol 4:901–906
Enyeart JA, Enyeart JJ (2009) Metabolites of an Epac-selective cAMP analog induce cortisol synthesis by adrenocortical cells through a cAMP-independent pathway. PLoS One 4:e6088
Etienne-Manneville S, Hall A (2002) Rho GTPases in cell biology. Nature 420:629–635
Fischmeister R, Castro LR, Abi-Gerges A, Rochais F, Jurevicius J, Leroy J, Vandecasteele G (2006) Compartmentation of cyclic nucleotide signaling in the heart: the role of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases. Circ Res 99:816–828
Fukuhara S, Sakurai A, Sano H, Yamagishi A, Somekawa S, Takakura N, Saito Y, Kangawa K, Mochizuki N (2005) Cyclic AMP potentiates vascular endothelial cadherin-mediated cell-cell contact to enhance endothelial barrier function through an Epac-Rap1 signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biol 25:136–146
Goichberg P, Kalinkovich A, Borodovsky N, Tesio M, Petit I, Nagler A, Hardan I, Lapidot T (2006) cAMP-induced PKCzeta activation increases functional CXCR4 expression on human CD34+ hematopoietic progenitors. Blood 107:870–879
Ho KK, Pinsky JL, Kannel WB, Levy D (1993) The epidemiology of heart failure: the Framingham Study. J Am Coll Cardiol 22:6A–13A
Holz GG, Chepurny OG, Schwede F (2008) Epac-selective cAMP analogs: new tools with which to evaluate the signal transduction properties of cAMP-regulated guanine nucleotide exchange factors. Cell Signal 20:10–20
Holz GG, Kang G, Harbeck M, Roe MW, Chepurny OG (2006) Cell physiology of cAMP sensor Epac. J Physiol 577:5–15
Hothi SS, Gurung IS, Heathcote JC, Zhang Y, Booth SW, Skepper JN, Grace AA, Huang CL (2008) Epac activation, altered calcium homeostasis and ventricular arrhythmogenesis in the murine heart. Pflugers Arch 457:253–270
Houslay MD, Baillie GS, Maurice DH (2007) cAMP-Specific phosphodiesterase-4 enzymes in the cardiovascular system: a molecular toolbox for generating compartmentalized cAMP signaling. Circ Res 100:950–966
Huston E, Lynch MJ, Mohamed A, Collins DM, Hill EV, MacLeod R, Krause E, Baillie GS, Houslay MD (2008) EPAC and PKA allow cAMP dual control over DNA-PK nuclear translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:12791–12796
Jing H, Yen JH, Ganea D (2004) A novel signaling pathway mediates the inhibition of CCL3/4 expression by prostaglandin E2. J Biol Chem 279:55176–55186
Kang G, Chepurny OG, Malester B, Rindler MJ, Rehmann H, Bos JL, Schwede F, Coetzee WA, Holz GG (2006) cAMP sensor Epac as a determinant of ATP-sensitive potassium channel activity in human pancreatic beta cells and rat INS-1 cells. J Physiol 573:595–609
Kang G, Joseph JW, Chepurny OG, Monaco M, Wheeler MB, Bos JL, Schwede F, Genieser HG, Holz GG (2003) Epac-selective cAMP analog 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP as a stimulus for Ca2 + -induced Ca2+ release and exocytosis in pancreatic beta-cells. J Biol Chem 278:8279–8285
Kassel KM, Wyatt TA, Panettieri RA Jr, Toews ML (2008) Inhibition of human airway smooth muscle cell proliferation by beta 2-adrenergic receptors and cAMP is PKA independent: evidence for EPAC involvement. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L131–L138
Kawasaki H, Springett GM, Mochizuki N, Toki S, Nakaya M, Matsuda M, Housman DE, Graybiel AM (1998) A family of cAMP-binding proteins that directly activate Rap1. Science 282:2275–2279
Keiper M, Stope MB, Szatkowski D, Bohm A, Tysack K, Vom Dorp F, Saur O, Oude Weernink PA, Evellin S, Jakobs KH, Schmidt M (2004) Epac- and Ca2+-controlled activation of Ras and extracellular signal-regulated kinases by Gs-coupled receptors. J Biol Chem 279:46497–46508
Kooistra MR, Corada M, Dejana E, Bos JL (2005) Epac1 regulates integrity of endothelial cell junctions through VE-cadherin. FEBS Lett 579:4966–4972
Kwak HJ, Park KM, Choi HE, Chung KS, Lim HJ, Park HY (2008) PDE4 inhibitor, roflumilast protects cardiomyocytes against NO-induced apoptosis via activation of PKA and Epac dual pathways. Cell Signal 20:803–814
Levy D, Garrison RJ, Savage DD, Kannel WB, Castelli WP (1990) Prognostic implications of echocardiographically determined left ventricular mass in the Framingham Heart Study. N Engl J Med 322:1561–1566
Lezoualc'h F (2009) Epac in melanoma: a contributor to tumor cell physiology? Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 297:797–799
Lezoualc'h F, Metrich M, Hmitou I, Duquesnes N, Morel E (2008) Small GTP-binding proteins and their regulators in cardiac hypertrophy. J Mol Cell Cardiol 44:623–632
Lincoln TM, Komalavilas P, Boerth NJ, MacMillan-Crow LA, Cornwell TL (1995) cGMP signaling through cAMP- and cGMP-dependent protein kinases. Adv Pharmacol 34:305–322
Lissitzky JC, Parriaux D, Ristorcelli E, Verine A, Lombardo D, Verrando P (2009) Cyclic AMP signaling as a mediator of vasculogenic mimicry in aggressive human melanoma cells in vitro. Cancer Res 69:802–809
Lorenowicz MJ, Fernandez-Borja M, Hordijk PL (2007) cAMP signaling in leukocyte transendothelial migration. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 27:1014–1022
Lorenowicz MJ, van Gils J, de Boer M, Hordijk PL, Fernandez-Borja M (2006) Epac1-Rap1 signaling regulates monocyte adhesion and chemotaxis. J Leukoc Biol 80:1542–1552
Lyle KS, Raaijmakers JH, Bruinsma W, Bos JL, de Rooij J (2008) cAMP-induced Epac-Rap activation inhibits epithelial cell migration by modulating focal adhesion and leading edge dynamics. Cell Signal 20:1104–1116
Maillet M, Robert SJ, Cacquevel M, Gastineau M, Vivien D, Bertoglio J, Zugaza JL, Fischmeister R, Lezoualc'h F (2003) Crosstalk between Rap1 and Rac regulates secretion of sAPPalpha. Nat Cell Biol 5:633–639
Maurice DH, Palmer D, Tilley DG, Dunkerley HA, Netherton SJ, Raymond DR, Elbatarny HS, Jimmo SL (2003) Cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase activity, expression, and targeting in cells of the cardiovascular system. Mol Pharmacol 64:533–546
McConnachie G, Langeberg LK, Scott JD (2006) AKAP signaling complexes: getting to the heart of the matter. Trends Mol Med 12:317–323
Mei FC, Qiao J, Tsygankova OM, Meinkoth JL, Quilliam LA, Cheng X (2002) Differential signaling of cyclic AMP: opposing effects of exchange protein directly activated by cyclic AMP and cAMP-dependent protein kinase on protein kinase B activation. J Biol Chem 277:11497–11504
Métrich M, Lucas A, Gastineau M, Samuel JL, Heymes C, Morel E, Lezoualc'h F (2008) Epac mediates beta-adrenergic receptor-induced cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ Res 102:959–965
Métrich M, Morel E, Berthouze M, Pereira L, Charron P, Gomez AM, Lezoualc'h F (2009) Functional characterization of the cAMP-binding proteins Epac in cardiac myocytes. Pharmacol Rep 61:146–153
Morel E, Marcantoni A, Gastineau M, Birkedal R, Rochais F, Garnier A, Lompre AM, Vandecasteele G, Lezoualc'h F (2005) cAMP-binding protein Epac induces cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. Circ Res 97:1296–1304
Movsesian MA, Bristow MR (2005) Alterations in cAMP-mediated signaling and their role in the pathophysiology of dilated cardiomyopathy. Curr Top Dev Biol 68:25–48
Namkoong S, Kim CK, Cho YL, Kim JH, Lee H, Ha KS, Choe J, Kim PH, Won MH, Kwon YG, Shim EB, Kim YM (2009) Forskolin increases angiogenesis through the coordinated cross-talk of PKA-dependent VEGF expression and Epac-mediated PI3K/Akt/eNOS signaling. Cell Signal 21:906–915
Niimura M, Miki T, Shibasaki T, Fujimoto W, Iwanaga T, Seino S (2009) Critical role of the N-terminal cyclic AMP-binding domain of Epac2 in its subcellular localization and function. J Cell Physiol 219:652–658
Oestreich EA, Malik S, Goonasekera SA, Blaxall BC, Kelley GG, Dirksen RT, Smrcka AV (2009) Epac and phospholipase Cepsilon regulate Ca2+ release in the heart by activation of protein kinase Cepsilon and calcium-calmodulin kinase II. J Biol Chem 284:1514–1522
Oestreich EA, Wang H, Malik S, Kaproth-Joslin KA, Blaxall BC, Kelley GG, Dirksen RT, Smrcka AV (2007) EPAC-mediated activation of phospholipase Cepsilon plays a critical role in beta -adrenergic receptor dependent enhancement of Ca2+ mobilization in cardiac myocytes. J Biol Chem 282:5488–5495
Ostroveanu A, van der Zee EA, Eisel UL, Schmidt M, Nijholt IM (2009) Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP 2 (Epac2) plays a specific and time-limited role in memory retrieval. Hippocampus (in press)
Pereira L, Métrich M, Fernandez-Velasco M, Lucas A, Leroy J, Perrier R, Morel E, Fischmeister R, Richard S, Benitah JP, Lezoualc'h F, Gomez AM (2007) The cAMP binding protein Epac modulates Ca2+ sparks by a Ca2+/calmodulin kinase signalling pathway in rat cardiac myocytes. J Physiol 583:685–694
Ponsioen B, Gloerich M, Ritsma L, Rehmann H, Bos JL, Jalink K (2009) Direct spatial control of Epac1 by cyclic AMP. Mol Cell Biol 29:2521–2531
Poppe H, Rybalkin SD, Rehmann H, Hinds TR, Tang XB, Christensen AE, Schwede F, Genieser HG, Bos JL, Doskeland SO, Beavo JA, Butt E (2008) Cyclic nucleotide analogs as probes of signaling pathways. Nat Methods 5:277–278
Purves GI, Kamishima T, Davies LM, Quayle JM, Dart C (2009) Exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) mediates cAMP-dependent but protein kinase A-insensitive modulation of vascular ATP-sensitive potassium channels. J Physiol 587:3639–3650
Qiao J, Mei FC, Popov VL, Vergara LA, Cheng X (2002) Cell cycle-dependent subcellular localization of exchange factor directly activated by cAMP. J Biol Chem 277:26581–26586
Rangarajan S, Enserink JM, Kuiperij HB, de Rooij J, Price LS, Schwede F, Bos JL (2003) Cyclic AMP induces integrin-mediated cell adhesion through Epac and Rap1 upon stimulation of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. J Cell Biol 160:487–493
Raymond DR, Wilson LS, Carter RL, Maurice DH (2007) Numerous distinct PKA-, or EPAC-based, signalling complexes allow selective phosphodiesterase 3 and phosphodiesterase 4 coordination of cell adhesion. Cell Signal 19:2507–2518
Regan CP, Adam PJ, Madsen CS, Owens GK (2000) Molecular mechanisms of decreased smooth muscle differentiation marker expression after vascular injury. J Clin Invest 106:1139–1147
Rehmann H, Arias-Palomo E, Hadders MA, Schwede F, Llorca O, Bos JL (2008) Structure of Epac2 in complex with a cyclic AMP analogue and RAP1B. Nature 455:124–127
Rehmann H, Das J, Knipscheer P, Wittinghofer A, Bos JL (2006) Structure of the cyclic-AMP-responsive exchange factor Epac2 in its auto-inhibited state. Nature 439:625–628
Robert S, Maillet M, Morel E, Launay JM, Fischmeister R, Mercken L, Lezoualc'h F (2005) Regulation of the amyloid precursor protein ectodomain shedding by the 5-HT4 receptor and Epac. FEBS Lett 579:1136–1142
Roscioni SS, Elzinga CR, Schmidt M (2008) Epac: effectors and biological functions. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 377:345–357
Sands WA, Woolson HD, Milne GR, Rutherford C, Palmer TM (2006) Exchange protein activated by cyclic AMP (Epac)-mediated induction of suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS-3) in vascular endothelial cells. Mol Cell Biol 26:6333–6346
Schmidt M, Evellin S, Weernink PA, von Dorp F, Rehmann H, Lomasney JW, Jakobs KH (2001) A new phospholipase-C-calcium signalling pathway mediated by cyclic AMP and a Rap GTPase. Nat Cell Biol 3:1020–1024
Sehrawat S, Cullere X, Patel S, Italiano J Jr, Mayadas TN (2008) Role of Epac1, an exchange factor for Rap GTPases, in endothelial microtubule dynamics and barrier function. Mol Biol Cell 19:1261–1270
Somekawa S, Fukuhara S, Nakaoka Y, Fujita H, Saito Y, Mochizuki N (2005) Enhanced functional gap junction neoformation by protein kinase A-dependent and Epac-dependent signals downstream of cAMP in cardiac myocytes. Circ Res 97:655–662
Ster J, De Bock F, Guerineau NC, Janossy A, Barrere-Lemaire S, Bos JL, Bockaert J, Fagni L (2007) Exchange protein activated by cAMP (Epac) mediates cAMP activation of p38 MAPK and modulation of Ca2+-dependent K+ channels in cerebellar neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:2519–2524
Tan KS, Nackley AG, Satterfield K, Maixner W, Diatchenko L, Flood PM (2007) Beta2 adrenergic receptor activation stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages via PKA- and NF-kappaB-independent mechanisms. Cell Signal 19:251–260
Tedgui A, Mallat Z (2006) Cytokines in atherosclerosis: pathogenic and regulatory pathways. Physiol Rev 86:515–581
Ulucan C, Wang X, Baljinnyam E, Bai Y, Okumura S, Sato M, Minamisawa S, Hirotani S, Ishikawa Y (2007) Developmental changes in gene expression of Epac and its upregulation in myocardial hypertrophy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 293:H1662–H1672
van Hinsbergh VW, van Nieuw Amerongen GP (2002) Endothelial hyperpermeability in vascular leakage. Vascul Pharmacol 39:171–172
Villarreal F, Epperson SA, Ramirez-Sanchez I, Yamazaki KG, Brunton LL (2009) Regulation of cardiac fibroblast collagen synthesis by adenosine: roles for Epac and PI3K. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 296:C1178–C1184
Vliem MJ, Ponsioen B, Schwede F, Pannekoek WJ, Riedl J, Kooistra MR, Jalink K, Genieser HG, Bos JL, Rehmann H (2008) 8-pCPT-2'-O-Me-cAMP-AM: an improved Epac-selective cAMP analogue. Chembiochem 9:2052–2054
Wang Z, Dillon TJ, Pokala V, Mishra S, Labudda K, Hunter B, Stork PJ (2006) Rap1-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinases by cyclic AMP is dependent on the mode of Rap1 activation. Mol Cell Biol 26:2130–2145
Wittchen ES, Worthylake RA, Kelly P, Casey PJ, Quilliam LA, Burridge K (2005) Rap1 GTPase inhibits leukocyte transmigration by promoting endothelial barrier function. J Biol Chem 280:11675–11682
Xu XJ, Reichner JS, Mastrofrancesco B, Henry WL Jr, Albina JE (2008) Prostaglandin E2 suppresses lipopolysaccharide-stimulated IFN-beta production. J Immunol 180:2125–2131
Yarwood SJ, Borland G, Sands WA, Palmer TM (2008) Identification of CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins as exchange protein activated by cAMP-activated transcription factors that mediate the induction of the SOCS-3 gene. J Biol Chem 283:6843–6853
Yeager M, Harris AL (2007) Gap junction channel structure in the early 21st century: facts and fantasies. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:521–528
Yokoyama U, Minamisawa S, Quan H, Akaike T, Jin M, Otsu K, Ulucan C, Wang X, Baljinnyam E, Takaoka M, Sata M, Ishikawa Y (2008) Epac1 is upregulated during neointima formation and promotes vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 295:H1547–H1555
Yokoyama U, Minamisawa S, Quan H, Akaike T, Suzuki S, Jin M, Jiao Q, Watanabe M, Otsu K, Iwasaki S, Nishimaki S, Sato M, Ishikawa Y (2008) Prostaglandin E2-activated Epac promotes neointimal formation of the rat ductus arteriosus by a process distinct from that of cAMP-dependent protein kinase A. J Biol Chem 283:28702–28709
Yokoyama U, Patel HH, Lai NC, Aroonsakool N, Roth DM, Insel PA (2008) The cyclic AMP effector Epac integrates pro- and anti-fibrotic signals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6386–6391
Zaldua N, Gastineau M, Hoshino M, Lezoualc'h F, Zugaza JL (2007) Epac signaling pathway involves STEF, a guanine nucleotide exchange factor for Rac, to regulate APP processing. FEBS Lett 581:5814–5818
Zhang CL, Katoh M, Shibasaki T, Minami K, Sunaga Y, Takahashi H, Yokoi N, Iwasaki M, Miki T, Seino S (2009) The cAMP sensor Epac2 is a direct target of antidiabetic sulfonylurea drugs. Science 325:607–610
Acknowledgments
The work of F.L. mentioned herein was supported by INSERM, AP-HP, Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale (équipe FRM), and the Agence Nationale de la Recherche (EPAC-06, EPAC-09). M.M. and M.B. were supported by a grant from the Fondation pour la Recherche Médicale and Lefoulon-Delalande, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Métrich, M., Berthouze, M., Morel, E. et al. Role of the cAMP-binding protein Epac in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 459, 535–546 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0747-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0747-y