Abstract
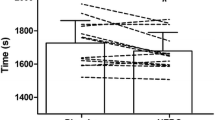
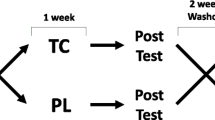
Montmorency tart cherries (Prunus cerasus L.) are rich in anthocyanins, compounds capable of augmenting fat oxidation and regulating metabolic dysfunction. The present study examined whether Montmorency tart cherry juice (MTCJ) supplementation could augment fat oxidation rates at rest and during FATMAX exercise, thus improve cardio-metabolic health. Eleven, healthy participants consumed MTCJ or placebo (PLA) twice daily, in a randomised, counterbalanced order for 20 days. Participants cycled at FATMAX for 1-h pre-, mid- (10 days) and post-supplementation whilst substrate oxidation rates were measured. Before exercise anthropometrics and resting metabolic rate were measured. Blood pressure, serum triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL, total antioxidant status (TAS) and glucose were measured immediately before and after exercise. No significant differences between conditions or interactions were observed for any functional and blood-based cardio-metabolic markers or fat oxidation during exercise or rest (P > 0.05). Pre-exercise TAS (P = 0.036) and HDL (P = 0.001) were significantly reduced from mid- to post-supplementation with MTCJ only. Twenty days’ MTCJ supplementation had no effect on fat oxidation; therefore, it is unnecessary for individuals in this participant cohort to consume MTCJ with exercise to improve cardio-metabolic biomarkers.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CHO:
-
Carbohydrate
- CRM:
-
Calorie restrictive mimetic
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- EE:
-
Energy expenditure
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- MFO:
-
Maximal fat oxidation
- MTCJ:
-
Montmorency tart cherry juice
- NZBE:
-
New Zealand blackcurrant extract
- PLA:
-
Placebo
- PVC:
-
Plasma volume change
- PPAR:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor
- RER:
-
Respiratory exchange ratio
- RMR:
-
Resting metabolic rate
- RPE:
-
Ratings of perceived exertion
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- TAS:
-
Total antioxidant status
- \(\dot {V}{O_2}\hbox{max}\) :
-
Volume of maximal oxygen uptake
- \(\dot {V}C{O_2}\) :
-
Volume of carbon dioxide production
- \(\dot {V}{O_2}\) :
-
Volume of oxygen uptake
References
Achten J, Gleeson M, Jeukendrup AE (2002) Determination of the exercise intensity that elicits maximal fat oxidation. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34(1):92–97
Ahmadi SA, Boroumand MA, Gohari-Moghaddam K, Tajik P, Dibaj SM (2008) The impact of low serum triglyceride on LDL-cholesterol estimation. Arch Iran Med 11(3):318–321. doi: 08113/aim.0014
Alkhatib A, Seijo M, Larumbe E, Naclerio F (2015) Acute effectiveness of a “fat-loss” product on substrate utilization, perception of hunger, mood state and rate of perceived exertion at rest and during exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 12:44. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-015-0105-8
Allgrove J, Farrell E, Gleeson M, Williamson G, Cooper K (2011) Regular dark chocolate consumption’s reduction of oxidative stress and increase of free-fatty-acid mobilization in response to prolonged cycling. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 21(2):113–123
Ataie-Jafari A, Hosseini S, Karimi F, Pajouhi M (2008) Effects of sour cherry juice on blood glucose and some cardiovascular risk factors improvements in diabetic women. Nutr Food Sci 38(4):355–360. https://doi.org/10.1108/00346650810891414
Bell PG, McHugh MP, Stevenson E, Howatson G (2014a) The role of cherries in exercise and health. Scand J Med Sci Sports 24(3):477–490. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12085
Bell PG, Walshe IH, Davison GW, Stevenson E, Howatson G (2014b) Montmorency cherries reduce the oxidative stress and inflammatory responses to repeated days high-intensity stochastic cycling. Nutrients 6(2):829–843. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu6020829
Bell PG, Walshe IH, Davison GW, Stevenson EJ, Howatson G (2015) Recovery facilitation with Montmorency cherries following high-intensity, metabolically challenging exercise. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 40(4):414–423. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2014-0244
Bell PG, Stevenson E, Davison GW, Howatson G (2016) The effects of montmorency tart cherry concentrate supplementation on recovery following prolonged, intermittent exercise. Nutrients. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8070441
Ben Ounis O, Elloumi M, Amri M, Trabelsi Y, Lac G, Tabka Z (2009) Impact of training and hypocaloric diet on fat oxidation and body composition in obese adolescents. Sci Sports 24(3):178–185
Bertoia ML, Rimm EB, Mukamal KJ, Hu FB, Willett WC, Cassidy A (2016) Dietary flavonoid intake and weight maintenance: three prospective cohorts of 124,086 US men and women followed for up to 24 years. Bmj 352:i17. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.i17
Besnier F, Lenclume V, Gerardin P, Fianu A, Martinez J, Naty N,.. . Favier F (2015) Individualized exercise training at maximal fat oxidation combined with fruit and vegetable-rich diet in overweight or obese women: the LIPOXmax-reunion randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 10(11):e0139246. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0139246
Black AE, Prentice AM, Goldberg GR, Jebb SA, Bingham SA, Livingstone MB, Coward WA (1993) Measurements of total energy expenditure provide insights into the validity of dietary measurements of energy intake. J Am Diet Assoc 93(5):572–579
Borg GA (1973) Perceived exertion: a note on “history” and methods. Med Sci Sports 5(2):90–93
Bowtell JL, Sumners DP, Dyer A, Fox P, Mileva KN (2011) Montmorency cherry juice reduces muscle damage caused by intensive strength exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 43(8):1544–1551. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31820e5adc
Brun JF, Romain AJ, Mercier J (2011) Maximal lipid oxidation during exercise (Lipox max): From physiological measurements to clinical applications. Facts and uncertainties. Sci Sports 26(2):57–71
Cohen J (1988) Statistical power analysis for the behavioural sciences, 2nd edn. Lawrence Earlbaum Associates, Hillsdale, NJ
Cook MD, Myers SD, Blacker SD, Willems ME (2015) New Zealand blackcurrant extract improves cycling performance and fat oxidation in cyclists. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(11):2357–2365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-015-3215-8
Cook MD, Myers SD, Gault ML, Edwards VC, Willems ME (2017) Dose effects of New Zealand blackcurrant on substrate oxidation and physiological responses during prolonged cycling. Eur J Appl Phys 117(6):1207–1216
Croci I, Hickman IJ, Wood RE, Borrani F, Macdonald GA, Byrne NM (2014) Fat oxidation over a range of exercise intensities: fitness versus fatness. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 39(12):1352–1359. https://doi.org/10.1139/apnm-2014-0144
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37(2):247–248
Fernandes I, Faria A, Calhau C, de Freitas V, Mateus N (2014) Bioavailability of anthocyanins and derivatives. J Funct Foods 7(Supplement C):54–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jff.2013.05.010
Frisard M, Ravussin E (2006) Energy metabolism and oxidative stress: impact on the metabolic syndrome and the aging process. Endocrine 29(1):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1385/endo:29:1:27
Gordon DJ, Probstfield JL, Garrison RJ, Neaton JD, Castelli WP, Knoke JD, Tyroler HA (1989) High-density lipoprotein cholesterol and cardiovascular disease. Four prospective American studies. Circulation 79(1):8–15
Guo H, Ling W (2015) The update of anthocyanins on obesity and type 2 diabetes: experimental evidence and clinical perspectives. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 16(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11154-014-9302-z
He J, Giusti MM (2010) Anthocyanins: natural colorants with health-promoting properties. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 1:163–187. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.food.080708.100754
Hidalgo M, Oruna-Concha MJ, Kolida S, Walton GE, Kallithraka S, Spencer JP, de Pascual-Teresa S (2012) Metabolism of anthocyanins by human gut microflora and their influence on gut bacterial growth. J Agric Food Chem 60(15):3882–3890. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf3002153
Hofman DL, van Buul VJ, Brouns FJ (2016) Nutrition, health, and regulatory aspects of digestible maltodextrins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 56(12):2091–2100. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.940415
Howatson G, Bell PG, Tallent J, Middleton B, McHugh MP, Ellis J (2012) Effect of tart cherry juice (Prunus cerasus) on melatonin levels and enhanced sleep quality. Eur J Nutr 51(8):909–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-011-0263-7
Huffman DM (2010) Exercise as a calorie restriction mimetic: implications for improving healthy aging and longevity. Interdiscip Top Gerontol 37:157–174. https://doi.org/10.1159/000320000
Jentjens RL, Jeukendrup AE (2005) High rates of exogenous carbohydrate oxidation from a mixture of glucose and fructose ingested during prolonged cycling exercise. Br J Nutr 93(4):485–492
Jeukendrup AE, Wallis GA (2005) Measurement of substrate oxidation during exercise by means of gas exchange measurements. Int J Sports Med 26(Suppl 1):28–37. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2004-830512
Keane KM, George TW, Constantinou CL, Brown MA, Clifford T, Howatson G (2016a) Effects of montmorency tart cherry (Prunus cerasus L.) consumption on vascular function in men with early hypertension. Am J Clin Nutr 103(6):1531–1539. https://doi.org/10.3945/ajcn.115.123869
Keane KM, Haskell-Ramsay CF, Veasey RC, Howatson G (2016b) Montmorency Tart cherries (Prunus cerasus L.) modulate vascular function acutely, in the absence of improvement in cognitive performance. Br J Nutr 116(11):1935–1944
Kelley DS, Rasooly R, Jacob RA, Kader AA, Mackey BE (2006) Consumption of Bing sweet cherries lowers circulating concentrations of inflammation markers in healthy men and women. J Nutr 136(4):981–986
Kelly B, King JA, Goerlach J, Nimmo MA (2013) The impact of high-intensity intermittent exercise on resting metabolic rate in healthy males. Eur J Appl Physiol 113(12):3039–3047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-013-2741-5
Kirakosyan A, Seymour EM, Llanes DEU, Kaufman PB, Bolling SF (2009) Chemical profile and antioxidant capacities of tart cherry products. Food Chem 115(1):20–25
Kirakosyan A, Seymour EM, Noon KR, Llanes DEU, Kaufman PB, Warber SL, Bolling SF (2010) Interactions of antioxidants isolated from tart cherry (Prunus cerasus) fruits. Food Chem 122(1):78–83
Krga I, Monfoulet LE, Konic-Ristic A, Mercier S, Glibetic M, Morand C, Milenkovic D (2016) Anthocyanins and their gut metabolites reduce the adhesion of monocyte to TNFalpha-activated endothelial cells at physiologically relevant concentrations. Arch Biochem Biophys 599:51–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2016.02.006
Li D, Wang P, Luo Y, Zhao M, Chen F (2017) Health benefits of anthocyanins and molecular mechanisms: update from recent decade. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57(8):1729–1741. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2015.1030064
Lynn A, Mathew S, Moore CT, Russell J, Robinson E, Soumpasi V, Barker ME (2014) Effect of a tart cherry juice supplement on arterial stiffness and inflammation in healthy adults: a randomised controlled trial. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 69(2):122–127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11130-014-0409-x
MacRae HS, Mefferd KM (2006) Dietary antioxidant supplementation combined with quercetin improves cycling time trial performance. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 16(4):405–419
Manach C, Scalbert A, Morand C, Remesy C, Jimenez L (2004) Polyphenols: food sources and bioavailability. Am J Clin Nutr 79(5):727–747
Martin KR, Bopp J, Neupane S, Vega-Lopez S (2010) 100% Tart cherry juice reduces plasma triglycerides and CVD risk in overweight and obese subjects. FASEB J 24(1):714–722
Melanson EL, Sharp TA, Seagle HM, Horton TJ, Donahoo WT, Grunwald GK, Hill JO (2002) Effect of exercise intensity on 24-h energy expenditure and nutrient oxidation. J Appl Physiol (1985) 92(3):1045–1052. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00706.2001
Mertz W, Tsui JC, Judd JT, Reiser S, Hallfrisch J, Morris ER,.. . Lashley E (1991) What are people really eating? The relation between energy intake derived from estimated diet records and intake determined to maintain body weight. Am J Clin Nutr 54(2):291–295
Meyer T, Gassler N, Kindermann W (2007) Determination of “Fatmax"with 1 h cycling protocols of constant load. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 32(2):249–256. https://doi.org/10.1139/h06-108
Montgomery MK, Turner N (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction and insulin resistance: an update. Endocr Connect 4(1):R1–Rr15. https://doi.org/10.1530/ec-14-0092
Overall J, Bonney SA, Wilson M, Beermann A, Grace MH, Esposito D, Lila MA, Komarnytsky S (2017) Metabolic effects of berries with structurally diverse anthocyanins. Int J Mol Sci 18(2):422
Perez-Martin A, Dumortier M, Raynaud E, Brun JF, Fedou C, Bringer J, Mercier J (2001) Balance of substrate oxidation during submaximal exercise in lean and obese people. Diabetes Metab 27(4 Pt 1):466–474
Poljsak B, Suput D, Milisav I (2013) Achieving the balance between ROS and antioxidants: when to use the synthetic antioxidants. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/956792
Radak Z, Zhao Z, Koltai E, Ohno H, Atalay M (2013) Oxygen consumption and usage during physical exercise: the balance between oxidative stress and ROS-dependent adaptive signaling. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(10):1208–1246. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2011.4498
Roberts JD, Roberts MG, Tarpey MD, Weekes JC, Thomas CH (2015) The effect of a decaffeinated green tea extract formula on fat oxidation, body composition and exercise performance. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 12(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-014-0062-7
Robinson SL, Hattersley J, Frost GS, Chambers ES, Wallis GA (2015) Maximal fat oxidation during exercise is positively associated with 24-hour fat oxidation and insulin sensitivity in young, healthy men. J Appl Physiol (1985) 118(11):1415–1422. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00058.2015
Romain AJ, Carayol M, Desplan M, Fedou C, Ninot G, Mercier J, Brun JF (2012) Physical activity targeted at maximal lipid oxidation: a meta-analysis. J Nutr Metab. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/285395
Romijn JA, Coyle EF, Sidossis LS, Gastaldelli A, Horowitz JF, Endert E, Wolfe RR (1993) Regulation of endogenous fat and carbohydrate metabolism in relation to exercise intensity and duration. Am J Phys-Endocr Metab 265(3):E380–E391
Seymour EM, Singer AA, Kirakosyan A, Urcuyo-Llanes DE, Kaufman PB, Bolling SF (2008) Altered hyperlipidemia, hepatic steatosis, and hepatic peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors in rats with intake of tart cherry. J Med Food 11(2):252–259. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2007.658
Seymour EM, Lewis SK, Urcuyo-Llanes DE, Tanone II, Kirakosyan A, Kaufman PB, Bolling SF (2009) Regular tart cherry intake alters abdominal adiposity, adipose gene transcription, and inflammation in obesity-prone rats fed a high fat diet. J Med Food 12(5):935–942. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2008.0270
Stinshoff K, Weisshaar D, Staehler F, Hesse D, Gruber W, Steier E (1977) Relation between concentrations of free glycerol and triglycerides in human sera. Clin Chem 23(6):1029–1032
Stump CS, Henriksen EJ, Wei Y, Sowers JR (2006) The metabolic syndrome: role of skeletal muscle metabolism. Ann Med 38(6):389–402. https://doi.org/10.1080/07853890600888413
Timmers S, Konings E, Bilet L, Houtkooper RH, van de Weijer T, Goossens GH, Schrauwen P (2011) Calorie restriction-like effects of 30 days of resveratrol supplementation on energy metabolism and metabolic profile in obese humans. Cell Metab 14(5):612–622. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2011.10.002
Venables MC, Jeukendrup AE (2008) Endurance training and obesity: effect on substrate metabolism and insulin sensitivity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40(3):495–502. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e31815f256f
Vendrame S, Del Bo C, Ciappellano S, Riso P, Klimis-Zacas D (2016) Berry fruit consumption and metabolic syndrome. Antioxidants (Basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox5040034
Winter E (2006) Sport and exercise physiology testing guidelines: volume i—sport testing: sport testing. Routledge, London
Wu X, Beecher GR, Holden JM, Haytowitz DB, Gebhardt SE, Prior RL (2006) Concentrations of anthocyanins in common foods in the United States and estimation of normal consumption. J Agric Food Chem 54(11):4069–4075. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf060300l
Zheng J, Zhou Y, Li S, Zhang P, Zhou T, Xu DP, Li HB (2017) Effects and mechanisms of fruit and vegetable juices on cardiovascular diseases. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18030555
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the participants for partaking in the study and to Camilla Holland and Neil Willmore for technical assistance. The authors would like to acknowledge the Cherry Marketing Institute for providing the tart cherry concentrate. This research was funded by the University of Hertfordshire Diamond Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TD, LB and MR conceived and designed the experiments; TD performed the experiments; TD, LB and MR analysed the data; TD, LB and MR wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Phillip D Chilibeck.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Desai, T., Bottoms, L. & Roberts, M. The effects of Montmorency tart cherry juice supplementation and FATMAX exercise on fat oxidation rates and cardio-metabolic markers in healthy humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 118, 2523–2539 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3978-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-018-3978-9