Abstract.
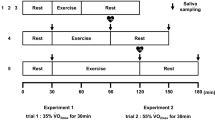
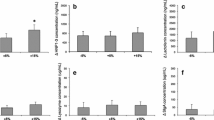
The incidence of upper respiratory tract infections (URTI) and salivary immunoglobulin A concentrations [IgAs] of nine individuals were examined during 12 weeks of moderate exercise training, and compared to ten sedentary controls. Changes in maximal oxygen uptake were assessed at initial, mid-point and final evaluations (T1–3), while changes in [IgAs] and salivary immunoglobulin concentration-salivary albumin concentration ratio ([IgAs]:[Albs]) were monitored at T1 and T3. During the 12 week period, symptoms of URTI were self-recorded daily. During the period of training the level of fitness significantly increased (P<0.05) in the exercise group. The number of days recording symptoms of influenza, but not of cold, and total light URTI symptoms was significantly reduced in the exercise group during the last weeks of training. A significant increase in [IgAs] and in [IgAs]:[Albs] was found in the exercise group after training. Both [IgAs] and [IgAs]:[Albs] were significantly related to the number of days showing symptoms of influenza (P<0.01) and the total number of days of sickness (P<0.05). These data provide quantitative support for the belief that regular, moderate exercise results in an increased [IgAs] at rest and [IgAs]:[Albs], which may contribute to a decreased risk of infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Klentrou, P., Cieslak, T., MacNeil, M. et al. Effect of moderate exercise on salivary immunoglobulin A and infection risk in humans. Eur J Appl Physiol 87, 153–158 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0609-1
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-002-0609-1