Abstract
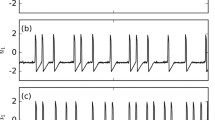
Stochastic resonance (SR) has been shown to enhance the signal-to-noise ratio and detection of low level signals in neurons. It is not yet clear how this effect of SR plays an important role in the information processing of neural networks. The objective of this article is to test the hypothesis that information transmission can be enhanced with SR when sub-threshold signals are applied to distal positions of the dendrites of hippocampal CA1 neuron models. In the computer simulation, random sub-threshold signals were presented repeatedly to a distal position of the main apical branch, while the homogeneous Poisson shot noise was applied as a background noise to the mid-point of a basal dendrite in the CA1 neuron model consisting of the soma with one sodium, one calcium, and five potassium channels. From spike firing times recorded at the soma, the mutual information and information rate of the spike trains were estimated. The simulation results obtained showed a typical resonance curve of SR, and that as the activity (intensity) of sub-threshold signals increased, the maximum value of the information rate tended to increased and eventually SR disappeared. It is concluded that SR can play a key role in enhancing the information transmission of sub-threshold stimuli applied to distal positions on the dendritic trees.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abenavoli A, Forti L, Bossi M, Bergamaschi A, Villa A, Malgaroli A (2002) Multimodal quantal release at individual hippocampal synapses: evidence for no lateral inhibition. J Neurosci 22: 6336–6346
Axmacher N, Mormann F, Fernandez G, Elger CE, Fell J (2006) Memory formation by neuronal synchronization. Brain Res Rev 52: 170–182
Benzi R, Sutera A, Vulpiani A (1981) The mechanism of stochastic resonance. J Phys A 14: L453–457
Brette R, Guigon E (2003) Reliability of spike timing is a general property of spiking model neurons. Neural Comput 15: 279–308
Bulsara A, Zador A (1996) Threshold detection of wideband signals: a noise-induced maximum in the mutual information. Phys Rev E 54: R2185–R2188
Bulsara A, Jacobs E, Zhou T, Moss F, Kiss L (1991) Stochastic resonance in a single neuron model: theory and analog simulation. J Theor Biol 152: 531–555
Collins J, Imhoff T, Grigg T (1996) Noise-enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via aperiodic stochastic resonance. J Neurophysiol 76: 642–645
Cook EP, Johnston D (1997) Active dendrites reduce location-dependent variability of synaptic input trains. J Neurophysiol 78: 2116–2128
Cox DR, Lewis PAW (1966) The statistical analysis of series of events. Methuen, London
Dayan P, Abbott LF (2001) Theoretical neuroscience: computational and mathematical modeling of neural systems. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Deco G, Schumann B (1997) Stochastic resonance in the mutual information between input and output spike trains of noisy central neurons. Phys D 117: 276–282
de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Lewen GD, Strong SP, Koberle R, Bialek W (1997) Reproducibility and variability in neural spike trains. Science 275(5307): 1805–1808
Destexhe A, Pare D (1999) Impact of network activity on the integrative properties of neocortical pyramidal neurons in vivo. J Neurophysiol 81: 1531–1547
Destexhe A, Rudolph M, Pare D (2003) The high-conductance state of neocortical neurons in vivo. Nat Rev 4: 739–751
Douglass J, Wilkins L, Pantazelou E, Moss F (1993) Noise enhancement of information transfer in crayfish mechanoreceptors by stochastic resonance. Nature 365: 337–340
Gammaitoni L, Hanggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F (1998) Stochastic resonance. Rev Mod Phys 70: 223–287
Kish LB, Harmer GP, Abbott D (2001) Information transfer rate of neurons: stochastic resonance of Shannonś information capacity. Fluctuation Noise Lett 1: L13–L19
Magee J, Johnston D (1995) Synaptic activation of voltage-gated channels in the dendrites of hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Science 268: 301–304
Moss F (2000) Stochastic resonance: looking forward. In: Walleczek J (eds) Self-organized biological dynamics & nonlinear control. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 236–256
Moss F, Pierson D, O’Gorman D (1994) Stochastic resonance: tutorial and update. Int J Bifurc Chaos 6: 1383–1397
Moss F, Ward LM, Sannita WG (2004) Stochastic resonance and sensory information processing: a tutorial and review of application. Clin Neurophys 115: 267–281
Nicolis C (1982) Stochastic aspects of climatic transitions—response to periodic forcing. Tellus 34: 1–9
Rieke F, Warland D, de Ruyter van Steveninck RR, Bialek W (1997) Spikes: exploring the neural code. The MIT Press, Cambridge, MA
Scott DW (1979) On optimal and data-based histograms. Biometrika 66: 605–610
Shannon CE (1949) Communication in the presence of noise. Proc IRE 37: 10–21
Simonotto E, Riani M, Seife C, Roberts M, Twitty J, Moss F (1997) Visual perception of stochastic resonance. Phys Rev Lett 78: 1186–1189
Snyder DL, Miller MI (1991) Random point processes in time and space, 2nd edn. Springer-Verlag, New York
Spruston N, Jaffe DB, Williams SH, Johnston D (1993) Voltage- and space-clamp errors associated with the measurement of electrically remote synaptic events. J Neurophysiol 70: 781–802
Stacey WC, Durand DM (2000) Stochastic resonance improves signal detection in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurophysiol 83: 1394–1402
Stacey WC, Durand DM (2001) Synaptic noise improves detection of subthreshold signals in hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Neurophysiol 86: 1104–1112
Stacey WC, Durand DM (2002) Noise and coupling affect signal detection and bursting in a simulated physiological neural network. J Neurophysiol 88: 2598–2611
Stein RB, Gossen ER, Jones KE (2005) Neuronal variability: noise or part of the signal?. Nat Rev 6: 389–397
Traub RD (1982) Simulation of intrinsic bursting in CA3 hippocampal neurons. Neuroscience 7: 1233–1242
Warman EN, Durand DM (1994) Reconstruction of hippocampal CA1 pyramidal cell electrophysiology by computer simulation. J Neurophysiol 83: 2192–2208
Zador A (1998) mpact of synaptic unreliability on the information transmitted by spiking neurons. J Neurophysiol 79: 1219–1229
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mino, H., Durand, D.M. Enhancement of information transmission of sub-threshold signals applied to distal positions of dendritic trees in hippocampal CA1 neuron models with stochastic resonance. Biol Cybern 103, 227–236 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0395-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-010-0395-5