Abstract
Introduction
Total splenectomy leads to an immunocompromised state, with an increased lifetime risk of infection. The lifetime risk of developing overwhelming postsplenectomy infection is 5 %, with a mortality rate of approximately 50 %. In addition to vaccination and antibiotic prophylaxis, partial splenectomy is believed to improve patient safety.
Methods
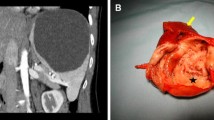
We performed partial splenectomy in seven patients using a radiofrequency (RF) technique with Habib® needles. In seven patients, an open access partial splenectomy was performed. In three patients, a partial splenectomy was performed simultaneously with intraabdominal tumour resection. In two patients, the upper pole of the spleen was removed due to tumours of the spleen. In one patient, a large symptomatic splenic cyst was resected and in another patient, a partial splenectomy was performed due to trauma. RF was applied using Habib® needles (AngioDynamics, Manchester, GA, 31816, USA).
Results
The partial splenectomy procedures were easy and safe in all seven patients. The RF application with the Habib® needles led to primary haemostasis. The blood loss was less than 50 ml in all cases. After a minimum follow-up of 1 year, there were no cases of infections or other adverse events related to the previous partial splenectomy.
Conclusion
In our experience, partial splenectomy with Habib® needles is easy to perform and safe for the patient. Thus, radiofrequency resection is a good alternative to total splenectomy in many patients and reduces the risk of postsplenectomy infections.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bisharat N, Omari H, Lavi I, Raz R (2001) Risk of infection and death among post-splenectomy patients. J Infect 3:182–186
de Porto APNA, Lammers AJJ, Bennink RJ et al (2010) Assessment of splenic function. Eur J Cli Microbiol Infect Dis: Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol 12:1465–1473
Jones P, Leder K, Woolley I et al (2010) Postsplenectomy infection—strategies for prevention in general practice. Aust Fam Phys 6:383–386
Waghorn DJ (2001) Overwhelming infection in asplenic patients: current best practice preventive measures are not being followed. J Clin Pathol 3:214–218
King H, Shumacker HB (1952) Splenic studies. Susceptibility to infection after splenectomy performed in infancy. Ann Surg 2:239–242
Davidson RN, Wall RA (2001) Prevention and management of infections in patients without a spleen. Clin Microbiol Infect: Off Publ Eur Soc Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 12:657–660
Holdsworth RJ, Irving AD, Cuschieri A (1991) Postsplenectomy sepsis and its mortality rate: actual versus perceived risks. Br J Surg 9:1031–1038
Spelman D, Buttery J, Daley A et al (2008) Guidelines for the prevention of sepsis in asplenic and hyposplenic patients. Int Med J 5:349–356
Cadili A, de Gara C (2008) Complications of splenectomy. Am J Med 5:371–375
Hassn A-F, Ouf S (2000) Portal vein thrombosis following splenectomy. Br J Surg 3:362–373
Ikeda M, Sekimoto M, Takiguchi S et al (2005) High incidence of thrombosis of the portal venous system after laparoscopic splenectomy: a prospective study with contrast-enhanced CT scan. Ann Surg 2:208–216
Romano F, Caprotti R, Conti M et al (2006) Thrombosis of the splenoportal axis after splenectomy. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg/Verh Dtsch Chir 5:483–488
Pai M, Navarra G, Ayav A et al (2008) Laparoscopic Habib 4X: a bipolar radiofrequency device for bloodless laparoscopic liver resection. HPB: Off J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc 4:261–264
Pai M, Frampton AE, Mikhail S et al (2012) Radiofrequency assisted liver resection: analysis of 604 consecutive cases. Eur J Surg Oncol: J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Surg Oncol 3:274–280
Ayav A, Jiao L, Dickinson R et al. (2008) Liver resection with a new multiprobe bipolar radiofrequency device. Arch Surg (Chicago, IL: 1960) 4:396–401, discussion 401
Curro G, Habib N, Jiao L et al (2008) Radiofrequency-assisted liver resection in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma and cirrhosis: preliminary results. Transplant Proc 10:3523–3525
Moore EE, Cogbill TH, Jurkovich GJ et al (1995) Organ injury scaling: spleen and liver (1994 revision). J Trauma 3:323–324
Patrzyk M, Glitsch A, Hoene A et al (2011) Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using a detachable clamp with and without partial splenic embolisation. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg/Verh Dtsch Chir 3:397–402
Zacharoulis D, Poultsidis A, Katsogridakis E et al (2008) Radiofrequency-assisted partial splenectomy: histopathological and immunological assessment of the splenic remnant in a porcine model. Surg Endosc 5:1309–1316
Vasilescu C, Tudor S, Popa M et al (2010) Robotic partial splenectomy for hydatid cyst of the spleen. Langenbeck’s Arch Surg/Verh Dtsch Chir 8:1169–1174
Bork U, Müller SA, Herpel E et al (2011) Partial splenectomy using a vascular stapler in a patient with a benign splenic cyst. Am Surg 1:118–119
Haghighi KS, Steinke K, Hazratwala K et al (2005) Controlled study of in-line ovine spleen transection assisted by radiofrequency ablation. J Trauma 4:841–844
Pikoulis E, Felekouras E, Papaconstantinou I et al (2005) A novel spleen-preserving laparoscopic technique using radiofrequency ablation in a porcine model. Surg Endosc 10:1329–1332
Velanovich V, Weaver M (2003) Partial splenectomy using a coupled saline-radiofrequency hemostatic device. Am J Surg 1:66–68
Habib NA, Spalding D, Navarra G, Nicholls J (2003) How we do a bloodless partial splenectomy. Am J Surg 2:164–166
Itamoto T, Fukuda S, Tashiro H et al (2006) Radiofrequency-assisted partial splenectomy with a new and simple device. Am J Surg 2:252–254
Jiao LR, Tierris I, Ayav A et al (2006) A new technique for spleen preservation with radiofrequency. Surgery 3:464–466
de Greef E, Hoffman I, Topal B et al (2008) Partial laparoscopic splenectomy for splenic abscess because of Salmonella infection: a case report. J Pediatr Surg 5:E35–E38
Gumbs AA, Bouhanna P, Bar-Zakai B et al (2008) Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using radiofrequency ablation. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 4:611–613
Rasekhi AR, Naderifar M, Bagheri MH et al (2009) Radiofrequency ablation of the spleen in patients with thalassemia intermedia: a pilot study. AJR Am J Roentgenol 5:1425–1429
Bong JJ, Kumar R, Spalding D (2011) A novel technique of partial splenectomy using radiofrequency ablation. J Gastrointest Surg: Off J Soc Surg Aliment Tract 2:371–372
Karadayi K, Turan M, Sen M (2011) A new technique for partial splenectomy with radiofrequency technology. Surg Laparosc Endosc Percutaneous Tech 5:358–361
Khelif K, Maassarani F, Dassonville M, de Laet M-H (2006) Laparoscopic partial splenectomy using radiofrequency ablation for nonparasitic splenic cysts in two children. J Laparoendosc Adv Surg Tech Part A 4:414–417
Pai M, Jiao LR, Khorsandi S et al (2008) Liver resection with bipolar radiofrequency device: Habib 4X. HPB: Off J Int Hepato Pancreato Biliary Assoc 4:256–260
Pai M, Spalding D, Jiao L, Habib N (2012) Use of bipolar radiofrequency in parenchymal transection of the liver, pancreas and kidney. Dig Surg 1:43–47
Pai M, Frampton AE, Mikhail S et al (2012) Radiofrequency assisted liver resection: analysis of 604 consecutive cases. Eur J Surg Oncol J Eur Soc Surg Oncol Br Assoc Sur Oncol 3:274–280
Szczepanik AB, Meissner AJ (2009) Partial splenectomy in the management of nonparasitic splenic cysts. World J Surg 4:852–856
Conflicts of Interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Juliane Liese and Sven Kohler contributed equally to this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liese, J., Kohler, S., Moench, C. et al. Partial spleen resection with a radiofrequency needle device—a pilot study. Langenbecks Arch Surg 398, 449–454 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-013-1054-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-013-1054-9