Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to examine the reliability of extended field-of-view (EFOV) ultrasound imaging to evaluate the cross-sectional area (CSA) and echo intensity of abdominal skeletal muscles.
Methods
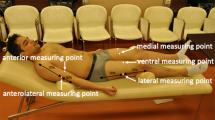
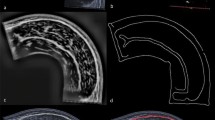
Twenty-seven healthy young males (age 18.6 ± 1.0 years, body mass index 20.9 ± 2.8 kg/m2, waist circumference 75.0 ± 7.9 cm, body fat 16.6 ± 5.9%) visited the laboratory on 2 days. EFOV ultrasound images of the rectus abdominis, abdominal oblique, and erector spinae muscles were acquired at the height of the third lumbar vertebra with the subject lying on a bed. We then analyzed CSA and echo intensity using ImageJ software and calculated intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) and the standard error of measurement (SEM).
Results
No significant differences (p = 0.149–0.679) were observed in CSA or echo intensity values for each skeletal muscle between days. ICC and SEM values in CSA for each skeletal muscle ranged between 0.944 and 0.958 and 4.9% and 7.3%, respectively. The corresponding values for echo intensity were 0.851–0.945 for ICC and 5.3–9.7% for SEM.
Conclusions
The present results indicate that EFOV ultrasound imaging has high repeatability for measuring CSA and echo intensity of abdominal skeletal muscle groups in healthy college-aged males.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ANOVAs:
-
Analyses of variance
- AU:
-
Arbitrary units
- CI:
-
Confidence interval
- CSA:
-
Cross-sectional area
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- EFOV:
-
Extended field-of-view
- FOV:
-
Field-of-view
- ICC:
-
Intra-class correlation coefficients
- L3:
-
Third lumbar vertebra
- MD:
-
Minimum difference
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- SD:
-
Standard deviations
- SEM:
-
Standard error of measurement
References
Abe T, Kondo M, Kawakami Y, Fukunaga T (1994) Prediction equations for body composition of Japanese adults by B-mode ultrasound. Am J Hum Biol 6:161–170
Ahtiainen JP, Hoffren M, Hulmi JJ, Pietikainen M, Mero AA, Avela J, Hakkinen K (2010) Panoramic ultrasonography is a valid method to measure changes in skeletal muscle cross-sectional area. Eur J Appl Physiol 108:273–279
Akima H, Hioki M, Yoshiko A, Koike T, Sakakibara H, Takahashi H, Oshida Y (2016) Intramuscular adipose tissue determined by T1-weighted MRI at 3T primarily reflects extramyocellular lipids. Magn Reson Imaging 34:397–403
Cruz-Jentoft AJ, Baeyens JP, Bauer JM, Boirie Y, Cederholm T, Landi F, Martin FC, Michel JP, Rolland Y, Schneider SM, Topinkova E, Vandewoude M, Zamboni M (2010) Sarcopenia: European consensus on definition and diagnosis. Report of the European Working Group on Sarcopenia in Older People. Age Aging 39:412
Faul F, Erdfelder E, Buchner A, Lang AG (2009) Statistical power analyses using G*Power 3.1: tests for correlation and regression analyses. Behav Res Methods 41:1149–1160
Hicks GE, Simonsick EM, Harris TB, Newman AB, Weiner DK, Nevitt MA, Tylavsky FA (2005) Cross-sectional associations between trunk muscle composition, back pain, and physical function in the health, aging and body composition study. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 60:882–887
Ishida Y, Kanehisa H, Carroll JF, Pollock ML, Graves JE, Ganzarella L (1997) Distribution of subcutaneous fat and muscle thicknesses in young and middle-aged women. Am J Hum Biol 9:247–255
Jenkins ND, Miller JM, Buckner SL, Cochrane KC, Bergstrom HC, Hill EC, Smith CM, Housh TJ, Cramer JT (2015) Test–retest reliability of single transverse versus panoramic ultrasound imaging for muscle size and echo intensity of the biceps brachii. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:1584–1591
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Melvin MN, Smith-Ryan AE, Wingfield HL, Fultz SN, Roelofs EJ (2014) Evaluation of muscle quality reliability and racial difference in body composition of overweight individuals. Ultrasound Med Biol 40:1973–1979
Nijboer-Oosterveld J, Van Alfen N, Pillen S (2011) New normal values for quantitative muscle ultrasound: obesity increases muscle echo intensity. Muscle Nerve 43:142–143
Noorkoiv M, Nosaka K, Blazevich AJ (2010) Assessment of quadriceps muscle cross-sectional area by ultrasound extended-field-of-view imaging. Eur J Appl Physiol 109:631–639
Palmer TB, Akehi K, Thiele RM, Smith DB, Thompson BJ (2014) Reliability of panoramic ultrasound imaging in simultaneously examining muscle size and quality of the hamstring muscles in young, healthy males and females. Ultrasound Med Biol 41:675–684
Pillen S, Arts IMP, Zwarts MJ (2008) Muscle ultrasound in neuromuscular disorders. Muscle Nerve 37:679–693
Pillen S, Tak RO, Zwarts MJ, Lammens MM, Verrijp KN, Arts IM, van der Laak JA, Hoogerbrugge PM, van Engelen BG, Verrips A (2009) Skeletal muscle ultrasound: correlation between fibrous tissue and echo intensity. Ultrasound Med Biol 35:443–446
Reimers K, Reimers CD, Wagner S, Paetzke I, Pongratz DE (1993) Skeletal muscle sonography: a correlative study of echogenicity and morphology. J Ultrasound Med 12:73–77
Rosenberg JG, Ryan ED, Sobolewski EJ, Scharville MJ, Thompson BJ, King GE (2014) Reliability of panoramic ultrasound imaging to simultaneously examine muscle size and quality of the medial gastrocnemius. Muscle Nerve 49:736–740
Ryan AS, Harduarsingh-Permaul AS (2014) Effects of weight loss and exercise on trunk muscle composition in older women. Clin Interv Aging 9:395–402. doi:10.2147/CIA.S56662
Scanlon TC, Fragala MS, Stout JR, Emerson NS, Beyer KS, Oliveira LP, Hoffman JR (2014) Muscle architecture and strength: adaptations to short-term resistance training in older adults. Muscle Nerve 49:584–592
Shrout PE, Fleiss JL (1979) Intraclass correlations: uses in assessing rater reliability. Psychol Bull 86:420–428
Tanaka NI, Miyatani M, Masuo Y, Fukunaga T, Kanehisa H (2007) Applicability of a segmental bioelectrical impedance analysis for predicting the whole body skeletal muscle volume. J Appl Physiol 103:1688–1695
Tanaka NI, Murakami H, Ohmori Y, Aiba N, Morita A, Watanabe S, Miyachi M (2016) Association of visceral fat with abdominal skeletal muscle distribution in overweight Japanese. Obes Res Clin Pract. doi:10.1016/j.orcp.2016.06.005
Teichtahl AJ, Urquhart DM, Wang Y, Wluka AE, Wijethilake P, O’Sullivan R, Cicuttini FM (2015) Fat infiltration of paraspinal muscles is associated with low back pain, disability, and structural abnormalities in community-based adults. Spine 15:1593–1601
Weir JP (2005) Quantifying test-retest reliability using the intraclass correlation coefficient and the SEM. J Strength Cond Res 19:231–240
Acknowledgements
This study was funding by the Suzuken Memorial Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Additional information
Communicated by Olivier Seynnes.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, N.I., Ogawa, M., Yoshiko, A. et al. Reliability of size and echo intensity of abdominal skeletal muscles using extended field-of-view ultrasound imaging. Eur J Appl Physiol 117, 2263–2270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3713-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-017-3713-y