Abstract
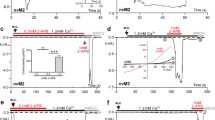
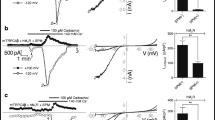
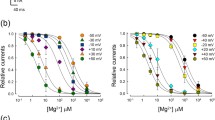
TRPM4b (in contrast to the short splice variant TRPM4a) is a Ca2+-activated but Ca2+-impermeable cation channel. We have studied TRPM4 currents in inside-out patches. Supramicromolar Ca2+ concentrations applied at the inner side, [Ca2+]i, activated TRPM4 with an EC50 value of 0.37 mM, a value that is much higher than that of whole-cell currents. Current amplitudes decreased above 1 mM [Ca2+]i, (IC50 9.3 mM). Sr2+ but not Ba2+could partially substitute for Ca2+. ATP, ADP, AMP and AMP-PNP all quickly and reversibly inhibited TRPM4 with IC50 values between 2 and 19 μM (at +100 mV). Adenosine also blocked TRPM4 at 630 μM. The block at high ATP concentrations was incomplete and was not affected by the presence of free Mg2+. ADP induced the most sensitive block with an IC50 of 2.2 μM. For inhibition of TRPM4 by free ATP4−, an IC50 value of 1.7±0.3 μM was calculated. GTP, UTP and CTP at concentrations up to 1 mM did not induce a similar block. Spermine blocked TRPM4 currents with an IC50 of 61 μM. In conclusion, TRPM4 is a channel that can be effectively modulated by intracellular nucleotides and polyamines.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clapham DE, Runnels LW, Strubing C (2001) The trp ion channel family. Nature Rev Neurosci 2:387–396
Fernandez AI, Cantabrana B, Sanchez M, Hidalgo A (1995) Extracellular and intracellular effects of polyamines on smooth muscle contractions. Life Sci 57:855–861
Guinamard R, Rahmati M, Lenfant J, Bois P (2002) Characterization of a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channel during dedifferentiation of cultured rat ventricular cardiomyocytes. J Membr Biol 188:127–135
Halonen J, Nedergaard J (2002) Adenosine 5′-monophosphate is a selective inhibitor of the brown adipocyte nonselective cation channel. J Membr Biol 188:183–197
Hofmann T, Chubanov V, Gudermann T, Montell C (2003) TRPM5 is a voltage-modulated and Ca2+-activated monovalent selective cation channel. Curr Biol 13:1153–1158
Hurwitz CG, Hu VY, Segal AS (2002) A mechanogated nonselective cation channel in proximal tubule that is ATP sensitive. Am J Physiol 283:F93–F104
Kerschbaum HH, Kozak JA, Cahalan MD (2003) Polyvalent cations as permeant probes of MIC and TRPM7 pores. Biophys J 84:2293–2305
Kubo Y, Murata Y (2001) Control of rectification and permeation by two distinct sites after the second transmembrane region in Kir2.1 K+ channel. J Physiol (Lond) 531:645–660
Launay P, Fleig A, Perraud AL, Scharenberg AM, Penner R, Kinet JP (2002) TRPM4 is a Ca2+-activated nonselective cation channel mediating cell membrane depolarization. Cell 109:397–407
Liman ER (2003) Regulation by voltage and adenine nucleotides of a Ca2+-activated cation channel from hamster vomeronasal sensory neurons. J Physiol (Lond) 548:777–787
Lopatin AN, Nichols CG (1996) [K+] dependence of polyamine-induced rectification in inward rectifier potassium channels (IRK1, Kir2.1). J Gen Physiol 108:105–113
Mott DD, Washburn MS, Zhang S, Dingledine RJ (2003) Subunit-dependent modulation of kainate receptors by extracellular protons and polyamines. J Neurosci 23:1179–1188
Nilius B, Prenen J, Droogmans G, Voets T, Vennekens R, Freichel M, Wissenbach U, Flockerzi V (2003) Voltage dependence of the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4. J Biol Chem 278:30813–30820
Nilius B, Prenen J, Vennekens R, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ, Droogmans G (2001) Modulation of the epithelial calcium channel, ECaC, by intracellular Ca2+. Cell Calcium 29:417–428
Nilius B, Prenen J, Vennekens R, Hoenderop JGJ, Bindels RJM, Droogmans G (2001) Pharmacological modulation of monovalent cation currents through the epithelial Ca2+ channel ECaC. Br J Pharmacol 134:453–462
Prawitt D, Monteilh-Zoller MK, Brixel L, Spangenberg C, Zabel B, Fleig A, Penner R (2003) TRPM5 is a transient Ca2+-activated cation channel responding to rapid changes in [Ca2+]i. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15166–15171
Sabirov RZ, Prenen J, Tomita T, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2000) Reduction of ionic strength activates single volume-regulated anion channels (VRAC) in endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch 439:315–320
Suh SH, Watanabe H, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) ATP and nitric oxide modulate a Ca2+-activated non-selective cation current in macrovascular endothelial cells. Pflugers Arch 444:438–445
Vennekens R, Voets T, Bindels RJ, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) Current understanding of mammalian TRP homologues. Cell Calcium 31:253–264
Voets T, Janssens A, Prenen J, Droogmans D, Nilius G (2003) Mg2+-dependent gating and strong inward rectification of the cation channel TRPV6. J Gen Physiol 121:245–260
Voets T, Prenen J, Fleig A, Vennekens R, Watanabe H, Hoenderop JGJ, Bindels RJM, Droogmans G, Penner R, Nilius B (2001) CaT1 and the calcium release-activated calcium channel manifest distinct pore properties. J Biol Chem 276:47767–47770
Voets T, Prenen J, Vriens J, Watanabe H, Janssens A, Wissenbach U, Bödding M, Droogmans G, Nilius B (2002) Molecular determinants of permeation through the cation channel TRPV4. J Biol Chem 277:33704–33710
Washburn MS, Dingledine R (1996) Block of alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (AMPA) receptors by polyamines and polyamine toxins. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:669–678
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs. J.-P. Kinnet and P. Launay (Department of Pathology, Harvard Medical Scholl, Boston, Mass., USA) for providing us with the tetracycline-inducible HEK 293 Flag-TRPM4-expressing cell line. This work was supported by the Belgian Federal Government, the Flemish Government, the Onderzoeksraad KU Leuven (GOA 99/07, F.W.O. G.0214.99, F.W.O. G. 0136.00; F.W.O. G.0172.03, Interuniversity Poles of Attraction Program, Prime Ministers Office IUAP) .
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nilius, B., Prenen, J., Voets, T. et al. Intracellular nucleotides and polyamines inhibit the Ca2+-activated cation channel TRPM4b. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 448, 70–75 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1221-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-003-1221-x