Abstract
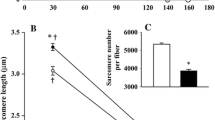
The purpose of the present study was to determine the effects of 14 days of microgravity on specific rat fast-twitch muscles, and to compare these data with previous data from rat fast-twitch muscles exposed to microgravity for 10 days (Kraemer et al. 2000). Hindlimb muscles containing predominately fast fibers [extensor digitorum longus (EDL), superficial “white” (GSW) and deep “red” (GDR) gastrocnemius] and the diaphragm (DIA) were removed from flight and ground-based control animals and analyzed for: muscle mass, fiber type distribution, cross-sectional area, and myosin heavy chain (MHC) isoform content. Gravitational unloading for 14 days caused significant decreases in muscle mass (8–9%) and cross-sectional area of almost all fiber types (10–35%) from both EDL and gastrocnemius muscles. However, microgravity had little effect on fiber type composition in these muscles with significant changes occurring only in the EDL type IID fiber population (9.5% decrease). Similarly, relative MHC isoform content was only slightly altered by exposure to microgravity (increased content of MHCIIa in flight EDL). No changes in area, fiber type percentages, or MHC isoform content were detected in the DIA following the 14-day spaceflight. Similar to data gathered following a 10-day spaceflight (Kraemer et al. 2000), the 14-day flight did not appear to cause significant slow-to-fast (I → IIA) or fast-to-faster (IIA → IID → IIB) transformations in hindlimb muscles containing predominantly fast-twitch fibers. However, the longer period of gravitational unloading did result in additional loss in muscle fiber cross-sectional area with involvement of more major fiber types.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams GR, Caiozzo VJ, Baldwin KM (2003) Skeletal muscle unweighting: spaceflight and ground-based models. J Appl Physiol 95:2185–2201
Allen DL, Bandstra ER, Harrison BC, Thorng S, Stodieck LS, Kostenuik PJ, Morony S, Lacey DL, Hammond TG, Leinwand LL, Argraves WS, Bateman TA, Barth JL (2009) Effects of spaceflight on murine skeletal muscle gene expression. J Appl Physiol 106:582–595. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.90780.2008
Baldwin KM (1996) Effect of spaceflight on the functional, biochemical, and metabolic properties of skeletal muscle. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:983–987. doi:10.1097/00005768-199608000-00008
Bär A, Pette D (1988) Three fast myosin heavy chains in adult rat skeletal muscle. FEBS Lett 235:153–155. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(88)81253-5
Berg HE, Eiken O, Miklavcic L, Mekjavic IB (2007) Hip, thigh and calf muscle atrophy and bone loss after 5-week bedrest inactivity. Eur J Appl Physiol 99:283–289. doi:10.1007/s00421-006-0346-y
Brooke MH, Kaiser KK (1970) Muscle fiber types: how many and what kind? Arch Neurol 23:369–379
Bruusgaard JC, Gundersen K (2008) In vivo time-lapse microscopy reveals no loss of murine myonuclei during weeks of muscle atrophy. J Clin Invest 118:1450–1457. doi:10.1172/JCI34022
Caiozzo VJ, Haddad F, Baker MJ, Herrick RE, Prietto N, Baldwin KM (1996) Microgravity-induced transformations of myosin isoforms and contractile properties of skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 81:123–132
D’Amelio F, Daunton NG (1992) Effects of spaceflight in the adductor longus muscle of rats flown in the Soviet Biosatellite COSMOS 2044. A study employing neural cell adhesion molecule (N-CAM) immunocytochemistry and conventional morphological techniques (light and electron microscopy). J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 51:415–431. doi:10.1097/00005072-199207000-00004
de Boer MD, Maganaris CN, Seynnes OR, Rennie MJ, Narici MV (2007) Time course of muscular, neural and tendinous adaptations to 23 day unilateral lower-limb suspension in young men. J Physiol 583:1079–1091. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2007.135392
Deschenes MR, Wilson MH, Kraemer WJ (2005) Neuromuscular adaptations to spaceflight are specific to postural muscles. Muscle Nerve 31:468–474. doi:10.1002/mus.20277
Eason JM, Schwartz GA, Pavlath GK, English AW (2000) Sexually dimorphic expression of myosin heavy chains in the adult mouse masseter. J Appl Physiol 89:251–258
Fisher JS, Hasser EM, Brown M (1998) Effects of ovariectomy and hindlimb unloading on skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 85:1316–1321
Fitts RH, Riley DR, Widrick JJ (2000) Physiology of a microgravity environment invited review: microgravity and skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 89(2):823–839
Guth L, Samaha FJ (1970) Procedure for the histochemical demonstration of actomyosin ATPase. Exp Neurol 28:365–367. doi:10.1016/0014-4886(70)90244-X
Hansen G, Martinuk KJ, Bell GJ, MacLean IM, Martin TP, Putman CT (2004) Effects of spaceflight on myosin heavy-chain content, fibre morphology and succinate dehydrogenase activity in rat diaphragm. Eur J Phys 448:239–247. doi:10.1007/s00424-003-1230-9
Harrison BC, Allen DL, Girten B, Stodieck LS, Kostenuik PJ, Bateman TA, Morony S, Lacey D, Leinwand LA (2003) Skeletal muscle adaptations to microgravity exposure in the mouse. J Appl Physiol 95:2462–2470
Henriksen EJ, Tischler ME, Woodman CR, Munoz KA, Stump CS, Kirby CR (1993) Elevated interstitial fluid volume in soleus muscles unweighted by spaceflight or suspension. J Appl Physiol 75:1650–1653
Ikemoto M, Nikawa T, Takeda S, Watanabe C, Kitano T, Baldwin KM, Izumi R, Nonaka I, Towatari T, Teshima S, Rokutan K, Kishi K (2001) Space shuttle flight (STS-90) enhances degradation of rat myosin heavy chain in association with activation of ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. FASEB 15:1279–1281
Ishihara A, Yamashiro J, Matsumoto A, Higashibata A, Ishioka N, Shimazu T, Ohira Y (2006) Comparison of cell body size and oxidative enzyme activity in motoneurons between the cervical and lumbar segments in the rat spinal cord after spaceflight and recovery. Neurochem Res 31:411–415. doi:10.1007/s11064-005-9027-1
Kobori M, Yamamuro T (1989) Effects of gonadectomy and estrogen administration on rat skeletal muscle. Clin Orthop Relat Res 243:306–311
Kraemer WJ, Staron RS, Gordon SE, Volek JS, Koziris LP, Duncan ND, Nindl BC, Gómez AL, Marx JO, Fry AC, Murray JD (2000) The effects of 10 days of spaceflight on the shuttle endeavor on predominantly fast-twitch muscles in the rat. Histochem Cell Biol 114:349–355
LaFramboise WA, Daood MJ, Guthrie RD, Moretti P, Schiaffino S, Ontell M (1990) Electrophoretic separation and immunological identification of type 2X myosin heavy chain in rat skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1035:109–112
Lalani R, Bhasin S, Byhower F, Tarnuzzer R, Grant M, Shen R, Asa S, Ezzat S, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF (2000) Myostatin and insulin-like growth factor-I and -II expression in the muscle of rats exposed to the microgravity environment of the NeuroLab space shuttle flight. J Endocrinol 167:417–428. doi:10.1677/joe.0.1670417
Lin J, Wu H, Tarr PT, Zhang C-Y, Wu Z, Boss O, Micheal LF, Puigserver P, Isotani E, Olson EN, Lowell BB, Bassel-Duby R, Spiegelman BM (2002) Transcriptional co-activator PGC-1a drives the formation of slow-twitch muscle fibres. Nature 418:797–801. doi:10.1038/nature00904
Martin TP, Edgerton VR, Grindeland RE (1988) Influence of spaceflight on rat skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 65:2318–2325
McClung JM, Davis JM, Carson JA (2007) Ovarian hormone status and skeletal muscle inflammation during recovery from disuse in rats. Exp Physiol 92:219–232. doi:10.1113/expphysiol.2006.035071
McCormick KM, Burns KL, Piccone CM, Gosselin LE, Brazeau GA (2004) Effects of ovariectomy and estrogen on skeletal muscle function in growing rats. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 25:21–27. doi:10.1023/B:JURE.0000021398.78327.39
Musacchia XJ, Steffen JM, Fell RD, Dombrowski MJ (1990) Skeletal muscle response to spaceflight, whole body suspension, and recovery in rats. J Appl Physiol 69:2248–2253
Nikawa T, Ishidoh K, Hirasaka K, Ishihara I, Ikemoto M, Kano M, Kominami E, Nonaka I, Ogawa T, Adams GR, Baldwin KM, Yasui N, Kishi K, Takeda S (2004) Skeletal muscle gene expression in space-flown rats. FASEB J 18:522–524
Ohira Y, Yoshinaga T, Nomura T, Kawano F, Ishihara A, Nonaka I, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (2002) Gravitational unloading effects on muscle fiber size, phenotype and myonuclear number. Adv Space Res 30:777–781. doi:10.1016/S0273-1177(02)00395-2
Ohira Y, Yoshinaga T, Ohara M, Kawano F, Wang XD, Higo Y, Terada M, Matsuoka Y, Roy RR, Edgerton VR (2006) The role of neural and mechanical influences in maintaining normal fast and slow muscle properties. Cells Tissues Organs 182:129–142. doi:10.1159/000093963
Pette D, Staron RS (1997) Mammalian skeletal muscle fiber type transition. Int Rev Cytol 170:143–223. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(08)61622-8
Prisk GK, Fine JM, Cooper TK, West JB (2006) Vital capacity, respiratory muscle strength, and pulmonary gas exchange during long-duration exposure to microgravity. J Appl Physiol 101:439–447. doi:10.1152/japplphysiol.01419.2005
Riley DA, Ellis S, Giometti CS, Hoh JF, Ilyina-Kakueva E, Oganov VS, Slocum GR, Bain JL, Sedlak FR (1992) Muscle sarcomere lesions and thrombosis after spaceflight and suspension unloading. J Appl Physiol 73:33S–43S
Riley DA, Ellis S, Slocum GR, Sedlak FR, Bain JL, Krippendorf BB, Lehman CT, Macias MY, Thompson JL, Vijayan K, De Bruin JA (1996) In-flight and postflight changes in skeletal muscles of SLS-1 and SLS-2 spaceflown rats. J Appl Physiol 81:133–144
Roy RR, Baldwin KM, Edgerton VR (1996a) Response of the neuromuscular unit to spaceflight: what has been learned from the rat model. Exerc Sport Sci Rev 24:399–425. doi:10.1249/00003677-199600240-00015
Roy RR, Roy ME, Talmadge RJ, Mendoza R, Grindeland RE, Vasques M (1996b) Size and myosin heavy chain profiles of rat hindlimb extensor muscle fibers after 2 weeks at 2G. Aviat Space Environ Med 67:854–858
Schiaffino S, Gorza L, Sartore S, Saggin L, Ausoni S, Vianello M, Gundersen K, Lomo T (1989) Three myosin heavy chain isoforms in type 2 skeletal muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 10:197–205. doi:10.1007/BF01739810
Staron RS, Kraemer WJ, Hikida RS, Reed DW, Murray JD, Campos GE, Gordon SE (1998) Comparison of soleus muscles from rats exposed to microgravity for 10 versus 14 days. Histochem Cell Biol 110:73–80. doi:10.1007/s004180050267
Taylor WE, Bhasin S, Lalani R, Datta A, Gonzalez-Cadavid NF (2002) Alteration of gene expression profiles in skeletal muscle of rats exposed to microgravity during a spaceflight. J Gravit Physiol 9:61–70
Tidball JG, Berchenko E, Frenette J (1999) Macrophage invasion does not contribute to muscle membrane injury during inflammation. J Leukoc Biol 65:492–498
Vandenburgh H, Chromiak J, Shansky J, Del Tatto M, Lemaire J (1999) Space travel directly induces skeletal muscle atrophy. FASEB J 13:1031–1038
Vestergaard M, Purup S, Henckel P, Tonner E, Flint DJ, Jensen LR, Sejrsen K (1995) Effects of growth hormone and ovariectomy on performance, serum hormones, insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins, and muscle fiber properties of prepubertal Friesian heifers. J Anim Sci 73:3574–3584
Vijayan K, Thompson JL, Riley DA (1998) Sarcomere lesion damage occurs mainly in slow fibers of reloaded rat adductor longus muscles. J Appl Physiol 85:1017–1023
Vijayan K, Thompson JL, Norenberg KM, Fitts RH, Riley DA (2001) Fiber-type susceptibility to eccentric contraction-induced damage of hindlimb-unloaded rat AL muscles. J Appl Physiol 90:770–776
Acknowledgments
This project was supported, in part, by the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine and by NASA grant NAGW-1196 to The Pennsylvania State University Center for Cell Research. We would like to thank the Ohio University College of Osteopathic Medicine Photographic and Graphic Departments for help with the figures. We are also grateful for the technical assistance of Michael Fussell, Don Nguyen, and Babak Mokari, and to the laboratory staff of the Pennsylvania State University Center for Cell Research for their assistance in sample collection.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schuenke, M.D., Reed, D.W., Kraemer, W.J. et al. Effects of 14 days of microgravity on fast hindlimb and diaphragm muscles of the rat. Eur J Appl Physiol 106, 885–892 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1091-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-009-1091-9