Abstract
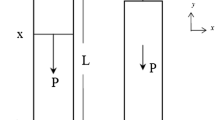
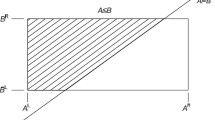
In this study, Galileo’s problem, namely that of the design of the bar subjected to axial external load, is generalized in the case when multiple axial loads are applied. The loads are modeled as interval variables to describe the ever existing uncertainty in their values. Modified interval arithmetic operation is suggested so as to reduce overestimation of inner axial loaded and needed safety factors. Special emphasis is placed on the cases in which functional relationships may exist among loads.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Degrauwe, D., Lombaert, G., De Roeck, G.: Improving interval analysis in finite element calculations by means of affine arithmetic. Comput. Struct. 88(3–4), 247–254 (2010)
de Figueiredo, L.H., Stolfi, J.: Affine arithmetic: concepts and applications. Numer. Algorithms 37(1–4), 147–158 (2004)
Delbecq, D.: Personal Communication, Atlantic University, Florida, October 23 (2015)
Dimitrova, N.S., Markov, S.M., Popova, E.D.: Extended interval arithmetic: new results and applications. In: Atanassova, L., Herzberger, J. (eds.) Computer Arithmetic and Enclosure Methods, pp. 225–232. North Holland, Amsterdam (1992)
Elishakoff, I.: Whys and Hows of Uncertainty Modeling: Probability, Fuzziness and Anti-optimization. Springer, Vienna (1999)
Galilei, G.: Discorsi e dimostrazioni matematiche intorno a due nuove scienze. Elzevir, Leyden (in Latin); (English translation: Discourses and Mathematical Demonstrations Relating to Two New Sciences (reissued Dover, New York, 1954) (1638). http://oll.libertyfund.org/titles/753
Gabriele, S., Culla, A.: Comparison of statistical and interval analysis for the energy flow uncertainties in structural vibrating systems. J. Sound Vib. 314(3–5), 672–692 (2008)
Gabriele, S.: The interval intersection method for FE model. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 305, 012091 (2011)
Gabriele, S., Varano, V.: Influence of the parameterization in the interval solution of elastic beams. J. Struct. 2014, 395213 (2014)
Gardenyes, E., Trepat, J.M., Janger, J.M.: Sigla\(\_\)PL/1: development and applications. In: Nickel, K.L.E. (ed.) Interval Mathematics, pp. 301–315. Academic Press, New York (1980)
Gardeñes, E., Sainz, M.Á., Jorba, L., Calm, R., Estela, R., Mielgo, H., Trepat, A.: Model intervals. Reliab. Comput. 7(2), 77–111 (2001)
Hansen, E.R., Walster, G.: Global Optimization Using Interval Analysis, 2nd edn. Marcel Dekker, New York (2004)
Kaucher, E.: Interval analysis in the extended interval space IR. Comput. Suppl. 2, 33–49 (1980)
Kupriyanova, L.: Inner estimation of the united solution set of interval linear algebraic system. Reliab. Comput. 1(1), 15–31 (1995)
Kurrer, K.-E.: The History of the Theory of Structures: From Arch Analysis to Computational Mechanics. Ernst & Sohn, Berlin (2008)
Markov, S.: On directed interval arithmetic and its applications. J. Univers. Comput. Sci. 1(7), 514–526 (1995)
Mielgo, H., Trepat, A.: Modal intervals: reason and ground semantics. In: Nickel, K. (ed.) Interval Mathematics 1985. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol. 212, pp. 27–35. Springer, Berlin (1986)
Moore, R.E., Kearfott, R.B., Michael, J., Cloud, M.J.: Introduction to Interval Analysis. SIAM Press, Philadelphia (2009)
Petroski, H.: Galileo and the marble column: a paradigm of human error in design. Struct. Saf. 11(1), 1–11 (1991)
Petroski, H.: Galileo’s confirmation of a false hypothesis: a paradigm of logical error in design. Civ. Eng. Syst. 9(3), 251–263 (1991)
Popova, E., Ullrich, C.P.: Directed Interval Arithmetic in Mathematica. Implementation and Applications. Technical report no. 96-3, Universitaet Basel, Switzerland (1996)
Popova, E., Kraemer, W.: Inner and outer bounds for parametric linear systems. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 199(2), 310–316 (2007)
Rump, S.M.: INTLAB—INTerval LABoratory. In: Csendes, Tibor (ed.) Developments in Reliable Computing, pp. 77–104. Kluwer, Dordrecht (1999)
Sainz, M.Á., Herrero, P., Armengol, J., Vehì, J.: Continuous minimax optimization using modal intervals. J. Math. Anal. Appl. 339, 18–30 (2008)
Sainz, M.A., Armengol, J., Calm, R., Herrero, P., Jorba, L., Vehi, J.: Modal Interval Analysis: New Tools for Numerical Information. Springer, Berlin (2014)
Shary, S.P.: Algebraic approach to the interval linear static identification, tolerance, and control problems, or one more application of Kaucher arithmetic. Reliab. Comput. 2(1), 3–33 (1996)
SIGLA/X Group: Modal intervals, basic tutorial. In: Proceedings of Applications of Interval Analysis to Systems and Control (MISC 99). Universitat de Girona, Spain, pp. 157–227 (1999). http://ima.udg.edu/SIGLA/X/mod_interval/ (read on 1 Feb 2013)
Sunaga, T.: Theory of an interval algebra and its application to numerical analysis. RAAG Mem. 2, 547–564 (1958)
Vehí, J., Rodellar, J., Sainz, M., Armengol, J.: Analysis of the robustness of predictive controllers via modal intervals. Reliab. Comput. 6(3), 281–301 (2000)
Wang, X., Qiu, Z.P., Elishakoff, I.: Non-probabilistic set-theoretic model for structural safety measure. Acta Mech. 198, 51–64 (2008)
Wang, Y.: Semantic tolerancing with generalized intervals. Comput. Aided Des. Appl. 4(1–4), 257–266 (2007)
Wu, D., Qiu, Z.P.: Comparison of two non-probabilistic approaches for the energy flow uncertainty in structural vibrating system. J. Sound Vib. 330(11), 2520–2535 (2011)
Acknowledgments
This study was conducted when S. Gabriele was a Visiting Associate Professor at the Florida Atlantic University. Their kind and warm hospitality is gratefully acknowledged. I. Elishakoff appreciates the support provided by the Southeast National Marine Renewable Energy Center. Stefano Gabriele thanks Prof. Evgenia D. Popova of Bulgarian Academy of Sciences. Authors are expressing appreciation to Mr. Damien Delbecq of the Advanced French Institute of Mechanics for deriving expression for number of cancellation operations. Authors express their sincere gratitude to anonymous reviewers for their numerous careful comments implementation of which led to elucidation of raised points.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elishakoff, I., Gabriele, S. & Wang, Y. Generalized Galileo Galilei problem in interval setting for functionally related loads. Arch Appl Mech 86, 1203–1217 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1086-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1086-4