Abstract
Introduction
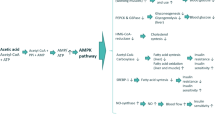
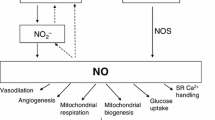
Inorganic nitrate ingestion has been posited to affect arterial blood pressure and vascular function.
Purpose
We sought to determine the acute effect of a red spinach extract (RSE) high in inorganic nitrate on vascular reactivity 1-h after ingestion in peripheral conduit and resistance arteries.
Methods
Fifteen (n = 15; males 8, females 7) apparently healthy subjects (aged 23.1 ± 3.3 years; BMI 27.2 ± 3.7 kg/m2) participated in this crossover design, double-blinded study. Subjects reported to the lab ≥2-h post-prandial and consumed RSE (1000 mg dose; ~90 mg nitrate) or placebo (PBO). Venipuncture was performed on three occasions: baseline, 30-min post-ingestion and between 65 to 75-min post-ingestion. Baseline vascular measurements [i.e., calf venous occlusion plethysmography, brachial artery flow-mediated dilation (FMD)], 30-min of continuous blood pressure (BP) and heart rate (HR) analysis, and follow-up vascular measurements beginning at 40-min post-ingestion were also performed.
Results
Humoral nitrate following RSE ingestion was significantly higher at 30- (+54 %; P = 0.039) and 65 to 75-min post-ingestion compared to baseline (+255 %, P < 0.001) and PBO at the same time points (P < 0.05). No significant changes in BP or HR occurred in either condition. Peak reactive hyperemia (RH) calf blood flow increased significantly (+13.7 %; P = 0.016) following RSE ingestion, whereas it decreased (−14.0 %; P = 0.008) following PBO ingestion. No significant differential FMD responses were detected (P > 0.05), though RH was decreased following the baseline measure in both conditions.
Conclusions
RSE significantly increased plasma nitrate 30-min post-ingestion, but acute microvascular (i.e., resistance vasculature) reactivity increases were isolated to the lower limb and no appreciable change in brachial artery FMD was observed.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ΔTr:
-
Systolic duration of the reflected pressure wave
- AgBP:
-
Augmented central pressure
- AgBP@75:
-
Augmented central pressure normalized to a heart rate of 75 bpm
- AIx:
-
Aortic augmentation index
- AIx@75:
-
Aortic augmentation index normalized to a heart rate of 75 bpm
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- BP:
-
Blood pressure
- CBF:
-
Calf blood flow
- PkCBF:
-
Peak CBF
- TCBF:
-
Total calf blood flow
- CDBP:
-
Central diastolic blood pressure
- CMAP:
-
Central mean arterial pressure
- CPP:
-
Central pulse pressure
- CSBP:
-
Central systolic blood pressure
- eNOS:
-
Endothelial nitric oxide synthase
- FBF:
-
Forearm blood flow
- PkFBF:
-
Peak FBF
- TFBF:
-
Total FBF
- FMD:
-
Flow-mediated dilation
- aFMD:
-
Absolute FMD
- %FMD:
-
Relative FMD
- nFMD:
-
FMD normalized to shear rate
- HR:
-
Heart rate
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- NOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- NO x :
-
Total nitrate and nitrite
- PBO:
-
Placebo
- PDBP:
-
Peripheral diastolic blood pressure
- PSBP:
-
Peripheral systolic blood pressure
- PWA:
-
Pulse wave analysis
- RH:
-
Reactive hyperemia
- RSE:
-
Red spinach extract
- T1r:
-
Time to reflection of the reflected pressure wave
- VOP:
-
Venous occlusion plethysmography
References
Adkisson EJ, Casey DP, Beck DT, Gurovich AN, Martin JS, Braith RW (2010) Central, peripheral and resistance arterial reactivity: fluctuates during the phases of the menstrual cycle. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235(1):111–118. doi:10.1258/ebm.2009.009186
Bahra M, Kapil V, Pearl V, Ghosh S, Ahluwalia A (2012) Inorganic nitrate ingestion improves vascular compliance but does not alter flow-mediated dilatation in healthy volunteers. Nitric Oxide 26(4):197–202. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2012.01.004
Bazaral MG, Welch M, Golding LA, Badhwar K (1990) Comparison of brachial and radial arterial pressure monitoring in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery. Anesthesiology 73(1):38–45
Behnke BJ, McDonough P, Padilla DJ, Musch TI, Poole DC (2003) Oxygen exchange profile in rat muscles of contrasting fibre types. J Physiol 549(Pt 2):597–605. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.035915
Benjamin N, O’Driscoll F, Dougall H, Duncan C, Smith L, Golden M, McKenzie H (1994) Stomach NO synthesis. Nature 368(6471):502. doi:10.1038/368502a0
Betik AC, Luckham VB, Hughson RL (2004) Flow-mediated dilation in human brachial artery after different circulatory occlusion conditions. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 286(1):H442–H448. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00314.2003
Cao Z, Bell JB, Mohanty JG, Nagababu E, Rifkind JM (2009) Nitrite enhances RBC hypoxic ATP synthesis and the release of ATP into the vasculature: a new mechanism for nitrite-induced vasodilation. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297(4):H1494–H1503. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.01233.2008
Cosby K, Partovi KS, Crawford JH, Patel RP, Reiter CD, Martyr S, Yang BK, Waclawiw MA, Zalos G, Xu X, Huang KT, Shields H, Kim-Shapiro DB, Schechter AN, Cannon RO 3rd, Gladwin MT (2003) Nitrite reduction to nitric oxide by deoxyhemoglobin vasodilates the human circulation. Nat Med 9(12):1498–1505. doi:10.1038/nm954
Dejam A, Hunter CJ, Schechter AN, Gladwin MT (2004) Emerging role of nitrite in human biology. Blood Cells Mol Dis 32(3):423–429. doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2004.02.002
Engelke KA, Halliwill JR, Proctor DN, Dietz NM, Joyner MJ (1996) Contribution of nitric oxide and prostaglandins to reactive hyperemia in human forearm. J Appl Physiol (1985) 81(4):1807–1814
Ferguson SK, Holdsworth CT, Wright JL, Fees AJ, Allen JD, Jones AM, Musch TI, Poole DC (2015) Microvascular oxygen pressures in muscles comprised of different fiber types: impact of dietary nitrate supplementation. Nitric Oxide 48:38–43. doi:10.1016/j.niox.2014.09.157
Gautier C, van Faassen E, Mikula I, Martasek P, Slama-Schwok A (2006) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase reduces nitrite anions to NO under anoxia. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341(3):816–821. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2006.01.031
Ghosh SM, Kapil V, Fuentes-Calvo I, Bubb KJ, Pearl V, Milsom AB, Khambata R, Maleki-Toyserkani S, Yousuf M, Benjamin N, Webb AJ, Caulfield MJ, Hobbs AJ, Ahluwalia A (2013) Enhanced vasodilator activity of nitrite in hypertension: critical role for erythrocytic xanthine oxidoreductase and translational potential. Hypertension 61(5):1091–1102. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.111.00933
Gilchrist M, Shore AC, Benjamin N (2011) Inorganic nitrate and nitrite and control of blood pressure. Cardiovasc Res 89(3):492–498. doi:10.1093/cvr/cvq309
Harms MP, Wesseling KH, Pott F, Jenstrup M, Van Goudoever J, Secher NH, Van Lieshout JJ (1999) Continuous stroke volume monitoring by modelling flow from non-invasive measurement of arterial pressure in humans under orthostatic stress. Clin Sci 97(3):291–301
Harris RA, Nishiyama SK, Wray DW, Richardson RS (2010) Ultrasound assessment of flow-mediated dilation. Hypertension 55(5):1075–1085. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.110.150821
Higashi Y, Sasaki S, Nakagawa K, Matsuura H, Kajiyama G, Oshima T (2001) A noninvasive measurement of reactive hyperemia that can be used to assess resistance artery endothelial function in humans. Am J Cardiol 87(1):121–125, A129
Hobbs DA, George TW, Lovegrove JA (2013) The effects of dietary nitrate on blood pressure and endothelial function: a review of human intervention studies. Nutr Res Rev 26(2):210–222. doi:10.1017/S0954422413000188
Hokanson DE, Sumner DS, Strandness DE Jr (1975) An electrically calibrated plethysmograph for direct measurement of limb blood flow. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 22(1):25–29
Imholz BP, Wieling W, van Montfrans GA, Wesseling KH (1998) Fifteen years experience with finger arterial pressure monitoring: assessment of the technology. Cardiovasc Res 38(3):605–616
Jansen JR, Schreuder JJ, Mulier JP, Smith NT, Settels JJ, Wesseling KH (2001) A comparison of cardiac output derived from the arterial pressure wave against thermodilution in cardiac surgery patients. Br J Anaesth 87(2):212–222
Jansson EA, Huang L, Malkey R, Govoni M, Nihlen C, Olsson A, Stensdotter M, Petersson J, Holm L, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JO (2008) A mammalian functional nitrate reductase that regulates nitrite and nitric oxide homeostasis. Nat Chem Biol 4(7):411–417. doi:10.1038/nchembio.92
Jellema WT, Wesseling KH, Groeneveld AB, Stoutenbeek CP, Thijs LG, van Lieshout JJ (1999) Continuous cardiac output in septic shock by simulating a model of the aortic input impedance: a comparison with bolus injection thermodilution. Anesthesiology 90(5):1317–1328
Johnson MA, Polgar J, Weightman D, Appleton D (1973) Data on the distribution of fibre types in thirty-six human muscles. An autopsy study. J Neurol Sci 18(1):111–129
Jones AM, Ferguson SK, Bailey SJ, Vanhatalo A, Poole DC (2016) Fiber type-specific effects of dietary nitrate. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 44(2):53–60. doi:10.1249/JES.0000000000000074
Joyner MJ, Dietz NM, Shepherd JT (2001) From Belfast to Mayo and beyond: the use and future of plethysmography to study blood flow in human limbs. J Appl Physiol (1985) 91(6):2431–2441
Lal SK, Henderson RJ, Cejnar M, Hart MG, Hunyor SN (1995) Physiological influences on continuous finger and simultaneous intra-arterial blood pressure. Hypertension 26(2):307–314
Lundberg JO, Govoni M (2004) Inorganic nitrate is a possible source for systemic generation of nitric oxide. Free Radic Biol Med 37(3):395–400. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.04.027
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Lundberg JM, Alving K (1994) Intragastric nitric oxide production in humans: measurements in expelled air. Gut 35(11):1543–1546
Lundberg JO, Weitzberg E, Gladwin MT (2008) The nitrate-nitrite-nitric oxide pathway in physiology and therapeutics. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7(2):156–167. doi:10.1038/nrd2466
Mahieu D, Kips J, Rietzschel ER, De Buyzere ML, Verbeke F, Gillebert TC, De Backer GG, De Bacquer D, Verdonck P, Van Bortel LM, Segers P, Asklepios I (2010) Noninvasive assessment of central and peripheral arterial pressure (waveforms): implications of calibration methods. J Hypertens 28(2):300–305. doi:10.1097/HJH.0b013e3283340a1a
Martin JS, Beck DT, Gurovich AN, Braith RW (2010) The acute effects of smokeless tobacco on central aortic blood pressure and wave reflection characteristics. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 235(10):1263–1268. doi:10.1258/ebm.2010.009376
Martin JS, Borges AR, Beck DT (2015a) Peripheral conduit and resistance artery function are improved following a single, 1-h bout of peristaltic pulse external pneumatic compression. Eur J Appl Physiol 115(9):2019–2029. doi:10.1007/s00421-015-3187-8
Martin JS, Borges AR, Christy JBT, Beck DT (2015b) Considerations for SphygmoCor radial artery pulse wave analysis: side selection and peripheral arterial blood pressure calibration. Hypertens Res 38(10):675–683. doi:10.1038/hr.2015.36
Meredith IT, Currie KE, Anderson TJ, Roddy MA, Ganz P, Creager MA (1996) Postischemic vasodilation in human forearm is dependent on endothelium-derived nitric oxide. Am J Physiol 270(4 Pt 2):H1435–H1440
Murgo JP, Westerhof N, Giolma JP, Altobelli SA (1981) Manipulation of ascending aortic pressure and flow wave reflections with the Valsalva maneuver: relationship to input impedance. Circulation 63(1):122–132
Patterson GC, Whelan RF (1955) The measurement of blood flow during reactive hyperaemia in man. J Physiol 127(1):13–14P
Pauca AL, O’Rourke MF, Kon ND (2001) Prospective evaluation of a method for estimating ascending aortic pressure from the radial artery pressure waveform. Hypertension 38(4):932–937
Penaz J, Voigt A, Teichmann W (1976) Contribution to the continuous indirect blood pressure measurement. Zeitschrift fur die gesamte innere Medizin und ihre Grenzgebiete 31(24):1030–1033
Petersson J, Carlstrom M, Schreiber O, Phillipson M, Christoffersson G, Jagare A, Roos S, Jansson EA, Persson AE, Lundberg JO, Holm L (2009) Gastroprotective and blood pressure lowering effects of dietary nitrate are abolished by an antiseptic mouthwash. Free Radic Biol Med 46(8):1068–1075. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.01.011
Picone D, Climie R, Keske M, Sharman J (2014) Non-invasive estimation of exercise central blood pressure by radial tonometry may be underestimated due to brachial-to-radial-systolic-blood-pressure-amplification and is related to upper limb blood flow velocity. Artery Res 8(4):124–125. doi:10.1016/j.artres.2014.09.062
Schutte AE, Huisman HW, van Rooyen JM, Malan NT, Schutte R (2004) Validation of the Finometer device for measurement of blood pressure in black women. J Hum Hypertens 18(2):79–84. doi:10.1038/sj.jhh.1001639
Sharman JE, Lim R, Qasem AM, Coombes JS, Burgess MI, Franco J, Garrahy P, Wilkinson IB, Marwick TH (2006) Validation of a generalized transfer function to noninvasively derive central blood pressure during exercise. Hypertension 47(6):1203–1208. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000223013.60612.72
Shepherd JT (2011) Circulation to skeletal muscle. In: Comprehensive physiology. Wiley, New York. doi:10.1002/cphy.cp020311
Shih YT, Cheng HM, Sung SH, Hu WC, Chen CH (2011) Quantification of the calibration error in the transfer function-derived central aortic blood pressures. Am J Hypertens 24(12):1312–1317. doi:10.1038/ajh.2011.146
Subramanian D, Gupta S (2016) Pharmacokinetic study of amaranth extract in healthy human subjects—a randomized trial. Nutrition. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2015.12.041
Totzeck M, Hendgen-Cotta UB, Luedike P, Berenbrink M, Klare JP, Steinhoff H-J, Semmler D, Shiva S, Williams D, Kipar A, Gladwin MT, Schrader J, Kelm M, Cossins AR, Rassaf T (2012) Nitrite regulates hypoxic vasodilation via myoglobin-dependent nitric oxide generation. Circulation 126(3):325–334. doi:10.1161/circulationaha.111.087155
Vanin AF, Bevers LM, Slama-Schwok A, van Faassen EE (2007) Nitric oxide synthase reduces nitrite to NO under anoxia. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(1):96–103. doi:10.1007/s00018-006-6374-2
Verbeke F, Segers P, Heireman S, Vanholder R, Verdonck P, Van Bortel LM (2005) Noninvasive assessment of local pulse pressure: importance of brachial-to-radial pressure amplification. Hypertension 46(1):244–248. doi:10.1161/01.HYP.0000166723.07809.7e
Webb AJ, Patel N, Loukogeorgakis S, Okorie M, Aboud Z, Misra S, Rashid R, Miall P, Deanfield J, Benjamin N, MacAllister R, Hobbs AJ, Ahluwalia A (2008) Acute blood pressure lowering, vasoprotective, and antiplatelet properties of dietary nitrate via bioconversion to nitrite. Hypertension 51(3):784–790. doi:10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.107.103523
White WB, Berson AS, Robbins C, Jamieson MJ, Prisant LM, Roccella E, Sheps SG (1993) National standard for measurement of resting and ambulatory blood pressures with automated sphygmomanometers. Hypertension 21(4):504–509
Wilkinson IB, Fuchs SA, Jansen IM, Spratt JC, Murray GD, Cockcroft JR, Webb DJ (1998) Reproducibility of pulse wave velocity and augmentation index measured by pulse wave analysis. J Hypertens 16(12 Pt 2):2079–2084
Wilkinson IB, MacCallum H, Flint L, Cockcroft JR, Newby DE, Webb DJ (2000) The influence of heart rate on augmentation index and central arterial pressure in humans. J Physiol 525(Pt 1):263–270
Zweier JL, Wang P, Samouilov A, Kuppusamy P (1995) Enzyme-independent formation of nitric oxide in biological tissues. Nat Med 1(8):804–809
Acknowledgments
This study was financially supported by DolCas Biotech LLC (Landing, NJ, USA) through a contract awarded to J.S.M. The authors wish to thank the participants for their time and compliance with demands associated with the study protocol.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Communicated by David C. Poole.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haun, C.T., Kephart, W.C., Holland, A.M. et al. Differential vascular reactivity responses acutely following ingestion of a nitrate rich red spinach extract. Eur J Appl Physiol 116, 2267–2279 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3478-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3478-8