Abstract
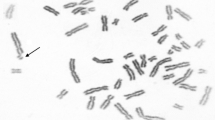
Objective: The objective of this study was to assess the genetic effect of occupational exposure to antineoplastic agents. Method: The influence of occupational handling of cytotoxic drugs was investigated by monitoring the frequency of sister chromatid exchanges (SCE), the percentage of cells with high frequencies of SCE (high-frequency cells, HFC), and the frequency of somatic mutation at the T-cell receptor (TCR) locus in mononuclear cells of exposed hospital nurses. These parameters were also measured in healthy donors and in cancer patients at the time of the diagnosis and following the administration of high doses of cytotoxic drugs requiring stem cell support. Results: Our results show that (a) SCE and HFC values in occupationally exposed nurses do not differ from controls, (b) patients with newly diagnosed cancer or following chemotherapy show a number of SCE comparable to those of healthy donors, but a significantly different percentage of HFC, (c) cigarette smokers of all categories studied show higher frequencies of SCE and HFC as compared to nonsmokers, but the differences are not statistically significant, (d) the mutation frequency at the TCR locus in oncology nurses is higher, but not significantly different from the frequency in the control group, and (e) the increase of mutation frequency is statistically significant and seems to be dose dependent in patients treated with high-dose chemotherapy. Conclusions: Our data suggest that SCE frequency and HFC percentage are not reliable indicators of exposure to possible mutagenic/carcinogenic effects of antineoplastic drugs; on the contrary, our observations indicate that anticancer therapy induces somatic mutations at the TCR locus and suggest an association between exposure to cytotoxic agents and the increase in somatic mutations.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 4 February 1999 / Accepted: 3 April 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lanza, A., Robustelli della Cuna, F., Zibera, C. et al. Somatic mutations at the T-cell antigen receptor in antineoplastic drug-exposed populations: comparison with sister chromatid exchange frequency. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 72, 315–322 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200050381
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004200050381