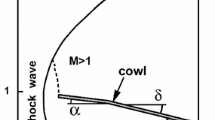
Abstract
The study addresses 2D and 3D turbulent transonic flows in divergent channels with a bend, where a shock wave is formed upstream of the sonic line/surface arisen over an expansion corner of the lower wall. Solutions of the Reynolds-averaged Navier–Stokes equations are obtained with a finite-volume solver of the second-order accuracy on fine meshes. Numerical simulations reveal a considerable hysteresis in the shock wave position versus the supersonic Mach number given at the inlet. A dependence of the hysteresis on the slopes of walls and length of channel is analyzed. The bifurcation band persists when unsteady perturbations are imposed at the inlet. A physical interpretation of the shock wave instability is suggested.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand, P., Lakshmanan, D., Saravanan, R.: Computational analysis of flow behaviour in curved section of the serpentine intake. Glob. J. Eng. Des. Technol. 3(4), 46–51 (2014)
Blazek, J.: Computational Fluid Dynamics: Principles and Applications. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2001)
Bur, R., Benay, R., Galli, A., Berthouze, P.: Experimental and numerical study of forced shock-wave oscillations. Aerosp. Sci. Technol. 10, 265–278 (2006)
Chung, K.-M.: Unsteadiness of transonic convex-corner flows. Exp. Fluids 37, 917–922 (2004)
Délery, J.M.: The different facets of an old but always present concern: shock-wave/boundary layer interaction. In: Sobieczky, H. (ed.) IUTAM Symposium Transsonicum IV, pp. 91–98. Kluwer, Dordrecht (2003)
Hsieh, T., Coakley, T.J.: Downstream boundary effects on the frequency of self-excited oscillations in diffuser flows. In: AIAA Paper, no. 87-0161 (1987)
Kuzmin, A.G.: Interaction of a shock wave with the sonic line. In: Sobieczky, H. (ed.) IUTAM Symposium Transsonicum IV, pp. 13–18. Kluwer, Dordrecht (2003)
Kuzmin, A.G.: Aerodynamic surfaces admitting jumps of the lift coefficient in transonic flight. In: Hafez, M.M., Oshima, K., Kwak, D. (eds.) Computational Fluid Dynamics Review 2010, pp. 543–562. World Scientific Publishing, Singapore (2010). (Chapter 22)
Kuzmin, A.: Shock wave instability in a channel with an expansion corner. Int. J. App. Mech. 7(2), 1550019: 1–9 (2015). (World Scientific Publishing)
Kuzmin, A.: Sensitivity analysis of transonic flow over J-78 wings. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2015, 579343 (2015). (Hindawi: 1–7)
Liu, H., Wang, B., Guo, Y., Zhang, H., Lin, W.: Effects of inflow Mach number and step height on supersonic flows over a backward-facing step. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2013, 147916: 1–11 (2013)
Matsuo, K., Kim, H.-D.: Normal shock wave oscillations in supersonic diffusers. Shock Waves 3, 25–33 (1993)
Menter, F.R.: Review of the shear-stress transport turbulence model experience from an industrial perspective. Int. J. Comput. Fluid Dyn. 23, 305–316 (2009)
Moerel, J.-L., Veraar, R.G., Halswijk, W.H.C., Pimentel, R., Corriveau, D., Hamel, N., Lesage, F., Vos, J.B.: Internal flow characteristics of a rectangular ramjet air intake. In: AIAA Paper, no. 2009–5076. pp. 1–26 (2009)
Nguyen, T.T.Q., Behr, M., Reinartz, B.U.: Numerical investigation of compressible turbulent boundary layer over expansion corner. In: AIAA Paper, no. 2009–7371. pp. 1–20 (2009)
Sajben, M., Bogar, T.J., Kroutil, J.C.: Characteristic frequency and length scales in transonic diffuser flow oscillations. In: AIAA Paper, no. 81-1291 (1981)
Sharcnet: Computing Tomorrow’s Solutions. https://www.sharcnet.ca/Software/Fluent14/help/cfx_thry/i1303039.html (2013)
Shifrin, E.G.: Plane vortex flow in the vicinity of the point of orthogonality of the sonic line to the velocity vector. In: Izv. Akad. Nauk SSSR, Mekh. Zhidk. Gaza, no. 6. pp. 144–146 (1966)
Sung, H.-G., Kim, S.-J., Yeom, H.-W., Heo, J.-Y.: On the assessment of compressibility effects of two-equation turbulence models for supersonic transition flow with flow separation. Int. J. Aeronaut. Space Sci. 14(4), 387–397 (2013)
Szumowski, A.P., Obermeier, F., Meier, G.E.A.: Oscillation modes of laval nozzle flow. Exp. Fluids 18, 145–152 (1995)
Xiao, Q., Tsai, H.M.: Computation of transonic diffuser flows by a lagged \(k\)-\(\omega \) turbulence model. J. Propuls. Power 19(3), 473–483 (2003)
Acknowledgments
This research was performed using computational resources provided by the Computational Center of St. Petersburg State University (http://cc.spbu.ru). The work was supported by the Russian Foundation for Basic Research under grant no. 13-08-00288.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuzmin, A. Shock wave bifurcation in channels with a bend. Arch Appl Mech 86, 787–795 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1062-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-015-1062-z