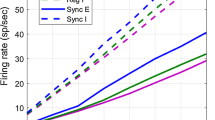
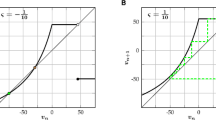
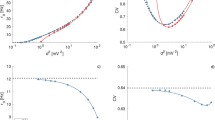
Abstract
Reduced models have long been used as a tool for the analysis of the complex activity taking place in neurons and their coupled networks. Recent advances in experimental and theoretical techniques have further demonstrated the usefulness of this approach. Despite the often gross simplification of the underlying biophysical properties, reduced models can still present significant difficulties in their analysis, with the majority of exact and perturbative results available only for the leaky integrate-and-fire model. Here an elementary numerical scheme is demonstrated which can be used to calculate a number of biologically important properties of the general class of non-linear integrate-and-fire models. Exact results for the first-passage-time density and spike-train spectrum are derived, as well as the linear response properties and emergent states of recurrent networks. Given that the exponential integrate-fire model has recently been shown to agree closely with the experimentally measured response of pyramidal cells, the methodology presented here promises to provide a convenient tool to facilitate the analysis of cortical-network dynamics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsiero M, Lüscher H-R, Lundstrom BN, Giugliano M (2007) The impact of input fluctuations on the frequency-current relationships of layer 5 pyramidal neurons in the rat medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci 27: 3274–3284
Badel L, Lefort S, Brette R, Petersen CCH, Gerstner W, Richardson MJE (2008) Dynamic I–V curves are reliable predictors of naturalistic pyramidal-neuron voltage traces. J Neurophysiol 99: 656–666
Brunel N, Hakim V (1999) Fast global oscillations in networks of integrate-and-fire neurons with low firing rates. Neural Comput 11: 1621–1671
Brunel N, Wang X-J (2003) What determines the frequency of fast network oscillations with irregular neural discharges?. J Neurophysiol 90: 415–430
Brunel N, Latham P (2003) Firing rate of noisy quadratic integrate- and-fire neurons. Neural Comput 15: 2281–2306
Brunel N, Hakim V, Richardson MJE (2003) Firing-rate resonance in a generalized integrate-and-fire neuron with subthreshold resonance. Phys Rev E 67:art-no 051916
Burkitt AN (2006a) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: I. Homogeneous synaptic input. Biol Cybern 95: 1–19
Burkitt AN (2006b) A review of the integrate-and-fire neuron model: II Inhomogeneous synaptic input and network properties. Biol Cybern 95: 97–112
Ermentrout GB, Kopell N (1986) Parabolic bursting in an excitable system coupled with a slow oscillation. SIAM J Appl Math 46: 233–253
Fourcaud-Trocmé N, Hansel D, van Vresswijk C, Brunel N (2003) How spike generation mechanisms determine the neuronal response to fluctuating inputs. J Neurosci 23: 11628–11640
Fourcaud-Trocmé N, Brunel N (2005) Dynamics of the instantaneous firing rate in response to changes in input statistics. J Comput Neurosci 18: 311–321
Fuhrmann G, Markram H, Tsodyks M (2002) Spike frequency adaptation and neocortical rhythms. J Neurophys 88: 761–770
Gerstner W, Kistler WM (2002) Spiking neuron models. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gigante G, Mattia M, Del Giudice P (2007) Diverse population-bursting modes of adapting spiking neurons. Phys Rev Lett 98:art-no 148101
Hodgkin A, Huxley A (1952) A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol 117: 500–544
Hohn N, Burkitt AN (2001) Shot noise in the leaky integrate-and-fire neuron. Phys Rev E 63:art-no 031902
Johannesma PIM (1968) In: Caianiello ER (ed) Neural networks. Springer, New York, pp 116–44
Jolivet A, Rauch A, Lüscher H-R, Gerstner W (2006) Predicting spike timing of neocortical pyramidal neurons by simple threshold models. J Comput Neurosci 21: 35–49
Jolivet R, Kobayashi R, Rauch A, Naud R, Shinomoto S, Gerstner W (2008) A benchmark test for a quantitative assessment of simple neuron models. J Neurosci Meth 169: 417–424
Knight BW (1972a) Dynamics of encoding in a population of neurons. J Gen Physiol 59: 734–766
Knight BW (1972b) The relationship between the firing rate of a single neuron and the level of activity in a population of neurons. J Gen Physiol 59: 767–778
Köndgen H, Geisler C, Fusi S, Wang X-J, Lüscher H-R, Giugliano M (2008) The dynamical response properties of neocortical neurons to temporally modulated noisy inputs in vitro. Cerebr Cortex. doi:10.1093/cercor/bhm235
Lansky P, Lanska V (1987) Diffusion approximation of the neuronal model with synaptic reversal potentials. Biol Cybern 56: 19–26
Lindner B, Schimansky-Geier L (2001) Transmission of noise coded versus additive signals through a neuronal ensemble. Phys Rev Lett 86: 2934–2937
Lindner B, Schimansky-Geier L, Longtin A (2002) Maximizing spike train coherence or incoherence in the leaky integrate-and-fire model. Phys Rev E 66:art-no 031916
Lindner B, Longtin A, Bulsara A (2003) Analytic expressions for rate and CV of a type I Neuron driven by white Gaussian noise. Neural Comput 15: 1761–1788
Lindner B, Garcia-Ojalvo J, Neiman A, Schimansky-Geier L (2004) Effects of noise in excitable systems. Phys Rep 392: 321–424
Paninski L, Pillow JW, Simoncelli EP (2004) Maximum likelihood estimation of a stochastic integrate-and-fire neural encoding model. Neural Comput 16: 2533–2561
Rauch A, La Camera G, Luscher H-R, Senn W, Fusi S (2003) Neocortical pyramidal cells respond as integrate-and-fire neurons to in vivo like input currents. J Neurophys 90: 1598–1612
Ricciardi LM (1977) Diffusion processes and related topics in biology. Springer, Berlin
Richardson MJE, Brunel N, Hakim V (2003) From subthreshold to firing-rate resonance. J Neurophysiol 89: 2538–2554
Richardson MJE (2004) Effects of synaptic conductance on the voltage distribution and firing rate of spiking neurons. Phys Rev E 69:art-no 051918
Richardson MJE, Gerstner W (2005) Synaptic shot noise and conductance fluctuations affect the membrane voltage with equal significance. Neural Comput 17: 923–947
Richardson MJE, Gerstner W (2006) Statistics of subthreshold neuronal voltage fluctuations due to conductance-based synaptic shot noise. Chaos 16:art-no 026106
Richardson MJE (2007) Firing-rate response of linear and nonlinear integrate-and-fire neurons to modulated current-based and conductance-based synaptic drive. Phys Rev E 76:article-no 021919
Risken H (1996) The Fokker–Planck equation. Springer, Berlin
Silberberg G, Bethge M, Markram H, Pawelzik K, Tsodyks M (2004) Dynamics of population rate codes in ensembles of neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 91: 704–709
Stein RB (1965) A theoretical analysis of neuronal variability. Biophys J 5: 173–194
DeWeese MR, Zador AM (2006) Non-Gaussian membrane potential dynamics imply sparse, synchronous activity in auditory cortex. J Neurosci 26: 12206–12218
Wolff L, Lindner B (2008) Method to calculate the moments of the membrane voltage in a model neuron driven by multiplicative filtered shot noise. Phys Rev E 77:article-no 041913
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Richardson, M.J.E. Spike-train spectra and network response functions for non-linear integrate-and-fire neurons. Biol Cybern 99, 381–392 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-008-0244-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-008-0244-y