Abstract.
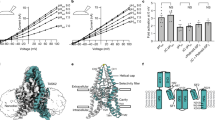
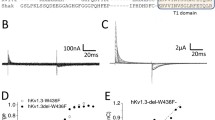
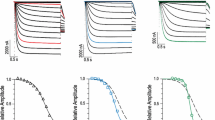
TASK-1 and -2 are members of the two-pore domain potassium (K+) channel family and are sensitive to changes in extracellular pH. The effects of mutating charged, extracellular-facing residues in TASK-1 and –2 were studied in Xenopus oocytes by two-electrode voltage clamp. Hydrogen ion block was independent of voltage with K d values of 149±17.9 nM [H+] (n=6) and 5.76±1.23 nM [H+] (n=7) for TASK-1 and -2, respectively. Compared to wild-type TASK-1, H72N, H98N, H98D and K210N displayed significant shifts in their K d values for hydrogen ion block ([H+]; 110±9.80 nM, 737±170 nM, 321±85.9 nM and 267±9.92 nM, respectively, n=6 each, P<0.05). Although significantly reducing its pH sensitivity, mutation of H98 in TASK-1 did not abolish pH sensitivity; this implies that H98 is not the only residue or domain involved in pH sensing of TASK-1. TASK-2 does not possess a histidine residue at the homologous position. However, the inclusion of such a residue failed to produce the expected increase in pH sensitivity; instead, a slight decrease was observed. Despite their structural homology and common sensitivity to pH, the TASK family of K+ channels apparently has diverse pH-sensing mechanisms.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morton, M.J., O'Connell, A.D., Sivaprasadarao, A. et al. Determinants of pH sensing in the two-pore domain K+ channels TASK-1 and -2. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 445, 577–583 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0901-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-002-0901-2