Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate whether the exposure to arsenic (As) causes alterations of liver enzymes in two groups of outdoor workers.
Methods
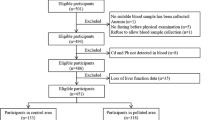
Total urinary As and the levels of AST/GOT, ALT/GPT, and GGT were measured on 80 traffic policemen and 50 police drivers. Personal air samples were obtained for assessing the exposure to As on a subgroup of 20 traffic policemen and 20 police drivers.
Results
Mean values of personal exposure to As, urinary As, AST/GOT, and ALT/GPT were significantly higher in traffic policemen than in the police drivers. Multiple linear regression models showed associations between urinary As and airborne As, ALT/GPT and the job variables, and BMI and urinary As.
Conclusions
These findings contribute toward the evaluation of the hepatic effects of exposure to As in the urban workers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abernathy CO, Thomas DJ, Calderon RL (2003) Health effects and risk assessment of arsenic. J Nutr 133(5 Suppl 1):1536S–1538S
Anawar HM (2012) Arsenic speciation in environmental samples by hydride generation and electrothermal atomic absorption spectrometry. Talanta 88:30–42
ATSDR (2007) Toxicological profile for arsenic. Atlanta GA: Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry. Available at: http://www.atsdr.cdc.gov/toxprofiles/tp2.pdf. Accessed 21 Oct 2012
Ciarrocca M, Tomei F, Caciari T et al (2012a) Exposure to arsenic in urban and rural areas and effects on thyroid hormones. Inhal Toxicol 24:589–598
Ciarrocca M, Tomei G, Palermo P et al (2012b) Environmental and biological monitoring of arsenic in outdoor workers exposed to urban air pollutants. Int J Hyg Environ Health 215:555–561
Clark JM, Brancati FL, Diehl AM (2003) The prevalence and etiology of elevated aminotransferase levels in the United States. Am J Gastroenterol 98:960–967
Das N, Paul S, Chatterjee D et al (2012) Arsenic exposure through drinking water increases the risk of liver and cardiovascular diseases in the population of West Bengal, India. BMC Public Health 12:639
Davidson CI, Goold WD, Mathison TP, Wiersma GB, Brown KW, Reilly MT (1985) Airborne trace elements in Great Smoky Mountains, Olympic, and Glacier National Parks. Environ Sci Technol 19(1):27–35
Drobná Z, Walton FS, Paul DS, Xing W, Thomas DJ, Stýblo M (2010) Metabolism of arsenic in human liver: the role of membrane transporters. Arch Toxicol 84:3–16
Francesconi KA, Kuehnelt D (2004) Determination of arsenic species: a critical review of methods and applications, 2000–2003. Analyst 129:373–395
Guha Mazumder DN (2001) Arsenic and Liver diseases. J Indian Med Assoc 99:311, 314–315, 318–320
International Agency for Research on Cancer. IARC Monographs on the Evaluation of Carcinogenic Risks to Humans (2004) Some drinking-water disinfectants and contaminants, including arsenic, vol 84. Lyon: IARC Press, pp 39–267
Islam K, Haque A, Karim R et al (2011) Dose-response relationship between arsenic exposure and the serum enzymes for liver function tests in the individuals exposed to arsenic: a cross sectional study in Bangladesh. Environ Health 10:64
Liu WS, Chung YT, Yang CY, Lin CC, Tsai KH, Yang WC et al (2012) Serum creatinine determined by Jaffe, enzymatic method, and isotope dilution-liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry in patients under hemodialysis. J Clin Lab Anal 26(3):206–214
Maio G, D’Argenio P, Stroffolini T et al (2000) Hepatitis C virus infection and alanine transaminase levels in the general population: a survey in a southern Italian town. J Hepatol 33:116–120
Maiti S, Chattopadhyay S, Deb B et al (2012) Antioxidant and metabolic impairment result in DNA damage in arsenic-exposed individuals with severe dermatological manifestations in Eastern India. Environ Toxicol 27:342–350
Morisco F, Di Lonardo A, Stroffolini T, Leone D, Caporaso N (2001) High prevalence of non-virus/non-alcohol-related alanine-aminotransferase increase in blood donors. Haematologica 86:1116
National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) (1998) Manual of analytical methods, 4th edn. Method 7900 Elements by ICP. DHHS NIOSH Publication No. 98-119
Pari L, Mohamed Jalaludeen A (2011) Protective role of sinapic acid against arsenic: induced toxicity in rats. Chem Biol Interact 194:40–47
Patlolla AK, Todorov TI, Tchounwou PB, van der Voet G, Centeno JA (2012) Arsenic-induced biochemical and genotoxic effects and distribution in tissues of Sprague–Dawley rats. Microchem J 105:101–107
Pendino GM, Mariano A, Surace P et al (2005) Prevalence and etiology of altered liver tests: a population-based survey in a Mediterranean town. Hepatology 41:1151–1159
Ruhl CE, Everhart JE (2003) Determinants of the association of overweight with elevated serum alanine aminotransferase activity in the United States. Gastroenterology 124:71–79
Scheig R (1996) Evaluation of tests used to screen patients with liver disorders. Prim Care 23:551–560
Schmidt E, Schmidt FW (1993) Enzyme diagnosis of liver diseases. Clin Biochem 26:241–251
Schumann G, Klauke R (2003) New IFCC reference procedures for the determination of catalytic activity concentrations of five enzymes in serum: preliminary upper reference limits obtained in hospitalized subjects. Clin Chim Acta 327:69–79
Stranges S, Freudenheim JL, Muti P et al (2004) Differential effect of alcohol drinking pattern on liver enzymes in men and women. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 28:949–956
Syczewska M, Urbanowicz W, Rzechuła H, Boroń-Kaczmarska A (2004) Relationship of serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT) to body weight, age and sex in blood donors population. Wiad Lek 57:427–430
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Casale, T., Rosati, M.V., Ciarrocca, M. et al. Assessment of liver function in two groups of outdoor workers exposed to arsenic. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 87, 745–752 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-013-0914-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-013-0914-5