Abstract
Purpose
Eccentric contractions (ECCs) induce muscle damage that is indicated by prolonged loss of muscle function and delayed onset muscle soreness. It is possible that ECCs affect motor nerves, and this may contribute to the prolonged decreases in force generating capability. The present study investigated the hypothesis that M-wave latency of biceps brachii would be increased after maximal elbow flexor ECCs resulting in prolonged loss of muscle strength.
Methods
Fifteen women performed exercise consisting of 60 maximal ECCs of the elbow flexors using their non-dominant arm. M-wave latency was assessed by the time taken from electrical stimulation applied to the Erb’s point to the onset of M-wave of the biceps brachii before, immediately after, and 1–4 days after exercise. Maximal voluntary isometric contraction (MVC) torque, range of motion (ROM) and muscle soreness using a numerical rating scale were also assessed before and after exercise.
Results
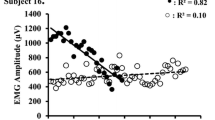
Prolonged decreases in MVC torque (1–4 days post-exercise: −54 to −15 %) and ROM (1–2 days: −32 to −22 %), and increased muscle soreness (peak: 4.2 out of 10) were evident after exercise (p < 0.05). The M-wave latency increased (p < 0.01) from 5.8 ± 1.0 ms before exercise to 6.5 ± 1.7 ms at 1 day and 7.2 ± 1.5 ms at 2 days after exercise for the exercised arm only. No significant changes in M-wave amplitude were evident after exercise.
Conclusion
The increased M-wave latency did not fully explain the prolonged decreases in MVC torque after eccentric exercise, but may indicate reversible motor nerve impairment.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CK:
-
Creatine kinase
- CNT:
-
Control conduction
- CV:
-
Coefficient of variation
- DOMS:
-
Delayed onset muscle soreness
- E–C coupling:
-
Excitation contraction coupling
- ECCs:
-
Eccentric contractions
- mdx:
-
Muscular dystrophy
- MFCV:
-
Muscle fiber conduction velocity
- MsN:
-
Musculocutaneous nerve
- NCV:
-
Nerve conduction velocity
- NMJ:
-
Neuromuscular junction
- NRS:
-
Numerical rating scale
- ROM:
-
Range of motion
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SR:
-
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
- t-tubule:
-
Transverse tubule
References
Buschbacher RM (2000) Manual of nerve conduction studies. Demos Medical Publishing, New York
Buschbacher RM, Weir SK, Bentley JG, Cottrell (2009) Normal motor nerve condcution studies using surface electrode recording from the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, deltoid, and biceps. PM R 1(2):101–106. doi:10.1016/j.pmrj.2008.08.002
Campbell WW (2008) Evaluation and management of peripheral nerve injury. Clin Neurophysiol 119(9):1951–1965. doi:10.1016/j.clinph.2008.03.018
Carter A, Dobridge J, Hackney AC (2001) Influence of estrogen on markers of muscle tissue damage following eccentric exercise. Fiziol Cheloveka 27(5):626–630. doi:10.1023/A:1012395831685
Chapman D, Newton M, McGuian M, Nosaka K (2011) Effect of slow-velocity lengthening contractions on muscle damage induced by fast-velocity lengthening contractions. J Strength Cond Res 25(1):211–219. doi:10.1519/JSC.0b013e3181bac2bd
Chen TC, Chen HL, Liu YC, Nosaka K (2014) Eccentric exercise-induced muscle damage of pre-adolescent and adolescent boys in comparison to young men. Eur J Appl Physiol 114(6):1183–1195. doi:10.1007/s00421-014-2848-3
Cleak MJ, Eston RG (1992) Muscle soreness, swelling, stiffness and stremgth loss after intense eccentric exercise. Br J Sports Med 26(4):267–272. doi:10.1136/bjsm.26.4.267
Colak T, Bamac B, Alemdar M, Macit Selekler H, Ozbek A, Colak S, Dincer O (2009) Nerve conduction studies of the axillary, musculocutaneous and radial nerves in elite ice hockey players. J Sports Med Phys Fitness 49(2):224–231
de Mouzon J, Testart J, Lefevre B, Pouly JL, Frydman R (1984) Time relationships between basal body temperature and ovulation or plasma progestins. Fertil Steril 41(2):254–259
Ekblom A, Hansson P (1988) Pain intensity measurements in patients with acute pain receiving afferent stimulation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51(4):481–486. doi:10.1136/jnnp.51.4.481
Hedayatpour N, Falla D, Arendt-Nielsen L, Vila-Cha C, Farina D (2009) Motor unit conduction velocity during sustained contraction after eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(10):1927–1933. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181a3a505
Hyldahl RD, Nelson B, Xin L, Welling T, Groscost L, Hubal MJ, Chipkin S, Clarkson PM, Parcell AC (2015) Extracellular matrix remodeling and its contribution to protective adaptation following lengthening contractions in human muscle. FASEB J 29(7):2894–2904. doi:10.1096/fj.14-266668
Ingalls C, Warren G, Williams J, Ward C, Armstrong R (1998) E–C coupling failure in mouse EDL muscle after in vivo eccentric contractions. J Appl Physiol 85(1):58–67
Kaplan PE (1976) Sensory and motor residual latency measurements in helathy patients and patients with neuropathy-part 1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 39(4):338–340. doi:10.1136/jnnp.39.4.338
Kon M, Tanabe K, Lee H, Kimura F, Akimoto T, Kono I (2007) Eccentric muscle contractions induce greater oxidative stress than concentric contractions in skeletal muscle. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 32(2):273–281. doi:10.1139/H06-115
Kouyoumdjian JA (2006) Peripheral nerve injuries: a retrospective survey of 456 cases. Muscle Nerve 34(6):785–788. doi:10.1002/mus.20624
Lee K, Kouzaki K, Ochi E, Kobayashi K, Tsutaki A, Hiranuma K, Kami K, Nakazato K (2014) Eccentric contractions of gastrocnemius muscle-induced nerve damage in rats. Muscle Nerve 50(1):87–94. doi:10.1002/mus.24120
Lundborg G, Gelberman RH, Minteer-Convery M, Lee YF, Hargens AR (1982) Median nerve compression in the carpal tunnel—functional response to experimentally induced controlled pressure. J Hand Surg Am 7(3):252–259
Maccabee PJ, Eberle LP, Stein IA, Willer JA, Lipitz ME, Kula RW, Marx T, Muntean EV, Amassian VE (2011) Upper leg conduction time distinguishes demyelinating neuropathies. Muscle Nerve 43(4):518–530. doi:10.1002/mus.21909
Mallik A, Weir AI (2005) Nerve conduction studies: essentials and pitfalls in practice. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76(Suppl 2):ii23–ii31. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2005.069138
Markofski MM, Braun WA (2014) Influence of menstrual cycle on indices of contraction-induced muscle damage. J Strength Cond Res 28(9):2649–2656. doi:10.1519/JSC.0000000000000429
Martins RS, Bastos D, Siqueira MG, Heise CO, Teixeira MJ (2013) Traumatic injuries of peripheral nerves: a review with emphasis on surgical indication. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 71(10):811–814. doi:10.1590/0004-282X20130127
Menorca RM, Fussell TS, Elfar JC (2013) Peripheral nerve trauma: mechanisms of injury and recovery. Hand Clin 29(3):317–330. doi:10.1016/j.hcl.2013.04.002
Muthalib M, Lee H, Millet GY, Ferrari M, Nosaka K (2011) The repeated-bout effect: influence on biceps brachii oxygenation and myoelectrical activity. J Appl Physiol 110(5):1390–1399. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.00191.2010
Newton MJ, Sacco P, Chapman D, Nosaka K (2013) Do dominant and non-dominant arms respond similarly to maximal eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors? J Sci Med Sport 16(2):166–171. doi:10.1016/j.jsams.2012.06.001
Nosaka K, Clarkson PM (1996) Changes in indicators of inflammation after eccentric exercise of the elbow flexors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28(8):953–961. doi:10.1097/00005768-199608000-00003
Piitulainen H, Bottas R, Komi P, Linnamo V, Avela J (2010) Impaired action potential conduction at high force levels after eccentric exercise. J Electromyogr Kinesiol 20(5):879–887. doi:10.1016/j.jelekin.2009.10.001
Piitulainen H, Botter A, Merletti R, Avela J (2011) Muscle fiber conduction velocity is more affected after eccentric than concentric exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 111(2):261–273. doi:10.1007/s00421-010-1652-y
Raastad T, Owe SG, Paulsen G, Enns D, Overgaard K, Crameri R, Kiil S, Belcastro A, Bergersen L, Hallen J (2010) Changes in calpain activity, muscle structure, and function after eccentric exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 42(1):86–95. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181ac7afa
Sayyed SG, Kumar A, Sharma SS (2006) Effects of U83836E on nerve functions, hyperalgesia and oxidative stress in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Life Sci 79(8):777–783. doi:10.1016/j.ifs.2006.02.033
Seddon HJ (1942) A classification of nerve injuries. Br Med J 2(4260):237–239
Simmons Z (2013) Electrodiagnosis of brachial plexopathies and proximal upper extremity neuropathies. Phys Med Rehabil Clin N Am 24(1):13–32. doi:10.1016/j.pmr.2012.08.021
Sung JY, Kuwabara S, Ogawara K, Kanai K, Hattori T (2002) Patterns of nerve conduction abnormalities in POEMS syndrome. Muscle Nerve 26(2):189–193. doi:10.1002/mus.10182
Takekura H, Fujinami N, Nishizawa T, Ogasawara H, Kasuga N (2001) Eccentric exercise-induced morphological changes in the membrane systems involved in excitation-contraction coupling in rat skeletal muscle. J Physiol 533(Pt 2):571–583. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7793.2001.0571a.x
Temucin CM, Nurlu G (2011) Measurement of motor root conduction time at the early stage of Guillain–Barre syndrome. Eur J Neurol 18(10):1240–1245. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2011.03365.x
Tenan MS, Peng YL, Hackney AC, Griffin L (2013) Menstrual cycle mediates vastus medialis and vastus medialis oblique muscle activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 45(11):2151–2157. doi:10.1249/MSS.0b013e318299a69d
Trojaborg W (1976) Motor and sensory conduction in the musculocutaneous nerve. J Neurosurg Psychiatry 39(9):890–899. doi:10.1136/jnnp.39.9.890
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Toshio Moritani.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kouzaki, K., Nosaka, K., Ochi, E. et al. Increases in M-wave latency of biceps brachii after elbow flexor eccentric contractions in women. Eur J Appl Physiol 116, 939–946 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3358-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-016-3358-2