Abstract.
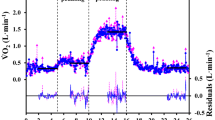
This study evaluated an ergo-spirometry system based on mixed expired gas for gas analyses and an inspiratory based determination of flow. There were 74 paired samples of oxygen uptake (VO2) and related variables including pulmonary ventilation (VE), fractional concentrations of expired CO2 and O2 (F ECO2 and F EO2, respectively), as well as CO2 output (VCO2) which were obtained from the metabolic cart and a Douglas bag system during 22 min submaximal and 5–8 min maximal running on a treadmill. For F ECO2 and VCO2 the metabolic cart gave readings that were 2.6% and 1.8% higher and for F EO2 0.2% lower than the Douglas bag method (P<0.05). For the metabolic cart and the Douglas bag method the coefficient of variation (CV) for repeated determinations of VO2 was 1.9% and 1.8%, respectively. For VO2 and VE, there were no significant differences between the two methods and the 95% confidence interval of the difference in VO2 was within –30 and +20 ml min–1. The CV of the differences in VO2 between the two systems was 2.4% and it is concluded that a metabolic cart method based on inspiratory flow rate is suitable for measurement of VO2 and VE during both submaximal and maximal exercise.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jensen, K., Jørgensen, S. & Johansen, L. A metabolic cart for measurement of oxygen uptake during human exercise using inspiratory flow rate. Eur J Appl Physiol 87, 202–206 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0616-2
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0616-2