Abstract
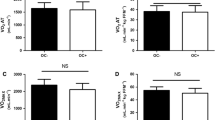
Nine untrained women using low dosage monophasic oral contraceptives (OC) performed an intermittent treadmill test on two different occasions within one pill-cycle to determine the effect of OC on performance and some commonly used metabolic markers. The first test was performed after 5–8 days of resuming the OC agents after menstrual bleeding while the other test was performed after 19–21 days. Performance time on the final exhausting run of six intermittent high intensity 20 s runs was no different between trials [mean days 5–8: 22.3 (SEM 1.2) s vs days 19–21: 22.7 (SEM 1.1) s]. There was no difference in heart rate [peak heart rate days 5–8: 183 (SEM 3) beats.min–1 vs days 19–21: 186 (SEM 2) beats.min–1], oxygen consumption during any run [run 5 of days 5–8: 1,392 (SEM 51) ml·min–1 vs run 5 of days 19–21: 1,494 (SEM 3) ml·min–1] or in any of the metabolic variables measured at any time in venous blood [peak blood lactate concentration days 5–8: 8.4 (SEM 0.3) mmol·l–1 vs days 19–21: 8.1 (SEM 0.5) mmol·l–1; peak blood glycerol concentration days 5–8: 0.39 (SEM 0.02) mmol·l–1 vs days 19–21: 0.38 (SEM 0.02) mmol·l–1; resting free fatty acids concentration days 5–8: 0.25 (SEM 0.05) mmol·l–1 vs days 19–21: 0.29 (SEM 0.07) mmol·l–1; peak blood glucose concentration days 5–8: 6.7 (SEM 0.5) mmol·l–1 vs days 19–21: 6.6 (SEM 0.2) mmol·l–1; peak capillary blood ammonia concentration days 5–8: 139 (SEM 18.3) µmol·l–1 vs days 19–21: 170 (SEM 18.0) µmol·l–1]. These results suggest neither intermittent high intensity exercise performance nor energy metabolism change between days 5–8 and days 19–21 of a low dosage monophasic OC pill during one pill-cycle.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lynch, N., De Vito, G. & Nimmo, M. Low dosage monophasic oral contraceptive use and intermittent exercise performance and metabolism in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 84, 296–301 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210000380
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004210000380