Abstract
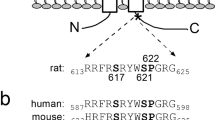
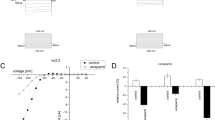
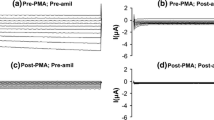
Intermediate-conductance (IK) Ca2+-activated K+ channels are expressed in many different cell types where they perform a variety of functions including cell volume regulation, transepithelial secretion, lymphocyte activation and cell cycle progression. IK channels are thought to be regulated by phosphorylation; however, whether kinases act directly on the channel is unclear. Using IK channels heterologously expressed in Xenopus oocytes, we demonstrate that IK channels are potently inhibited (60%) by the catalytic subunit of protein kinase A (PKA). Inhibition of IK channel current by PKA is abolished by mutation of four phosphorylation residues (S312, T327, S332, and T348) in the putative calmodulin-binding region of the channel. Evidence for direct modulation of the IK channel by PKA was further demonstrated using GST fusion proteins. The major site of phosphorylation was found to be serine 332; however, other residues were also phosphorylated. We conclude that IK channels can be directly regulated by the cAMP second-messenger system. The mechanism appears to involve direct phosphorylation by PKA of a modulatory locus in the cytoplasmic region of the channel, the site at which calmodulin is thought to interact. Modulation of IK channels by protein kinases may be an important mechanism regulating cell function.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bielefeldt K, Jackson MB (1994) Intramolecular and intermolecular enzymatic modulation of ion channels in excised membrane patches. Biophys J 66:1904–1914
Chung SK, Reinhart PH, Martin BL, Brautigan D, Levitan IB (1991) Protein kinase activity closely associated with a reconstituted calcium-activated potassium channel. Science 253:560–562
Del Carlo B, Pellegrini M, Pellegrino M (2003) Modulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels of human erythrocytes by endogenous protein kinase C. Biochim Biophys Acta 1612:107–116
Devor DC, Singh AK, Lambert LC, DeLuca A, Frizzell RA, Bridges RJ (1999) Bicarbonate and chloride secretion in Calu-3 human airway epithelial cells. J Gen Physiol 113:743–760
DiChiara T, Reinhart P (1997) Redox modulation of hslo Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J Neurosci 17:4942–4955
Esguerra M, Wang J, Foster CD, Adelman JP, North RA, Levitan IB (1994) Cloned Ca(2+)-dependent K+ channel modulated by a functionally associated protein kinase. Nature 369:563–565
Fanger CM, Ghanshani S, Logsdon NJ, Rauer H, Kalman K, Zhou J, Beckingham K, Chandy KG, Cahalan MD, Aiyar J (1999) Calmodulin mediates calcium-dependent activation of the intermediate conductance KCa channel, IKCa1. J Biol Chem 274:5746–5754
Furness JB, Robbins HL, Selmer IS, Hunne B, Chen MX, Hicks GA, Moore S, Neylon CB (2003) Expression of intermediate conductance potassium channel immunoreactivity in neurons and epithelial cells of the rat gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 314:179–189
Gerlach AC, Gangopadhyay NN, Devor DC (2000) Kinase-dependent regulation of the intermediate conductance, calcium-dependent potassium channel, hIK1. J Biol Chem 275:585–598
Grifman M, Arbel A, Ginzberg D, Glick D, Elgavish S, Shaanan B, Soreq H (1997) In vitro phosphorylation of acetylcholinesterase at non-consensus protein kinase A sites enhances the rate of acetylcholine hydrolysis. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 51:179–187
Hall SK, Armstrong DL (2000) Conditional and unconditional inhibition of calcium-activated potassium channels by reversible protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 275:3749–3754
Hayashi M, Kunii C, Takahata T, Ishikawa T (2004) ATP-dependent regulation of SK4/IK1-like currents in rat submandibular acinar cells: possible role of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Am J Physiol 286:C635–C646
Huang Y, Rane SG (1994) Potassium channel induction by the Ras/Raf signal transduction cascade. J Biol Chem 269:31183–31189
Indolfi C, Stabile E, Coppola C, Gallo A, Perrino C, Allevato G, Cavuto L, Torella D, Di Lorenzo E, Troncone G, Feliciello A, Avvedimento E, Chiariello M (2001) Membrane-bound protein kinase A inhibits smooth muscle cell proliferation in vitro and in vivo by amplifying cAMP-protein kinase A signals. Circ Res 88:319–324
Ishii T, Silvia C, Hirschberg B, Bond C, Adelman J, Maylie J (1997) A human intermediate conductance calcium-activated potassium channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:11651–11656
Jensen BS, Strobaek D, Olesen SP, Christophersen P (2001) The Ca2+-activated K+ channel of intermediate conductance: a molecular target for novel treatments? Curr Drug Targets 2:401–422
Joiner WJ, Khanna R, Schlichter LC, Kaczmarek LK (2001) Calmodulin regulates assembly and trafficking of SK4/IK1 Ca2+-activated K+ channels. J Biol Chem 276:37980–37985
Keen JE, Khawaled R, Farrens DL, Neelands T, Rivard A, Bond CT, Janowsky A, Fakler B, Adelman JP, Maylie J (1999) Domains responsible for constitutive and Ca(2+)-dependent interactions between calmodulin and small conductance Ca(2+)-activated potassium channels. J Neurosci 19:8830–8838
Kemp BE, Graves DJ, Benjamini E, Krebs EG (1977) Role of multiple basic residues in determining the substrate specificity of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem 252:4888–4894
Khanna R, Chang MC, Joiner WJ, Kaczmarek LK, Schlichter LC (1999) hSK4/hIK1, a calmodulin-binding KCa channel in human T lymphocytes. Roles in proliferation and volume regulation. J Biol Chem 274:14838–14849
Levitan IB (1999) It is calmodulin after all! Mediator of the calcium modulation of multiple ion channels. Neuron 22:645–648
Levitan IB (1999) Modulation of ion channels by protein phosphorylation. How the brain works. Adv Second Messenger Phosphoprotein Res 33:3–22
Lhuillier L, Dryer SE (1999) TGFbeta1 regulates the gating properties of intermediate-conductance KCa channels in developing parasympathetic neurons. J Neurophysiol 82:1627–1631
Lhuillier L, Dryer SE (2000) Developmental regulation of neuronal KCa channels by TGFbeta 1: transcriptional and posttranscriptional effects mediated by Erk MAP kinase. J Neurosci 20:5616–5622
Logsdon NJ, Kang J, Togo JA, Christian EP, Aiyar J (1997) A novel gene, hKCa4, encodes the calcium-activated potassium channel in human T lymphocytes. J Biol Chem 272:32723–32726
Marx SO, Reiken S, Hisamatsu Y, Gaburjakova M, Gaburjakova J, Yang YM, Rosemblit N, Marks AR (2001) Phosphorylation-dependent regulation of ryanodine receptors: a novel role for leucine/isoleucine zippers. J Cell Biol 153:699–708
Neylon CB (2002) Potassium channels and vascular proliferation. Vasc Pharmacol 38:35–41
Neylon CB, Avdonin P, Dilley R, Larsen M, Tkachuk V, Bobik A (1994) Different electrical responses to vasoactive agonists in morphologically distinct smooth muscle cell types. Circ Res 75:733–741
Neylon CB, Lang RJ, Fu Y, Bobik A, Reinhart PH (1999) Molecular cloning and characterization of the intermediate-conductance Ca(2+)-activated K(+) channel in vascular smooth muscle: relationship between K(Ca) channel diversity and smooth muscle cell function. Circ Res 85:e33–43
Pedarzani P, Krause M, Haug T, Storm JF, Stuhmer W (1998) Modulation of the Ca2+-activated K+ current sIAHP by a phosphatase-kinase balance under basal conditions in rat CA1 pyramidal neurons. J Neurophysiol 79:3252–3256
Pellegrino M, Pellegrini M (1998) Modulation of Ca2+-activated K+ channels of human erythrocytes by endogenous cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Pflugers Arch 436:749–756
Pena TL, Rane SG (1999) The fibroblast intermediate conductance K(Ca) channel, FIK, as a prototype for the cell growth regulatory function of the IK channel family. J Membr Biol 172:249–257
Pena TL, Chen SH, Konieczny SF, Rane SG (2000) Ras/MEK/ERK Up-regulation of the fibroblast KCa channel FIK is a common mechanism for basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor-beta suppression of myogenesis. J Biol Chem 275:13677–13682
Prevarskaya NB, Skryma RN, Vacher P, Daniel N, Djiane J, Dufy B (1995) Role of tyrosine phosphorylation in potassium channel activation. Functional association with prolactin receptor and JAK2 tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 270:24292–24299
Reinhart PH, Levitan IB (1995) Kinase and phosphatase activities intimately associated with a reconstituted calcium-dependent potassium channel. J Neurosci 15:4572–4579
Reinhart PH, Chung S, Martin BL, Brautigan DL, Levitan IB (1991) Modulation of calcium-activated potassium channels from rat brain by protein kinase A and phosphatase 2A. J Neurosci 11:1627–1635
Schroder RL, Jensen BS, Strobaek D, Olesen SP, Christophersen P (2000) Activation of the human, intermediate-conductance, Ca2+-activated K+ channel by methylxanthines. Pflugers Arch 440:809–818
Seibert FS, Chang XB, Aleksandrov AA, Clarke DM, Hanrahan JW, Riordan JR (1999) Influence of phosphorylation by protein kinase A on CFTR at the cell surface and endoplasmic reticulum. Biochim Biophys Acta 1461:275–283
Torgersen KM, Vang T, Abrahamsen H, Yaqub S, Tasken K (2002) Molecular mechanisms for protein kinase A-mediated modulation of immune function. Cell Signal 14:1–9
Tseng-Crank J, Foster C, Krause J, Mertz R, Godinot N, DiChiara T, Reinhart P (1994) Cloning, expression, and distribution of functionally distinct Ca2+-activated K+ channel isoforms from human brain. Neuron 13:1315–1330
Vandorpe DH, Shmukler BE, Jiang L, Lim B, Maylie J, Adelman JP, Franceschi L de, Cappellini MD, Brugnara C, Alper SL (1998) cDNA cloning and functional characterization of the mouse Ca2+-gated K+ channel, mIK1. Roles in regulatory volume decrease and erythroid differentiation. J Biol Chem 273:21542–21553
Vogalis F, Harvey JR, Furness JB (2002) TEA- and apamin-resistant K(Ca) channels in guinea-pig myenteric neurons: slow AHP channels. J Physiol (Lond) 538:421–433
Von Hahn T, Thiele I, Zingaro L, Hamm K, Garcia-Alzamora M, Kottgen M, Bleich M, Warth R (2001) Characterisation of the rat SK4/IK1 K(+) channel. Cell Physiol Biochem 11:219–230
Wissmann R, Bildl W, Neumann H, Rivard AF, Klocker N, Weitz D, Schulte U, Adelman JP, Bentrop D, Fakler B (2002) A helical region in the C terminus of small-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels controls assembly with apo-calmodulin. J Biol Chem 277:4558–4564
Wulf A, Schwab A (2002) Regulation of a calcium-sensitive K+ channel (cIK1) by protein kinase C. J Membr Biol 187:71–79
Xia XM, Fakler B, Rivard A, Wayman G, Johnson-Pais T, Keen JE, Ishii T, Hirschberg B, Bond CT, Lutsenko S, Maylie J, Adelman JP (1998) Mechanism of calcium gating in small-conductance calcium-activated potassium channels. Nature 395:503–507
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by a National Institute of Health grant (to P.H.R.), and an American Heart Association Postdoctoral Fellowship (to T.D.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neylon, C.B., D’Souza, T. & Reinhart, P.H. Protein kinase A inhibits intermediate conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 448, 613–620 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1302-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-004-1302-5