Abstract
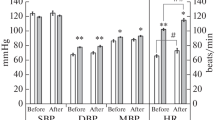
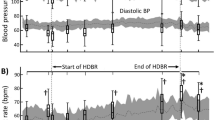
Orthostatic intolerance is common after space flight and head-down tilt (HDT) bed rest. We hypothesized that HDT-induced impairments of arterial blood pressure (AP) control would be more marked during exercise and that recovery of baroreflex function after very long-term HDT would be delayed. Six subjects were studied before (BDC) during (day 60, D60; D113) and after (recovery day 0, R0; R3; R15) 120 days of HDT. Supine resting subjects were exposed to repeated 1 min passive tilts to upright at 3-min interval. During 50 W steady-state exercise corresponding tilt had a 2-min duration at 4-min interval. The amplitudes of the tilt-induced transient beat-by-beat deviations in AP and rate (HR) were determined during the gravity transients. At rest these deviations did not change over time, but during exercise the total peak-to-nadir range of deviations in systolic AP (SAP) at up-tilt and down-tilt increased to 168±16% (mean±SEM) of BDC at D113 with no clear recovery upto and including R15. Counter-regulatory HR responses were not increased proportionally and especially not tachycardic responses to up-tilt, resulting in a reduction of baroreflex sensitivity (ΔRR-interval/ΔSAP) by 55±9% of BDC at D113 with no recovery upto and including R15. We conclude that prolonged bed rest cause long-lasting impairments in AP control and baroreflex function in exercising humans.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beck L, Baisch F, Gaffney FA, Buckey JC, Arbeille P, Patat F, ten Harkel AD, Hillebrecht A, Schulz H, Karemaker JM, et al (1992) Cardiovascular response to lower body negative pressure before, during, and after ten days head-down tilt bedrest. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 604:43–52
Blomqvist CG, Stone HL (1983). Cardiovascular adjustments to gravitational stress. American Physiological Society, Bethesda
Buckey JC Jr, Lane LD, Levine BD, Watenpaugh DE, Wright SJ, Moore WE, Gaffney FA, Blomqvist CG (1996) Orthostatic intolerance after spaceflight. J Appl Physiol 81:7–18
Convertino VA, Doerr DF, Eckberg DL, Fritsch JM, Vernikos-Danellis J (1990) Head-down bed rest impairs vagal baroreflex responses and provokes orthostatic hypotension. J Appl Physiol 68:1458–1464
Convertino VA, Adams WC, Shea JD, Thompson CA, Hoffler GW (1991) Impairment of carotid-cardiac vagal baroreflex in wheelchair-dependent quadriplegics. Am J Physiol 260:R576–R580
Convertino VA, Doerr DF, Guell A, Marini JF (1992) Effects of acute exercise on attenuated vagal baroreflex function during bed rest. Aviat Space Environ Med 63:999–1003
Convertino VA, Fritsch JM (1992) Attenuation of human carotid-cardiac vagal baroreflex responses after physical detraining. Aviat Space Environ Med 63:785–788
Eckberg DL, Fritsch JM (1992) Influence of ten-day head-down bedrest on human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex function. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl 604:69–76
Eckberg DL, Sleight P (eds) (1992) Human baroreflexes in health and disease. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 199–200
Eiken O, Convertino VA, Doerr DF, Dudley GA, Morariu G, Mekjavic IB (1992) Characteristics of the carotid baroreflex in man during normal and flow-restricted exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 144:325–331
Ferretti G, Antonutto G, Denis C, Hoppeler H, Minetti AE, Narici MV, Desplanches D (1997) The interplay of central and peripheral factors in limiting maximal O2 consumption in man after prolonged bed rest. J Physiol 501(Pt 3):677–686
Fritsch-Yelle JM, Charles JB, Jones MM, Beightol LA, Eckberg DL (1994) Spaceflight alters autonomic regulation of arterial pressure in humans. J Appl Physiol 77:1776–1783
Fritsch JM, Charles JB, Bennett BS, Jones MM, Eckberg DL (1992) Short-duration spaceflight impairs human carotid baroreceptor-cardiac reflex responses. J Appl Physiol 73:664–671
Haruna Y, Suzuki Y (1997) Blood pressure and heart rate responses to sudden change of posture during 20 days of simulated microgravity (−6 degrees head-down tilt). J Gravit Physiol 4:P37–38
Haruna Y, Suzuki Y, Kawakubo K, Gunji A (1997) Baroreflex during exercise in different postures before and after 20-days bed rest. J Gravit Physiol 4:S53–S57
Hughson RL, Maillet A, Gharib C, Fortrat JO, Yamamoto Y, Pavy-Letraon A, Riviere D, Guell A (1994) Reduced spontaneous baroreflex response slope during lower body negative pressure after 28 days of head-down bed rest. J Appl Physiol 77:69–77
Kamiya A, Iwase S, Kitazawa H, Mano T, Vinogradova OL, Kharchenko IB (2000) Baroreflex control of muscle sympathetic nerve activity after 120 days of 6 degrees head-down bed rest. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 278:R445–R452
Levine BD, Lane LD, Watenpaugh DE, Gaffney FA, Buckey JC, Blomqvist CG (1996) Maximal exercise performance after adaptation to microgravity. J Appl Physiol 81:686–694
Levine BD, Zuckerman JH, Pawelczyk JA (1997) Cardiac atrophy after bed-rest deconditioning: a nonneural mechanism for orthostatic intolerance. Circulation 96:517–525
Levine BD, Pawelczyk JA, Ertl AC, Cox JF, Zuckerman JH, Diedrich A, Biaggioni I, Ray CA, Smith ML, Iwase S, Saito M, Sugiyama Y, Mano T, Zhang R, Iwasaki K, Lane LD, Buckey JC Jr, Cooke WH, Baisch FJ, Eckberg DL, Blomqvist CG (2002) Human muscle sympathetic neural and haemodynamic responses to tilt following spaceflight. J Physiol 538:331–340
Linnarsson D, Rosenhamer G (1968) Exercise and arterial pressure during simulated increase of gravity. Acta Physiol Scand 74:50–57
Linnarsson D, Sundberg CJ, Tedner B, Haruna Y, Karemaker JM, Antonutto G, Di Prampero PE (1996) Blood pressure and heart rate responses to sudden changes of gravity during exercise. Am J Physiol 270:H2132–H2142
Melcher A, Donald DE (1981) Maintained ability of carotid baroreflex to regulate arterial pressure during exercise. Am J Physiol 241:H838–H849
Montmerle S, Spaak J, Linnarsson D (2002) Lung function during and after prolonged head-down bed rest. J Appl Physiol 92:75–83
Papelier Y, Escourrou P, Gauthier JP, Rowell LB (1994) Carotid baroreflex control of blood pressure and heart rate in men during dynamic exercise. J Appl Physiol 77:502–506
Papelier Y, Escourrou P, Helloco F, Rowell LB (1997) Muscle chemoreflex alters carotid sinus baroreflex response in humans. J Appl Physiol 82:577–583
Parker P, Celler BG, Potter EK, McCloskey DI (1984) Vagal stimulation and cardiac slowing. J Auton Nerv Syst 11:226–231
Potts JT, Shi XR, Raven PB (1993) Carotid baroreflex responsiveness during dynamic exercise in humans. Am J Physiol 265:H1928–1938
Rowell LB, O’Leary DS (1990) Reflex control of the circulation during exercise: chemoreflexes and mechanoreflexes. J Appl Physiol 69:407–418
Rowell LB, O’Leary DS, Kellogg JDL (1996) Integration of cardiovascular control systems in dynamic exercise. American Physiological Society, Bethesda
Sander-Jensen K, Secher NH, Astrup A, Christensen NJ, Giese J, Schwartz TW, Warberg J, Bie P (1986) Hypotension induced by passive head-up tilt: endocrine and circulatory mechanisms. Am J Physiol 251:R742–R748
Sanders JS, Ferguson DW, Mark AL (1988) Arterial baroreflex control of sympathetic nerve activity during elevation of blood pressure in normal man: dominance of aortic baroreflexes. Circulation 77:279–288
Spaak J, Sundblad P, Linnarsson D (1998) Human carotid baroreflex during isometric lower arm contraction and ischemia. Am J Physiol 275:H940–H945
Spaak J, Sundblad P, Linnarsson D (2001) Impaired pressor response after spaceflight and bed rest: evidence for cardiovascular dysfunction. Eur J Appl Physiol 85:49–55
Spaak J, Montmerle S, Sundblad P, Linnarsson D (2005) Long-term bed rest-induced reductions in stroke volume during rest and exercise: cardiac dysfunction vs. volume depletion. J Appl Physiol 98:648–654
Sundberg CJ, Kaijser L (1992) Effects of graded restriction of perfusion on circulation and metabolism in the working leg; quantification of a human ischaemia-model. Acta Physiol Scand 146:1–9
Sundblad P, Haruna Y, Tedner B, Linnarsson D (2000a) Short-term cardiovascular responses to rapid whole-body tilting during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol 81:259–270
Sundblad P, Spaak J, Linnarsson D (2000b) Cardiovascular responses to upright and supine exercise in humans after 6 weeks of head-down tilt (−6 degrees). Eur J Appl Physiol 83:303–309
Sundblad P, Spaak J, Linnarsson D (2000c) Haemodynamic and baroreflex responses to whole-body tilting in exercising men before and after 6 weeks of bedrest. Eur J Appl Physiol 82:397–406
Toska K, Eriksen M (1993) Respiration-synchronous fluctuations in stroke volume, heart rate and arterial pressure in humans. J Physiol 472:501–512
Traon AP, Sigaudo D, Vasseur P, Maillet A, Fortrat JO, Hughson RL, Gauquelin-Koch G, Gharib C (1998) Cardiovascular responses to orthostatic tests after a 42-day head-down bed-rest. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 77:50–59
Warner HR, Cox A (1962) A mathematical model of heart rate control by sympathetic and vagus efferent information. J Appl Physiol 17:349–355
Yang T, Senturia JB, Levy MN (1994) Antecedent sympathetic stimulation alters time course of chronotropic response to vagal stimulation in dogs. Am J Physiol 266:H1339–H1347
Acknowledgements
The collaboration of the subjects and the staff of the Institute of Bio-Medical Problems, Moscow is gratefully acknowledged. This study was supported by the European Space Agency, the National Swedish Space Board, the Swedish Medical Research Council (Grant no. 5020) and Fraenckel’s Foundation for Medical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Linnarsson, D., Spaak, J. & Sundblad, P. Baroreflex impairment during rapid posture changes at rest and exercise after 120 days of bed rest. Eur J Appl Physiol 96, 37–45 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-0062-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-0062-z