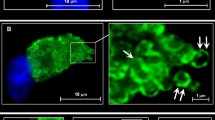
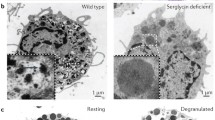
Abstract
During degranulation, mast cells secrete a specific set of mediators defined as “secretome” including the preformed mediators that have already been synthesized by a cell and contained in the cytoplasmic granules. This group includes serine proteases, in particular, chymase and tryptase. Biological significance of chymase depends on the mechanisms of degranulation and is characterized by selective effects on the cellular and non-cellular components of the specific tissue microenvironment. Chymase is known to be closely involved in the mechanisms of inflammation and allergy, angiogenesis, and oncogenesis, remodeling of the extracellular matrix of the connective tissue and changes in organ histoarchitectonics. Number of chymase-positive mast cells in the intra-organ population, and the mechanisms of biogenesis and secretome degranulation appear to be the informative criteria for interpreting the state of the internal organs, characterizing not only the diagnostic efficacy but also the properties of targets of pharmacotherapy. In this review, we discussed the current state of knowledge about mast cell chymase as one of the mast cell secretome proteases. Main issues of the reviewed publications are highlighted with our microscopic images of mast cell chymase visualized using immunohistochemical staining.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akahoshi M, Song CH, Piliponsky AM, Metz M, Guzzetta A, Abrink M, Schlenner SM, Feyerabend TB, Rodewald HR, Pejler G, Tsai M, Galli SJ (2011) Mast cell chymase reduces the toxicity of Gila monster venom, scorpion venom, and vasoactive intestinal polypeptide in mice. J Clin Invest 121:4180–4191
Ammendola M, Sacco R, Sammarco G, Luposella M, Patruno R, Gadaleta CD, Sarro GD, Ranieri G (2016) Mast cell-targeted strategies in cancer therapy. Transfus Med Hemother 43:109–113
Annichkov NM, Kostantinov IE (2007) [A. A. Maksimov: on the 100th anniversary of the unitarian theory of hematopoiesis]. Arkh Patol 69:3–7
Atiakshin D, Samoilova V, Buchwalow I, Boecker W, Tiemann M (2017) Characterization of mast cell populations using different methods for their identification. Histochem Cell Biol 147:683–694
Atiakshin D, Buchwalow I, Samoilova V, Tiemann M (2018a) Tryptase as a polyfunctional component of mast cells. Histochem Cell Biol 149:461–477
Atiakshin D, Buchwalow I, Tiemann M (2018b) Mast cell proteases in formation of the specific tissue microenvironment: pathogenic and diagnostic aspects. Therapy 6:128–140 (in Russian)
Bacani C, Frishman WH (2006) Chymase: a new pharmacologic target in cardiovascular disease. Cardiol Rev 14:187–193
Badertscher K, Bronnimann M, Karlen S, Braathen LR, Yawalkar N (2005) Mast cell chymase is increased in chronic atopic dermatitis but not in psoriasis. Arch Dermatol Res 296:503–506
Balcells E, Meng QC, Johnson WH Jr, Oparil S, Dell’Italia LJ (1997) Angiotensin II formation from ACE and chymase in human and animal hearts: methods and species considerations. Am J Physiol 273:H1769–H1774
Befus AD, Pearce FL, Gauldie J, Horsewood P, Bienenstock J (1982) Mucosal mast cells. I. Isolation and functional characteristics of rat intestinal mast cells. J Immunol 128:2475–2480
Bienenstock J, Befus AD, Pearce F, Denburg J, Goodacre R (1982) Mast cell heterogeneity: derivation and function, with emphasis on the intestine. J Allergy Clin Immunol 70:407–412
Blank U, Madera-Salcedo IK, Danelli L, Claver J, Tiwari N, Sanchez-Miranda E, Vazquez-Victorio G, Ramirez-Valadez KA, Macias-Silva M, Gonzalez-Espinosa C (2014) Vesicular trafficking and signaling for cytokine and chemokine secretion in mast cells. Front Immunol 5:453
Borland JA, Kelsall C, Yacoub MH, Chester AH (2005) Expression, localisation and function of ACE and chymase in normal and atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Vascul Pharmacol 42:99–108
Bot I, Shi GP, Kovanen PT (2015) Mast cells as effectors in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 35:265–271
Buchwalow IB, Boecker W (2010) Immunohistochemistry: basics and methods. Springer, Heidelberg
Buchwalow I, Boecker W, Tiemann M (2015) The contribution of Paul Ehrlich to histochemistry: a tribute on the occasion of the centenary of his death. Virchows Arch 466:111–116
Buchwalow I, Atiakshin D, Samoilova V, Boecker W, Tiemann M (2018a) Identification of autofluorescent cells in human angioimmunoblastic T-cell lymphoma. Histochem Cell Biol 149:169–177
Buchwalow I, Samoilova V, Boecker W, Tiemann M (2018b) Multiple immunolabeling with antibodies from the same host species in combination with tyramide signal amplification. Acta Histochem 120:405–411
Buckley M, Walls AF (2008) Identification of mast cells and mast cell subpopulations. Methods Mol Med 138:285–297
Bykov VL (2010) Development and heterogeneity of mast cells. Morfologiia 117:86–92
Caughey GH (2007) Mast cell tryptases and chymases in inflammation and host defense. Immunol Rev 217:141–154
Caughey GH (2011) Mast cell proteases as protective and inflammatory mediators. Adv Exp Med Biol 716:212–234
Caughey GH (2016) Mast cell proteases as pharmacological targets. Eur J Pharmacol 778:44–55
Cha SI, Chang CS, Kim EK, Lee JW, Matthay MA, Golden JA, Elicker BM, Jones K, Collard HR, Wolters PJ (2012) Lung mast cell density defines a subpopulation of patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Histopathology 61:98–106
Chen H, Xu Y, Yang G, Zhang Q, Huang X, Yu L, Dong X (2017) Mast cell chymase promotes hypertrophic scar fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis by activating TGF-beta1/Smads signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med 14:4438–4442
Crivellato E, Beltrami CA, Mallardi F, Ribatti D (2004) The mast cell: an active participant or an innocent bystander? Histol Histopathol 19:259–270
Crivellato E, Travan L, Ribatti D (2015) The phylogenetic profile of mast cells. Methods Mol Biol 1220:11–27
da Silva EZ, Jamur MC, Oliver C (2014) Mast cell function: a new vision of an old cell. J Histochem Cytochem 62:698–738
de Souza Junior DA, Borges AC, Santana AC, Oliver C, Jamur MC (2015a) Mast cell proteases 6 and 7 stimulate angiogenesis by inducing endothelial cells to release angiogenic factors. PLoS ONE 10:e0144081
de Souza Junior DA, Santana AC, da Silva EZ, Oliver C, Jamur MC (2015b) The role of mast cell specific chymases and tryptases in tumor angiogenesis. Biomed Res Int 2015:142359
DeBruin EJ, Gold M, Lo BC, Snyder K, Cait A, Lasic N, Lopez M, McNagny KM, Hughes MR (2015) Mast cells in human health and disease. Methods Mol Biol 1220:93–119
Dell’Italia LJ, Collawn JF, Ferrario CM (2018) Multifunctional role of chymase in acute and chronic tissue injury and remodeling. Circ Res 122:319–336
Dong X, Geng Z, Zhao Y, Chen J, Cen Y (2013) Involvement of mast cell chymase in burn wound healing in hamsters. Exp Ther Med 5:643–647
Dudeck A, Koberle M, Goldmann O, Meyer N, Dudeck J, Lemmens S, Rohde M, Roldan NG, Dietze-Schwonberg K, Orinska Z, Medina E, Hendrix S, Metz M, Zenclussen AC, von Stebut E, Biedermann T (2018) Mast cells as protectors of health. J Allergy Clin Immunol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2018.10.054
Dvorak AM (1989) Human mast cells. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 114:1–107
Ehrlich P (1878) Beiträge für Theorie und Praxis der histologischen Färbung, vol Doktor. Leipzig University, Leipzig, p 65
Enoksson M, Ejendal KF, McAlpine S, Nilsson G, Lunderius-Andersson C (2011a) Human cord blood-derived mast cells are activated by the Nod1 agonist M-TriDAP to release pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. J Innate Immun 3:142–149
Enoksson M, Lyberg K, Moller-Westerberg C, Fallon PG, Nilsson G, Lunderius-Andersson C (2011b) Mast cells as sensors of cell injury through IL-33 recognition. J Immunol 186:2523–2528
Fang KC, Raymond WW, Lazarus SC, Caughey GH (1996) Dog mastocytoma cells secrete a 92-kD gelatinase activated extracellularly by mast cell chymase. J Clin Invest 97:1589–1596
Fang KC, Raymond WW, Blount JL, Caughey GH (1997) Dog mast cell α-chymase activates progelatinase B by cleaving the Phe88–Gln89 and Phe91–Glu92 bonds of the catalytic domain. J Biol Chem 272:25628–25635
Forteza R, Lauredo I, Abraham WM, Conner GE (1999) Bronchial tissue kallikrein activity is regulated by hyaluronic acid binding. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 21:666–674
Frank BT, Rossall JC, Caughey GH, Fang KC (2001) Mast cell tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 is cleaved and inactivated extracellularly by α-chymase. J Immunol 166:2783–2792
Fu Z, Thorpe M, Hellman L (2015) rMCP-2, the major rat mucosal mast cell protease, an analysis of its extended cleavage specificity and its potential role in regulating intestinal permeability by the cleavage of cell adhesion and junction proteins. PLoS ONE 10:e0131720
Furubayashi K, Takai S, Jin D, Miyazaki M, Katsumata T, Inagaki S, Kimura M, Tanaka K, Nishimoto M, Fukumoto H (2008) Chymase activates promatrix metalloproteinase-9 in human abdominal aortic aneurysm. Clin Chim Acta 388:214–216
Gaber MA, Seliet IA, Ehsan NA, Megahed MA (2014) Mast cells and angiogenesis in wound healing. Anal Quant Cytopathol Histpathol 36:32–40
Galli SJ (1990) New insights into “the riddle of the mast cells”: microenvironmental regulation of mast cell development and phenotypic heterogeneity. Lab Invest 62:5–33
Galli SJ, Tsai M (2008) Mast cells: versatile regulators of inflammation, tissue remodeling, host defense and homeostasis. J Dermatol Sci 49:7–19
Galli SJ, Tsai M, Marichal T, Tchougounova E, Reber LL, Pejler G (2015) Approaches for analyzing the roles of mast cells and their proteases in vivo. Adv Immunol 126:45–127
Glajcar A, Szpor J, Pacek A, Tyrak KE, Chan F, Streb J, Hodorowicz-Zaniewska D, Okon K (2017) The relationship between breast cancer molecular subtypes and mast cell populations in tumor microenvironment. Virchows Arch 470:505–515
Guidolin D, Ruggieri S, Annese T, Tortorella C, Marzullo A, Ribatti D (2017) Spatial distribution of mast cells around vessels and glands in human gastric carcinoma. Clin Exp Med 17:531–539
He A, Shi GP (2013) Mast cell chymase and tryptase as targets for cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Curr Pharm Des 19:1114–1125
He S, Walls AF (1998) Human mast cell chymase induces the accumulation of neutrophils, eosinophils and other inflammatory cells in vivo. Br J Pharmacol 125:1491–1500
Henningsson F, Hergeth S, Cortelius R, Abrink M, Pejler G (2006) A role for serglycin proteoglycan in granular retention and processing of mast cell secretory granule components. FEBS J 273:4901–4912
Ibaraki T, Muramatsu M, Takai S, Jin D, Maruyama H, Orino T, Katsumata T, Miyazaki M (2005) The relationship of tryptase- and chymase-positive mast cells to angiogenesis in stage I non-small cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 28:617–621
Irani AM, Schwartz LB (1989) Mast cell heterogeneity. Clin Exp Allergy 19:143–155
Jiang Y, Wu Y, Hardie WJ, Zhou X (2017) Mast cell chymase affects the proliferation and metastasis of lung carcinoma cells in vitro. Oncol Lett 14:3193–3198
Johnson JL, Jackson CL, Angelini GD, George SJ (1998) Activation of matrix-degrading metalloproteinases by mast cell proteases in atherosclerotic plaques. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:1707–1715
Kitamura Y (1989) Heterogeneity of mast cells and phenotypic change between subpopulations. Annu Rev Immunol 7:59–76
Kitamura Y, Oboki K, Ito A (2007) Development of mast cells. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 83:164–174
Kofford MW, Schwartz LB, Schechter NM, Yager DR, Diegelmann RF, Graham MF (1997) Cleavage of type I procollagen by human mast cell chymase initiates collagen fibril formation and generates a unique carboxyl-terminal propeptide. J Biol Chem 272:7127–7131
Kolset SO, Tveit H (2008) Serglycin–structure and biology. Cell Mol Life Sci 65:1073–1085
Kolset SO, Zernichow L (2008) Serglycin and secretion in human monocytes. Glycoconj J 25:305–311
Kondo K, Muramatsu M, Okamoto Y, Jin D, Takai S, Tanigawa N, Miyazaki M (2006) Expression of chymase-positive cells in gastric cancer and its correlation with the angiogenesis. J Surg Oncol 93:36–42 (Discussion 42–33)
Konstantinov IE (2000) In search of Alexander A. Maximow: the man behind the unitarian theory of hematopoiesis. Perspect Biol Med 43:269–276
Kosanovic D, Dahal BK, Wygrecka M, Reiss I, Gunther A, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Schermuly RT, Banat GA (2013) Mast cell chymase: an indispensable instrument in the pathological symphony of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis? Histol Histopathol 28:691–699
Kosanovic D, Luitel H, Dahal BK, Cornitescu T, Janssen W, Danser AH, Garrelds IM, De Mey JG, Fazzi G, Schiffers P, Iglarz M, Fischli W, Ghofrani HA, Weissmann N, Grimminger F, Seeger W, Reiss I, Schermuly RT (2015) Chymase: a multifunctional player in pulmonary hypertension associated with lung fibrosis. Eur Respir J 46:1084–1094
Kovanen PT (1997) Chymase-containing mast cells in human arterial intima: implications for atherosclerotic disease. Heart Vessels Suppl 12:125–127
Lefrancais E, Duval A, Mirey E, Roga S, Espinosa E, Cayrol C, Girard JP (2014) Central domain of IL-33 is cleaved by mast cell proteases for potent activation of group-2 innate lymphoid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:15502–15507
Leskinen MJ, Lindstedt KA, Wang Y, Kovanen PT (2003) Mast cell chymase induces smooth muscle cell apoptosis by a mechanism involving fibronectin degradation and disruption of focal adhesions. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:238–243
Li T, Zhang X, Cheng HJ, Zhang Z, Ahmad S, Varagic J, Li W, Cheng CP, Ferrario CM (2018) Critical role of the chymase/angiotensin-(1–12) axis in modulating cardiomyocyte contractility. Int J Cardiol 264:137–144
Lindstedt KA, Wang Y, Shiota N, Saarinen J, Hyytiainen M, Kokkonen JO, Keski-Oja J, Kovanen PT (2001a) Activation of paracrine TGF-beta1 signaling upon stimulation and degranulation of rat serosal mast cells: a novel function for chymase. FASEB J 15:1377–1388
Lindstedt L, Lee M, Kovanen PT (2001b) Chymase bound to heparin is resistant to its natural inhibitors and capable of proteolyzing high density lipoproteins in aortic intimal fluid. Atherosclerosis 155:87–97
Lipitsa T, Naukkarinen A, Laitala J, Harvima IT (2016) Complement C3 is expressed by mast cells in cutaneous vasculitis and is degraded by chymase. Arch Dermatol Res 308:575–584
Magnusson SE, Pejler G, Kleinau S, Abrink M (2009) Mast cell chymase contributes to the antibody response and the severity of autoimmune arthritis. FASEB J 23:875–882
Malone DG, Irani AM, Schwartz LB, Barrett KE, Metcalfe DD (1986) Mast cell numbers and histamine levels in synovial fluids from patients with diverse arthritides. Arthritis Rheum 29:956–963
Margulis A, Nocka KH, Brennan AM, Deng B, Fleming M, Goldman SJ, Kasaian MT (2009) Mast cell-dependent contraction of human airway smooth muscle cell-containing collagen gels: influence of cytokines, matrix metalloproteases, and serine proteases. J Immunol 183:1739–1750
McPherson EA, Luo Z, Brown RA, LeBard LS, Corless CC, Speth RC, Bagby SP (2004) Chymase-like angiotensin II-generating activity in end-stage human autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:493–500
Metcalfe DD, Baram D, Mekori YA (1997) Mast cells. Physiol Rev 77:1033–1079
Meyer N, Woidacki K, Maurer M, Zenclussen AC (2017) Safeguarding of fetal growth by mast cells and natural killer cells: deficiency of one is counterbalanced by the other. Front Immunol 8:711
Mukai K, Tsai M, Saito H, Galli SJ (2018) Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol Rev 282:121–150
Mulloy B, Lever R, Page CP (2017) Mast cell glycosaminoglycans. Glycoconj J 34:351–361
Nagata M, Shijubo N, Walls AF, Ichimiya S, Abe S, Sato N (2003) Chymase-positive mast cells in small sized adenocarcinoma of the lung. Virchows Arch 443:565–573
Nagata S, Varagic J, Kon ND, Wang H, Groban L, Simington SW, Ahmad S, Dell’Italia LJ, VonCannon JL, Deal D, Ferrario CM (2015) Differential expression of the angiotensin-(1–12)/chymase axis in human atrial tissue. Ther Adv Cardiovasc Dis 9:168–180
Nishikori Y, Kakizoe E, Kobayashi Y, Shimoura K, Okunishi H, Dekio S (1998) Skin mast cell promotion of matrix remodeling in burn wound healing in mice: relevance of chymase. Arch Dermatol Res 290:553–560
Okamoto Y, Takai S, Miyazaki M (2004) Significance of chymase inhibition for prevention of adhesion formation. Eur J Pharmacol 484:357–359
Omoto Y, Tokime K, Yamanaka K, Habe K, Morioka T, Kurokawa I, Tsutsui H, Yamanishi K, Nakanishi K, Mizutani H (2006) Human mast cell chymase cleaves pro-IL-18 and generates a novel and biologically active IL-18 fragment. J Immunol 177:8315–8319
Pejler G, Abrink M, Ringvall M, Wernersson S (2007) Mast cell proteases. Adv Immunol 95:167–255
Pejler G, Knight SD, Henningsson F, Wernersson S (2009) Novel insights into the biological function of mast cell carboxypeptidase A. Trends Immunol 30:401–408
Pejler G, Ronnberg E, Waern I, Wernersson S (2010) Mast cell proteases: multifaceted regulators of inflammatory disease. Blood 115:4981–4990
Redegeld FA, Yu Y, Kumari S, Charles N, Blank U (2018) Non-IgE mediated mast cell activation. Immunol Rev 282:87–113
Ribatti D, Crivellato E (2016) The role of mast cell in tissue morphogenesis. Thymus, duodenum, and mammary gland as examples. Exp Cell Res 341:105–109
Robida PA, Puzzovio PG, Pahima H, Levi-Schaffer F, Bochner BS (2018) Human eosinophils and mast cells: birds of a feather flock together. Immunol Rev 282:151–167
Ronnberg E, Pejler G (2012) Serglycin: the master of the mast cell. Methods Mol Biol 836:201–217
Rubinstein I, Nadel JA, Graf PD, Caughey GH (1990) Mast cell chymase potentiates histamine-induced wheal formation in the skin of ragweed-allergic dogs. J Clin Invest 86:555–559
Saarinen J, Kalkkinen N, Welgus HG, Kovanen PT (1994) Activation of human interstitial procollagenase through direct cleavage of the Leu83–Thr84 bond by mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem 269:18134–18140
Schwartz LB (1987) Mediators of human mast cells and human mast cell subsets. Ann Allergy 58:226–235
Schwartz LB (1990) Tryptase, a mediator of human mast cells. J Allergy Clin Immunol 86:594–598
Schwartz LB, Atkins PC, Bradford TR, Fleekop P, Shalit M, Zweiman B (1987a) Release of tryptase together with histamine during the immediate cutaneous response to allergen. J Allergy Clin Immunol 80:850–855
Schwartz LB, Bradford TR, Irani AM, Deblois G, Craig SS (1987b) The major enzymes of human mast cell secretory granules. Am Rev Respir Dis 135:1186–1189
Schwartz LB, Irani AM, Roller K, Castells MC, Schechter NM (1987c) Quantitation of histamine, tryptase, and chymase in dispersed human T and TC mast cells. J Immunol 138:2611–2615
Seldin DC, Adelman S, Austen KF, Stevens RL, Hein A, Caulfield JP, Woodbury RG (1985a) Homology of the rat basophilic leukemia cell and the rat mucosal mast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:3871–3875
Seldin DC, Austen KF, Stevens RL (1985b) Purification and characterization of protease-resistant secretory granule proteoglycans containing chondroitin sulfate di-B and heparin-like glycosaminoglycans from rat basophilic leukemia cells. J Biol Chem 260:11131–11139
Shukla SA, Veerappan R, Whittimore JS, Ellen Miller L, Youngberg GA (2006) Mast cell ultrastructure and staining in tissue. Methods Mol Biol 315:63–76
Silverman AJ, Sutherland AK, Wilhelm M, Silver R (2000) Mast cells migrate from blood to brain. J Neurosci 20:401–408
Singh J, Shah R, Singh D (2016) Targeting mast cells: uncovering prolific therapeutic role in myriad diseases. Int Immunopharmacol 40:362–384
Supajatura V, Ushio H, Wada A, Yahiro K, Okumura K, Ogawa H, Hirayama T, Ra C (2002) Cutting edge: VacA, a vacuolating cytotoxin of Helicobacter pylori, directly activates mast cells for migration and production of proinflammatory cytokines. J Immunol 168:2603–2607
Suttle MM, Harvima IT (2016) Mast cell chymase in experimentally induced psoriasis. J Dermatol 43:693–696
Taipale J, Lohi J, Saarinen J, Kovanen PT, Keski-Oja J (1995) Human mast cell chymase and leukocyte elastase release latent transforming growth factor-beta 1 from the extracellular matrix of cultured human epithelial and endothelial cells. J Biol Chem 270:4689–4696
Tani K, Ogushi F, Kido H, Kawano T, Kunori Y, Kamimura T, Cui P, Sone S (2000) Chymase is a potent chemoattractant for human monocytes and neutrophils. J Leukoc Biol 67:585–589
Tchougounova E, Lundequist A, Fajardo I, Winberg JO, Abrink M, Pejler G (2005) A key role for mast cell chymase in the activation of pro-matrix metalloprotease-9 and pro-matrix metalloprotease-2. J Biol Chem 280:9291–9296
Tejada T, Tan L, Torres RA, Calvert JW, Lambert JP, Zaidi M, Husain M, Berce MD, Naib H, Pejler G, Abrink M, Graham RM, Lefer DJ, Naqvi N, Husain A (2016) IGF-1 degradation by mouse mast cell protease 4 promotes cell death and adverse cardiac remodeling days after a myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:6949–6954
Theoharides TC, Alysandratos KD, Angelidou A, Delivanis DA, Sismanopoulos N, Zhang B, Asadi S, Vasiadi M, Weng Z, Miniati A, Kalogeromitros D (2012) Mast cells and inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:21–33
Urata H (2007) Chymase and matrix metalloproteinase. Hypertens Res 30:3–4
Urata H, Ganten D (1993) Cardiac angiotensin II formation: the angiotensin—I converting enzyme and human chymase. Eur Heart J 14(Suppl. I):177–182
Urata H, Kinoshita A, Misono KS, Bumpus FM, Husain A (1990) Identification of a highly specific chymase as the major angiotensin II-forming enzyme in the human heart. J Biol Chem 265:22348–22357
Vartio T, Seppa H, Vaheri A (1981) Susceptibility of soluble and matrix fibronectins to degradation by tissue proteinases, mast cell chymase and cathepsin G. J Biol Chem 256:471–477
Veerappan A, Thompson M, Savage AR, Silverman ML, Chan WS, Sung B, Summers B, Montelione KC, Benedict P, Groh B, Vicencio AG, Peinado H, Worgall S, Silver RB (2016) Mast cells and exosomes in hyperoxia-induced neonatal lung disease. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 310:L1218–L1232
Vukman KV, Forsonits A, Oszvald A, Toth EA, Buzas EI (2017) Mast cell secretome: soluble and vesicular components. Semin Cell Dev Biol 67:65–73
Waern I, Lundequist A, Pejler G, Wernersson S (2013) Mast cell chymase modulates IL-33 levels and controls allergic sensitization in dust-mite induced airway inflammation. Mucosal Immunol 6:911–920
Wasse H, Naqvi N, Husain A (2012) Impact of mast cell chymase on renal disease progression. Curr Hypertens Rev 8:15–23
Welker P, Kramer S, Groneberg DA, Neumayer HH, Bachmann S, Amann K, Peters H (2008) Increased mast cell number in human hypertensive nephropathy. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 295:F1103–F1109
Welle M (1997) Development, significance, and heterogeneity of mast cells with particular regard to the mast cell-specific proteases chymase and tryptase. J Leukoc Biol 61:233–245
Welle MM, Audige L, Belz JP (1997) The equine endometrial mast cell during the puerperal period: evaluation of mast cell numbers and types in comparison to other inflammatory changes. Vet Pathol 34:23–30
Wernersson S, Pejler G (2014) Mast cell secretory granules: armed for battle. Nat Rev Immunol 14:478–494
Zanini A, Chetta A, Saetta M, Baraldo S, D’Ippolito R, Castagnaro A, Neri M, Olivieri D (2007) Chymase-positive mast cells play a role in the vascular component of airway remodeling in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 120:329–333
Zhao L, Yamaguchi Y, Ge X, Robinson WH, Morser J, Leung LLK (2018) Chemerin 156F, generated by chymase cleavage of prochemerin, is elevated in joint fluids of arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 20:132
Zhou X, Wei T, Cox CW, Jiang Y, Roche WR, Walls AF (2018) Mast cell chymase impairs bronchial epithelium integrity by degrading cell junction molecules of epithelial cells. Allergy 00:1–11
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Atiakshin, D., Buchwalow, I. & Tiemann, M. Mast cell chymase: morphofunctional characteristics. Histochem Cell Biol 152, 253–269 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-019-01803-6
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-019-01803-6