Abstract
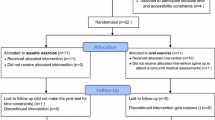
To prevent falls in Japan, both gait and resistance training of the lower extremities are recommended. However, resistance training for the elderly induces muscle damage. Recently, aquatic exercise using water buoyancy and resistance have commonly been performed by the elderly. We have now produced new water-resistance equipment. The purpose of the present study was to evaluate the efficacy of aquatic exercise training using the new equipment for the elderly. Subjects were divided into two groups: a resistance group of 12 subjects (using water-resistance equipment) and a non-resistance group of eight subjects (without the equipment). The aquatic exercise training was 90 min, three times per week for 8 weeks, and mostly consisted of walking. All subjects underwent anthropometric measurements, physical performance testing, and profile of mood states (POMS). Significant improvements were observed in muscle strength in plantar flexion, and the timed up and go test (TUG) in both groups. Additionally, 10-m obstacle walking and 5-m maximum walking speed and length with eye-open were significantly improved in the resistance group. Also, a low negative correlation was found between the degree of change in TUG and POMS (tension and anxiety) scores in the resistance group. As it became easier to maintain posture, stand, and move, tension and anxiety in everyday life were alleviated with improvement of strength of the lower extremities and balance function. The present aquatic exercise training using water-resistance equipment may be used by the elderly to improve balance and walking ability, which are associated with the prevention of falls.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Devereux K, Robertson D, Briffa NK (2005) Effects of a water-based training on women 65 years and over: a randomised controlled trial. Aust J Physiother 51:102–108
Ferrell KM (1998) Aquatics for people with arthritis. Lippincotts Prim Care Pract 2:102–104
Greenlund LJ, Nair KS (2003) Sarcopenia-consequences, mechanisms, and potential therapies. Mech Ageing Dev 124:287–299
Gusi N, Tomas-Carus P, Häkkinen A, Häkkinen K, Ortega-Alonso A (2006) Exercise in waist-high warm water decreases pain and improves health-related quality of life and strength in the lower extremities in women with fibromyalgia. Arthritis Rheum 55:66–73
Hauer K, Rost B, Rütschle K, Opitz H, Specht N, Bärtsch P, Oster P, Schlierf G (2001) Exercise training for rehabilitation and secondary prevention of falls in geriatric patients with a history of injurious falls. J Am Geriatr Soc 49:10–20
Konlian C (1999) Aquatic therapy: making a wave in the treatment of low back injuries. Orthop Nurs 18:11–18
Landers KA, Hunter GR, Wetzstein CJ, Bamman MM, Weinsier RL (2001) The interrelationship among muscle mass, strength, and the ability to perform physical tasks of daily living in younger and older women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 56:B443–B438
Liu-Ambrose T, Khan KM, Eng JJ, Janssen PA, Lord SR, McKay HA (2004) Resistance and agility training reduce fall risk in women aged 75 to 85 with low bone mass: a 6-month randomized, controlled trial. J Am Geriatr Soc 52:657–665
Moening D, Scheidt A, Shepardson L, Davies GJ (1993) Biomechanical comparison of water running and treadmill running. Isokinet Exerc Sci 3:207–215
Pantoja PD, Alberton CL, Pilla C, Vendrusculo AP, Kruel LF (2009) Effect of resistive exercise on muscle damage in water and on land. J Strength Cond Res 23:1051–1054
Podsiadlo D, Richardson S (1991) The timed “Up & Go”: a test of basic functional mobility for frail elderly persons. J Am Geriatr Soc 39:142–148
Potier TG, Alexander CM, Seynnes OR (2009) Effects of eccentric strength training on biceps femoris muscle architecture and knee joint range of movement. Eur J Appl Physiol 105:939–944
Roth SM, Martel GF, Ivey FM, Lemmer JT, Metter EJ, Hurley BF, Rogers MA (2000) High-volume, heavy-resistance strength training and muscle damage in young and older women. J Appl Physiol 88:1112–1118
Sayer AA, Syddall HE, Martin HJ, Dennison EM, Anderson FH, Cooper C (2006) Falls, sarcopenia, and growth in early life: findings from the Hertfordshire cohort study. Am J Epidemiol 164:665–671
Shono T, Fujishima K, Hotta N, Ogaki T, Ueda T (2001) Physiological responses to water-walking in middle aged women. J Physiol Anthropol Appl Human Sci 20:119–123
Shono T, Masumoto K, Fujishima K, Hotta N, Ogaki T, Adachi T (2007) Gait patterns and muscle activity in the lower extremities of elderly women during underwater treadmill walking against water flow. J Physiol Anthropol 26:579–586
Simmons V, Hansen PD (1996) Effectiveness of water exercise on postural mobility in the well elderly: an experimental study on balance enhancement. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 51:M233–M238
Simoneau E, Martin A, Van Hoecke J (2007) Adaptations to long-term strength training of ankle joint muscles in old age. Eur J Appl Physiol 100:507–514
Suomi R, Koceja DM (2000) Postural sway characteristics in women with lower extremity arthritis before and after an aquatic exercise intervention. Arch Phys Med Rehabil 81:780–785
Tokuno CD, Carpenter MG, Thorstensson A, Garland SJ, Cresswell AG (2007) Control of the triceps surae during the postural sway of quiet standing. Acta Physiol 191:229–236
Tokuno CD, Garland SJ, Carpenter MG, Thorstensson A, Cresswell AG (2008) Sway-dependent modulation of the triceps surae H-reflex during standing. J Appl Physiol 104:1359–1365
Wang TJ, Belza B, Elaine Thompson F, Whitney JD, Bennett K (2007) Effects of aquatic exercise on flexibility, strength and aerobic fitness in adults with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Adv Nurs 57:141–152
Wolfson L, Judge J, Whipple R, King M (1995) Strength is a major factor in balance, gait, and the occurrence of falls. Health Soc Work 50:64–67
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the subjects who participated in the present study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jean-René Lacour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Katsura, Y., Yoshikawa, T., Ueda, SY. et al. Effects of aquatic exercise training using water-resistance equipment in elderly. Eur J Appl Physiol 108, 957–964 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1306-0
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1306-0