Abstract.
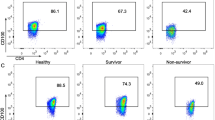
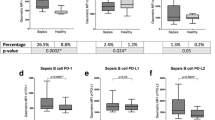
Background and aims: Lymphocyte apoptosis may influence immune responsiveness in systemic inflammation. Therefore, we investigated whether early signs of apoptosis (i.e., annexin-V binding and cell shrinkage) in peripheral lymphocytes were different among patients with severe sepsis, critically ill, nonseptic patients after major surgery, and healthy individuals. Patients/methods: Ten patients with severe sepsis and ten critically ill, nonseptic patients after major surgery admitted to a surgical intensive care unit in a university hospital were included in the study. In addition, ten healthy blood donors were included for comparison. We investigated early signs of apoptosis using flow cytometric measurement of annexin-V binding to the cell surface and cell shrinkage of peripheral lymphocytes. Results: The percentage of apoptotic lymphocytes determined as annexin-V positive and propidium iodide negative cells was increased in freshly prepared cells of patients with severe sepsis (11.4±0.5%) and critically ill, nonseptic patients after major surgery (18.5±2.0%) relative to healthy blood donors (4.4±0.5%) (P<0.05). No significant difference between patients with severe sepsis and patients after major surgery were found. Annexin-V binding increased significantly after OKT-3 stimulation of lymphocytes in patients with severe sepsis (34.4±1.6%), patients after major surgery (33.8±3.4%), and healthy blood donors (21.1±2.8%). No significant difference among groups was detected following OKT-3 stimulation. Furthermore, freshly isolated peripheral lymphocytes of patients with severe sepsis and critically ill, nonseptic patients after major surgery revealed a significantly higher proportion of cell shrinkage than in healthy blood donors (55.0±2.2%, 21.5±2.4% vs 3.6±0.7%; P<0.05). Conclusion: Circulating lymphocytes of critically ill patients show a high degree of early signs of cellular apoptosis. This may contribute to hyporesponsiveness of immune cells in systemic inflammation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received in revised form: 6 September 2000
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schroeder, S., Lindemann, C., Decker, D. et al. Increased susceptibility to apoptosis in circulating lymphocytes of critically ill patients. Langenbeck's Arch Surg 386, 42–46 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004230000181
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004230000181