Abstract
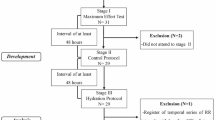
Post-exercise cardiac vagal reactivation is well-investigated; however, the effect of water intake during this period has not been well studied. Therefore, our aim was to assess the influence of water intake on the cardiac vagal reactivation after 30 min of a submaximal cycling exercise. Ten healthy subjects (eight men) aged 23–35 years were evaluated. A 3-day testing cycle duration, subjects were randomly chosen to drink either 500 ml (experimental visit) or 50 ml (control visit) of water immediately after the 30-min cycling exercise at a workload representing 80% of a previously measured anaerobic threshold. A cardiac vagal index (CVI) was obtained using the 4-s exercise test measured before and after (10 and 30 min) exercise at each testing day. Data analysis (2 × 3 ANOVA for repeated measures) showed higher cardiac vagal activity at the 30-min post-exercise period when 500 ml of water was ingested. CVI values for the 500 and 50 ml trials were 1.55 ± 0.04 vs. 1.49 ± 0.04, P = 0.003 (mean ± SEM), respectively. Heart rate and blood pressure values were relatively the same. In conclusion, water intake of about 500 ml immediately after 30 min of cycling exercise accelerates post-exercise cardiac vagal reactivation. These results suggest that post-exercise hydration might be beneficial not only for thermoregulation, but also for vagal reactivation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai Y, Saul JP, Albrecht P, Hartley LH, Lilly LS, Cohen RJ, Colucci WS (1989) Modulation of cardiac autonomic activity during and immediately after exercise. Am J Physiol 256:H132–H141
Araújo CGS, França CL (1996) Fast and large water ingestion increases cardiac vagal tone as assessed by 4-second exercise test [abstract]. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28:S173
Araújo CGS, Nóbrega AC, Castro CL (1992) Heart rate responses to deep breathing and 4-seconds of exercise before and after pharmacological blockade with atropine and propranolol. Clin Auton Res 2:35–40
Araújo CGS, Ricardo DR, Almeida MB (2003) Intra and interdays reliability of the 4-second exercise test. Rev Bras Med Esporte 9:299–303
Brown CM, Barberini L, Dulloo AG, Montani JP (2005) Cardiovascular responses to water drinking: does osmolality play a role? Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 289:R1687–R1692
Callegaro CC, Moraes RS, Negrao CE, Trombetta IC, Rondon MU, Teixeira MS, Silva SC, Ferlin EL, Krieger EM, Ribeiro JP (2007) Acute water ingestion increases arterial blood pressure in hypertensive and normotensive subjects. J Hum Hypertens 21:564–570
Charkoudian N, Halliwill JR, Morgan BJ, Eisenach JH, Joyner MJ (2003) Influences of hydration on post-exercise cardiovascular control in humans. J Physiol 552:635–644
Furlan R, Piazza S, Dell’Orto S, Gentile E, Cerutti S, Pagani M, Malliani A (1993) Early and late effects of exercise and athletic training on neural mechanisms controlling heart rate. Cardiovasc Res 27:482–488
Goldberger JJ, Le FK, Lahiri M, Kannankeril PJ, Ng J, Kadish AH (2006) Assessment of parasympathetic reactivation after exercise. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 290:H2446–H2452
Halliwill JR, Taylor JA, Eckberg DL (1996a) Impaired sympathetic vascular regulation in humans after acute dynamic exercise. J Physiol 495(Pt 1):279–288
Halliwill JR, Taylor JA, Hartwig TD, Eckberg DL (1996b) Augmented baroreflex heart rate gain after moderate-intensity, dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol 270:R420–R426
Hautala A, Tulppo MP, Makikallio TH, Laukkanen R, Nissila S, Huikuri HV (2001) Changes in cardiac autonomic regulation after prolonged maximal exercise. Clin Physiol 21:238–245
Hayashi N, Nakamura Y, Muraoka I (1992) Cardiac autonomic regulation after moderate and exhaustive exercises. Ann Physiol Anthropol 11:333–338
Jordan J (2002) Acute effect of water on blood pressure. What do we know? Clin Auton Res 12:250–255
Jordan J (2005) Effect of water drinking on sympathetic nervous activity and blood pressure. Curr Hypertens Rep 7:17–20
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Black BK, Ali Y, Farley M, Costa F, Diedrich A, Robertson RM, Biaggioni I, Robertson D (2000) The pressor response to water drinking in humans: a sympathetic reflex? Circulation 101:504–509
Jordan J, Shannon JR, Grogan E, Biaggioni I, Robertson D (1999) A potent pressor response elicited by drinking water. Lancet 353:723
Kannankeril PJ, Le FK, Kadish AH, Goldberger JJ (2004) Parasympathetic effects on heart rate recovery after exercise. J Investig Med 52:394–401
Knopfli BH, Bar-Or O, Araújo CGS (2005) Effect of ipratropium bromide on EIB in children depends on vagal activity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 37:354–359
Lazzoli JK, Soares PP, Nóbrega AC, Araújo CGS (2003) Electrocardiographic criteria for vagotonia-validation with pharmacological parasympathetic blockade in healthy subjects. Int J Cardiol 87:231–236
Lipp A, Tank J, Franke G, Arnold G, Luft FC, Jordan J (2005) Osmosensitive mechanisms contribute to the water drinking-induced pressor response in humans. Neurology 65:905–907
Mathias CJ, Young TM (2004) Water drinking in the management of orthostatic intolerance due to orthostatic hypotension, vasovagal syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Eur J Neurol 11:613–619
Mourot L, Bouhaddi M, Tordi N, Rouillon JD, Regnard J (2004) Short- and long-term effects of a single bout of exercise on heart rate variability: comparison between constant and interval training exercises. Eur J Appl Physiol 92:508–517
Nóbrega AC, Araújo CGS (1993) Heart rate transient at the onset of active and passive dynamic exercise. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:37–41
Nóbrega AC, Castro CL, Araújo CGS (1990) Relative roles of the sympathetic and parasympathetic systems in the 4-s exercise test. Braz J Med Biol Res 23:1259–1262
Nóbrega AC, Williamson JW, Araújo CGS, Friedman DB (1994) Heart rate and blood pressure responses at the onset of dynamic exercise: effect of Valsalva manoeuvre. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 68:336–340
Oliveira RB, Vianna LC, Ricardo DR, Almeida MB, Araújo CGS (2006) Influence of different respiratory maneuvers on exercise-induced cardiac vagal inhibition. Eur J Appl Physiol 97:607–612
Raj SR, Biaggioni I, Black BK, Rali A, Jordan J, Taneja I, Harris PA, Robertson D (2006) Sodium paradoxically reduces the gastropressor response in patients with orthostatic hypotension. Hypertension 48:329–334
Ricardo DR, de Almeida MB, Franklin BA, Araújo CGS (2005) Initial and final exercise heart rate transients: influence of gender, aerobic fitness, and clinical status. Chest 127:318–327
Rossi P, Andriesse GI, Oey PL, Wieneke GH, Roelofs JM, Akkermans LM (1998) Stomach distension increases efferent muscle sympathetic nerve activity and blood pressure in healthy humans. J Neurol Sci 161:148–155
Routledge HC, Chowdhary S, Coote JH, Townend JN (2002) Cardiac vagal response to water ingestion in normal human subjects. Clin Sci (Lond) 103:157–162
Schroeder C, Bush VE, Norcliffe LJ, Luft FC, Tank J, Jordan J, Hainsworth R (2002) Water drinking acutely improves orthostatic tolerance in healthy subjects. Circulation 106:2806–2811
Thijs RD, Reijntjes RH, van Dijk JG (2003) Water drinking as a potential treatment for idiopathic exercise-related syncope: a case report. Clin Auton Res 13:103–105
van Orshoven NP, Oey PL, van Schelven LJ, Roelofs JM, Jansen PA, Akkermans LM (2004) Effect of gastric distension on cardiovascular parameters: gastrovascular reflex is attenuated in the elderly. J Physiol 555:573–583
Wasserman K, Whipp BJ, Koyl SN, Beaver WL (1973) Anaerobic threshold and respiratory gas exchange during exercise. J Appl Physiol 35:236–243
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to the subjects for their cooperation. We would also like to thank Joshua Abella for reviewing the English grammar in this manuscript. Lauro Casqueiro Vianna and Bruno Moreira Silva were supported by CNPq—Brazil scholarships and Dr. Claudio Gil S. Araújo is recipient of a CNPq—Brazil research grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vianna, L.C., Oliveira, R.B., Silva, B.M. et al. Water intake accelerates post-exercise cardiac vagal reactivation in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 102, 283–288 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0584-7
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-007-0584-7