Abstract
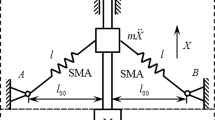
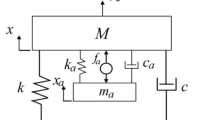
The solutions to H ∞ and H 2 optimization problems of a variant dynamic vibration absorber (DVA) applied to suppress vibration in beam structures are derived analytically. The H ∞ optimum parameters such as tuning frequency and damping ratios are expressed based on fixed-point theory to minimize the resonant vibration amplitude, as well as, the H 2 optimum parameters to minimize the total vibration energy or the mean square motion of a beam under random force excitation as analytical formulas. The reduction in maximum amplitude responses and mean square motion of a beam using the traditional vibration absorber is compared with the proposed dynamic absorber. Numerical results show the non-traditional DVA under optimum conditions has better vibration suppression performance on beam structures than the traditional design of DVA. Furthermore, comparing H ∞ and H 2 optimization procedures shows that for a beam under random force excitation, use of H2 optimum parameters resulting in smaller mean square motion than the other optimization.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Frahm, H.: Device for damping vibrations of bodies. U.S. Patent No. 989, 3576–3580 (1911)
Ormondroyd J., Den Hartog J.P.: The theory of the dynamic vibration absorber. ASME J. Appl. Mech. 50(7), 9–22 (1928)
Crandall S.H., Mark W.D.: Random Vibration in Mechanical Systems. Academic Press, New York (1963)
Asami T., Nishihara O.: Closed-form exact solution to H∞ optimization of dynamic vibration absorbers (application to different transfer functions and damping systems). J. Vib. Acoust. 125, 398–405 (2003)
Asami T., Nishihara O., Baz M.: Analytical solutions to H∞ and H2 optimization of dynamic vibration absorbers attached to damped linear systems. J. Vib. Acoust. 124, 284–295 (2002)
Zillettin M., Elliott S.J., Rustighi E.: Optimisation of dynamic vibration absorbers to minimise kinetic energy and maximise internal power dissipation. J. Sound Vib. 331, 4093–4100 (2012)
Tigli O.F.: Optimum vibration absorber (tuned mass damper) design for linear damped systems subjected to random loads. J. Sound Vib. 331, 3035–3049 (2012)
Ozer M.B., Royston T.J.: Extending Den Hartog’s vibration absorber technique to multi-degree-of-freedom systems. ASME J. Vib. Acoust. 127, 341–350 (2005)
Rice H.J.: Design of multiple vibration absorber systems using modal data. J. Sound Vib. 160(2), 378–385 (1993)
Hadi M., Arfiadi Y.: Optimum design of absorber for MDOF structures. J. Struct. Eng. 124, 1272–1280 (1998)
Wong W.O., Tang S.L., Cheung Y.L.: Design of dynamic vibration absorber for vibration isolation of beams under point or distributed loads. J. Sound Vib. 301, 898–908 (2007)
Cheung Y.L., Wong W.O.: H∞ and H2 optimizations of dynamic vibration absorber for suppressing vibrations in plates. J. Sound Vib. 320, 29–42 (2009)
Zuo L.: Effective, robust vibration control using series multiple tuned-mass dampers. J. Vib. Acoust. 131(3), 031003 (2009)
Yamaguchi H., Harnpornchai N.: Fundamental characteristics of multiple tuned mass dampers for suppressing harmonically forced oscillations. Earthq. Eng. Struct. Dyn. 22, 51–62 (1993)
Zuo L., Nayfeh S.A.: Minimax optimization of multi-degree-of-freedom tuned-mass dampers. J. Sound Vib. 272, 893–908 (2004)
Ren M.Z.: A variant design of the dynamic vibration absorber. J. Sound Vib. 245, 762–770 (2001)
Liu K., Liu J.: The damped dynamic vibration absorbers: revisited and new results. J. Sound Vib. 284, 181–189 (2005)
Liu K.: Optimal design of damped dynamic vibration absorber for damped primary systems. CSME Trans. 34, 119–135 (2010)
Wong W.O., Cheung Y.L.: Optimal design of a damped dynamic vibration absorber for vibration control of structure excited by ground motion. Eng. Struct. 30, 282–286 (2008)
Chtiba M.O., Choura S., Nayfeh A.H., El-Borgi S.: Vibration confinement and energy harvesting in flexible structures using collocated absorbers and piezoelectric devices. J. Sound Vib. 329, 261–276 (2010)
Cheung Y.L., Wong W.O.: H2 optimization of a non-traditional dynamic vibration absorber for vibration control of structures under random force excitation. J. Sound Vib. 330, 1039–1044 (2011)
Cheung Y.L., Wong W.O.: H-infinity optimization of variant design of the dynamic vibration absorber-revisited and new results. J. Sound Vib. 330, 3901–3912 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Noori, B., Farshidianfar, A. Optimum design of dynamic vibration absorbers for a beam, based on H ∞ and H 2 Optimization. Arch Appl Mech 83, 1773–1787 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-013-0777-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00419-013-0777-y