Abstract
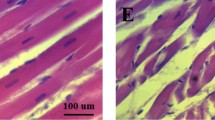
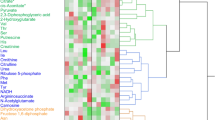
Exhaustive exercise and endurance exercise training modify the physiological status of the body differently. The present study aimed to evaluate the alteration in biochemical composition with exhaustive and endurance exercises in rats using metabolomics strategy. The metabolite profile of liver tissue was investigated on gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS). Data further underwent partial least-squares-discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) to compare the effects on metabolites in sedentary control, exhaustively exercised and endurance trained rats. GC–MS detected 115 highly reproducible peaks in chromatograms from individual liver tissue extracts, and we identified 55 of them. The three groups showed significant differences in metabolic profile. Changes in liver metabolism involved metabolites such as amino acids, fatty acids, organic acids, and carbohydrates. Endurance training elevated the greater rate of tricarboxylic acid cycle and antioxidant activity, and exhaustive exercise led to accumulated urea markers and an inflammation response in liver. In addition, GC–MS-based metabolomic analysis is a promising tool to investigate a pathological status with different exercise programs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin KM, Fitts RH, Booth FW, Winder WW, Holloszy JO (1975) Depletion of muscle and liver glycogen during exercise. Protective effect of training. Pflugers Arch 354:203–212
Bedford TG, Tipton CM, Wilson NC, Oppliger RA, Gisolfi CV (1979) Maximum oxygen consumption of rats and its changes with various experimental procedures. J Appl Physiol 47:1278–1283
Bloomer RJ (2008) Effect of exercise on oxidative stress biomarkers. Adv Clin Chem 46:1–50
Bray MS, Hagberg JM, Pérusse L, Rankinen T, Roth SM, Wolfarth B, Bouchard C (2009) The human gene map for performance and health-related fitness phenotypes: the 2006–2007 update. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41:35–73
Burniston JG (2008) Changes in the rat skeletal muscle proteome induced by moderate-intensity endurance exercise. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:1077–1086
Chan EC, Koh PK, Mal M, Cheah PY, Eu KW, Backshall A, Cavill R, Nicholson JK, Keun HC (2009) Metabolic profiling of human colorectal cancer using high-resolution magic angle spinning nuclear magnetic resonance (HR-MAS NMR) spectroscopy and gas chromatography mass spectrometry (GC/MS). J Proteome Res 8:352–361
Chorell E, Moritz T, Branth S, Antti H, Svensson MB (2009) Predictive metabolomics evaluation of nutrition-modulated metabolic stress responses in human blood serum during the early recovery phase of strenuous physical exercise. J Proteome Res 8:2966–2977
Davies KJ, Quintanilha AT, Brooks GA, Packer L (1982) Free radicals and tissue damage produced by exercise. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 107:1198–1205
Eberlein M, Scheibner KA, Black KE, Collins SL, Chan-Li Y, Powell JD, Horton MR (2008) Anti-oxidant inhibition of hyaluronan fragment-induced inflammatory gene expression. J Inflamm (Lond) 5:20–30
Ellis DI, Dunn WB, Griffin JL, Allwood JW, Goodacre R (2007) Metabolic fingerprinting as a diagnostic tool. Pharmacogenomics 8:1243–1266
Fiehn O (2002) Metabolomics—the link between genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol Biol 48:155–171
Fiehn O, Kopka J, Dörmann P, Altmann T, Trethewey RN, Willmitzer L (2000) Metabolite profiling for plant functional genomics. Nat Biotechnol 18:1157–1161
Gill JM, Cooper AR (2008) Physical activity and prevention of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Sports Med 38:807–824
Gill JM, Hardman AE (2003) Exercise and postprandial lipid metabolism: an update on potential mechanisms and interactions with high-carbohydrate diets. J Nutr Biochem 14:122–132
Gomez-Cabrera MC, Domenech E, Viña J (2008) Moderate exercise is an antioxidant: upregulation of antioxidant genes by training. Free Radic Biol Med 44:126–131
Gutteridge JM (1999) Redox imbalance in the critically ill. Br Med Bull 55:49–75
Hellsten Y, Frandsen U, Orthenblad N, Sjødin B, Richter EA (1997) Xanthine oxidase in human skeletal muscle following eccentric exercise: a role in inflammation. J Physiol 498:239–248
Huang CC, Tsai SC, Lin WT (2008) Potential ergogenic effects of l-arginine against oxidative and inflammatory stress induced by acute exercise in aging rats. Exp Gerontol 43:571–577
Idle JR, Gonzalez FJ (2007) Metabolomics. Cell Metab 6:348–351
Lee SH, Woo HM, Jung BH, Lee J, Kwon OS, Pyo HS, Choi MH, Chung BC (2007) Metabolomic approach to evaluate the toxicological effects of nonylphenol with rat urine. Anal Chem 79:6102–6110
Leeuwenburgh C, Ji LL (1995) Glutathione depletion in rested and exercised mice: biochemical consequence and adaptation. Arch Biochem Biophys 316:941–949
Li X, Xu Z, Lu X, Yang X, Yin P, Kong H, Yu Y, Xu G (2009) Comprehensive two-dimensional gas chromatography/time-of -flight mass spectrometry for metabonomics: biomarker discovery for diabetes mellitus. Anal Chim Acta 633:257–262
Lin WT, Yang SC, Tsai SC, Huang CC, Lee NY (2006) l-Arginine attenuates xanthine oxidase and myeloperoxidase activities in hearts of rats during exhaustive exercise. Br J Nutr 95:67–75
Litvinova L, Viru A (1995) Effect of exercise and adrenal insufficiency on urea production in rat. Eur J Appl Physiol 70:536–540
Liu CC, Huang CC, Lin WT, Hsieh CC, Huang SY, Lin SJ, Yang SC (2005) Lycopene supplementation attenuated xanthine oxidase and myeloperoxidase activities in skeletal muscle tissues of rats after exhaustive exercise. Br J Nutr 94:595–601
Mooren FC, Blöming D, Lechtermann A, Lerch MM, Völker K (2002) Lymphocyte apoptosis after exhaustive and moderate exercise. J Appl Physiol 93:147–153
Mougios V (2006) Exercise biochemistry. Human kinetics, Champaign, pp 129-131
Oztasan N, Taysi S, Gumustekin K, Altinkaynak K, Aktas O, Timur H, Siktar E, Keles S, Akar S, Akcay F, Dane S, Gul M (2004) Endurance training attenuates exercise-induced oxidative stress in erythrocytes in rat. Eur J Appl Physiol 91:622–627
Poortmans JR (1988) Protein metabolism. In: Poortmans JRP (ed) Principles of exercise biochemistry. Karger, Basel, pp 164–193
Powers SK, Jackson MJ (2008) Exercise-induced oxidative stress: cellular mechanisms and impact on muscle force production. Physiol Rev 88:1243–1276
Radák Z, Asano K, Inoue M, Kizaki T, Oh-Ishi S, Suzuki K, Taniguchi N, Ohno H (1995) Superoxide dismutase derivative reduces oxidative damage in skeletal muscle of rats during exhaustive exercise. J Appl Physiol 79:129–135
Shyur LF, Huang CC, Lo CP, Chiu CY, Chen YP, Wang SY, Chang ST (2008) Hepatoprotective phytocompounds from Cryptomeria japonica are potent modulators of inflammatory mediators. Phytochemistry 69:1348–1358
Skenderi KP, Tsironi M, Lazaropoulou C, Anastasiou CA, Matalas AL, Kanavaki I, Thalmann M, Goussetis E, Papassotiriou I, Chrousos GP (2008) Changes in free radical generation and antioxidant capacity during ultramarathon foot race. Eur J Clin Invest 38:159–165
Smolka MB, Zoppi CC, Alves AA, Silveira LR, Marangoni S, Pereira-Da-Silva L, Novello JC, Macedo DV (2000) HSP72 as a complementary protection against oxidative stress induced by exercise in the soleus muscle of rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279:R1539–R1545
Suzuki K, Nakaji S, Yamada M, Totsuka M, Sato K, Sugawara K (2002) Systemic inflammatory response to exhaustive exercise. Cytokine kinetics. Exerc Immunol Rev 8:6–48
Tanimura Y, Shimizu K, Tanabe K, Otsuki T, Yamauchi R, Matsubara Y, Iemitsu M, Maeda S, Ajisaka R (2008) Exercise-induced oxidative DNA damage and lymphocytopenia in sedentary young males. Med Sci Sports Exerc 40:1455–1462
Thompson PD, Franklin BA, Balady GJ, Blair SN, Corrado D, Estes NA 3rd, Fulton JE, Gordon NF, Haskell WL, Link MS, Maron BJ, Mittleman MA, Pelliccia A, Wenger NK, Willich SN, Costa F; American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism; American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; American College of Sports Medicine (2007) Exercise and acute cardiovascular events placing the risks into perspective: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Council on Nutrition, Physical Activity, and Metabolism and the Council on Clinical Cardiology. Circulation 115:2358–2368
Tsai K, Hsu TG, Hsu KM, Cheng H, Liu TY, Hsu CF, Kong CW (2001) Oxidative DNA damage in human peripheral leukocytes induced by massive aerobic exercise. Free Radic Biol Med 31:1465–1472
Viña J, Gimeno A, Sastre J, Desco C, Asensi M, Pallardó FV, Cuesta A, Ferrero JA, Terada LS, Repine JE (2000a) Mechanism of free radical production in exhaustive exercise in humans and rats; role of xanthine oxidase and protection by allopurinol. IUBMB Life 49:539–544
Viña J, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Lloret A, Marquez R, Miñana JB, Pallardó FV, Sastre J (2000b) Free radicals in exhaustive physical exercise: mechanism of production, and protection by antioxidants. IUBMB Life 50:271–277
Viru A (1987) Metabolization of structural proteins during exercise. Sports Med 4:95–128
Vollaard NB, Shearman JP, Cooper CE (2005) Exercise-induced oxidative stress: myths, realities and physiological relevance. Sports Med 35:1045–1062
Woo HM, Kim KM, Choi MH, Jung BH, Lee J, Kong G, Nam SJ, Kim S, Bai SW, Chung BC (2009) Mass spectrometry based metabolomic approaches in urinary biomarker study of women’s cancers. Clin Chim Acta 400:63–69
Yan B, A J, Wang G, Lu H, Huang X, Liu Y, Zha W, Hao H, Zhang Y, Liu L, Gu S, Huang Q, Zheng Y, Sun J (2009) Metabolomic investigation into variation of endogenous metabolites in professional athletes subject to strength-endurance training. J Appl Physiol 106:531–538
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Science Council of Taiwan (NSC-97-2410-H029-037-MY2). The authors thank the Metabolomics Core Facility (Agricultural Biotechnology Research Center, Academia Sinica) for GC–MS analysis. We also thank Laura Heraty for her careful reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Susan Ward.
C.-C. Huang and W.-T. Lin contributed equally and appear in alphabetical order.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, CC., Lin, WT., Hsu, FL. et al. Metabolomics investigation of exercise-modulated changes in metabolism in rat liver after exhaustive and endurance exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 108, 557–566 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1247-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1247-7