Abstract
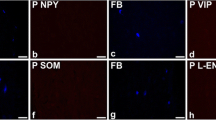
Resiniferatoxin (RTX) is used as an experimental drug in therapy of neurogenic urinary bladder disorders. The present study investigated the chemical coding of sympathetic chain ganglia (SChG) neurons supplying porcine urinary bladder after intravesical RTX instillation. The SChG neurons were visualized with retrograde tracing method and their chemical profile was disclosed with double-labeling immunohistochemistry using antibodies against dopamine β-hydroxylase (DβH; marker of noradrenergic neurons), neuropeptide Y (NPY), vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), somatostatin (SOM), galanin, Leu5-enkephalin and neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS). It was found that in both the control (n = 5) and RTX-treated pigs (n = 5), the vast majority (90.4 ± 2.8 and 89.7 ± 2.3 %, respectively) of FB-positive (FB+) nerve cells were DβH+. RTX instillation caused a decrease in the number of FB+/DβH+ neurons immunopositive to NPY (71.1 ± 12.1 vs 43.2 ± 6.7 %), VIP (21.3 ± 10.7 vs 5.3 ± 4.3 %) or SOM (16.5 ± 4.6 vs 2.3 ± 2.6 %) and a distinct increase in the number of FB+/DβH+ neurons immunoreactive to nNOS (0.8 ± 1 vs 5.3 ± 1.9 %). The present study for the first time has provided some information that therapeutic effects of RTX on the mammalian urinary bladder can be partly mediated by SChG neurons.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelhamid RE, Kovács KJ, Honda CN, Nunez MG, Larson AA (2013) Resiniferatoxin (RTX) causes a uniquely protracted musculoskeletal hyperalgesia in mice by activation of TRPV1 receptors. J Pain 14(12):1629–1641. doi:10.1016/j.jpain.2013.07.021
Andersson KE, Arner A (2004) Urinary bladder contraction and relaxation: physiology and pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 84:935–986. doi:10.1152/physrev.00038.2003
Avelino A, Cruz F (2000) Peptide immunoreactivity and ultrastructure of rat urinary bladder nerve fibers after topical desensitization by capsaicin or resiniferatoxin. Auton Neurosci 86:37–46. doi:10.1016/S1566-0702(00)00204-6
Avelino A, Cruz C, Cruz F (2002a) Nerve growth factor regulates galanin and c-jun overexpression occurring in dorsal root ganglion cells after intravesical resiniferatoxin application. Brain Res 951:264–269. doi:10.1016/S0006-8993(02)03171-2
Avelino A, Cruz C, Nagy I, Cruz F (2002b) Vanilloid receptor 1 expression in the rat urinary tract. Neuroscience 109(4):787–798. doi:10.1016/S0306-4522(01)00496-1
Bates BD, Mitchell K, Keller JM, Chan CC, Swaim WD, Yaskovich R, Mannes AJ, Iadarola MJ (2010) Prolonged analgesic response of cornea to topical resiniferatoxin, a potent TRPV1 agonist. Pain 149(3):522–528. doi:10.1016/j.pain.2010.03.024
Birder LA, Kanai AJ, de Groat WC, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Burke NE, Dineley KE, Watkins S, Reynolds IJ, Caterina MJ (2001) Vanilloid receptor expression suggests a sensory role for urinary bladder epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(23):13396–13401. doi:10.1073/pnas.231243698
Bitran M, Torres G, Tapia W, Huidobro-Toro JP (1996) Neuropeptide Y inhibits 3[H]noradrenaline release in the rat vas deferens independently of cAMP levels. Neurochem Int 28(3):309–317. doi:10.1016/0197-0186(95)00084-4
Bossowska A, Majewski M (2012a) The influence of resiniferatoxin on the chemical coding of neurons in dorsal root ganglia supplying the urinary bladder in the female pig. Pol J Vet Sci 15(1):135–142. doi:10.2478/v10181-011-0124-6
Bossowska A, Majewski M (2012b) Botulinum toxin type A-induced changes in the chemical coding of dorsal root ganglion neurons supplying the porcine urinary bladder. Pol J Vet Sci 15(2):345–353. doi:10.2478/v10181-012-0053-2
Bossowska A, Crayton R, Radziszewski P, Kmiec Z, Majewski M (2009) Distribution and neurochemical characterization of sensory dorsal root ganglia neurons supplying porcine urinary bladder. J Physiol Pharmacol 4:77–81
Browning KN, Babic T, Holmes GM, Swartz E, Travagli RA (2013) A critical re-evaluation of the specificity of action of perivagal capsaicin. J Physiol 591(Pt 6):1563–1580. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2012.246827
Burliński PJ, Gonkowski S, Całka J (2011) Tetrodotoxin- and resiniferatoxin-induced changes in paracervical ganglion ChAT- and nNOS-IR neurons supplying the urinary bladder in female pigs. Acta Vet Hung 59(4):455–463. doi:10.1556/AVet.033
Burliński PJ, Czujkowska A, Arciszewski MB (2012) Całka J (2012) Upregulation of LENK and VIP in paracervical ganglion neurons supplying the urinary bladder of tetrodotoxin- and resiniferatoxin-treated female pigs. Acta Vet Hung 60(3):383–393. doi:10.1556/AVet.033
Burliński PJ, Burlińska AM, Gonkowski S, Całka J (2013) Resiniferatoxin and tetrodotoxin induced NPY and TH immunoreactivity changes within the paracervical ganglion neurons supplying the urinary bladder. J Mol Neurosci 49(1):62–67. doi:10.1007/s12031-012-9889-z
Burnett AL (1995) Nitric oxide control of lower genitourinary tract functions: a review. Urology 45:1071–1083. doi:10.1016/S0090-4295(99)80136-8
Chancellor MB, de Groat WC (1999) Intravesical capsaicin and resiniferatoxin therapy: spicing up the ways to treat the overactive bladder. J Urol 162(1):3–11. doi:10.1097/00005392-199907000-00002
Chernaeva L, Charakchieva S (1988) Leucine-enkephalin- and neuropeptide Y-modulation of [3H]noradrenaline release in the oviduct of mature and juvenile rabbits. Gen Pharmacol 19(1):137–142. doi:10.1016/0306-3623(88)90019-5
Cruz F, Dinis P (2007) Resiniferatoxin and botulinum toxin type A for treatment of lower urinary tract symptoms. Neurourol Urodyn 26(6 Suppl):920–927. doi:10.1002/nau.20479
Cruz F, Guimaräes M, Silva C, Reis M (1997) Suppression of bladder hyperreflexia by intravesical resiniferatoxin. Lancet 350(9078):640–641. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(05)63330-2
Dahlöf P, Persson K, Lundberg JM, Dahlöf C (1988) Neuropeptide Y (NPY) induced inhibition of preganglionic nerve stimulation evoked release of adrenaline and noradrenaline in the pithed rat. Acta Physiol Scand 132:51–57. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.1988.tb08297.x
Dalmose AL, Hvistendahl JJ, Olsen LH, Eskild-Jensen A, Djurhuus JC, Swindle MM (2000) Surgically induced urologic models in swine. J Invest Surg 13(3):133–145. doi:10.1080/08941930050075829
de Groat WC, Wickens C (2013) Organization of neural switching circuity underlying reflex micturition. Acta Physiol (Oxf.) 207(1):66–84. doi:10.1111/apha.12014
de Paiva A, Meunier FA, Molgó J, Aoki KR, Dolly JO (1999) Functional repair of motor end plates after botulinum neurotoxin type A poisoning: biphasic switch of synaptic activity between nerve sprouts and their parent terminals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(6):3200–3205. doi:10.1073/pnas.96.6.3200
Foster HE Jr, Lake AG (2014) Use of vanilloids in urologic disorders. Prog Drug Res 68:307–317
Gevaert T, Vandepitte J, Ost D, Nilius B, De Ridder D (2007) Autonomus contractile activity in the isolated rat bladder is modulated by a TRPV1 dependent mechanism. Neurourol Urodyn 26(3):424–432. doi:10.1002/nau.20313
Iravani MM, Zar MA (1994) Presence of neuropeptide Y in the rat seminal vesicle and its effects on noradrenaline- and nerve-induced contractions. Br J Pharmacol 113(3):877–882. doi:10.111/j.1476-5381.1994.tb17074.x
Jobling P (2011) Autonomic control of the urogenital tract. Auton Neurosci 165(1):113–126. doi:10.1016/j.autneu.2010.07.004
Kaleczyc J, Timmermans JP, Majewski M, Łakomy M, Scheuermann DW (1995) Distribution and immunohistochemical characteristics of neurons in the porcine caudal mesenteric ganglion projecting to the vas deferens and seminal vesicle. Cell Tissue Res 282(1):59–68. doi:10.1007/BF00319133
Keast JR (1999) Unusual autonomic ganglia: connections, chemistry and plasticity of pelvic ganglia. Int Rev Cytol 193:1–69. doi:10.1016/S0074-7696(08)61778-7
Kokubun S, Sato T, Ogawa C, Kudo K, Goto K, Fuji Y, Shimizu Y, Ichikawa H (2015) Distribution of TRPV1 and TRPV2 in the human stellate ganglion and spinal cord. Neurosci Lett 590:6–11. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2015.01.074
Kuzmuk KN, Schook LB (2011) Pigs as a model for biomedical sciences. In: Rothschild MF, Ruvinsky A (eds) The genetics of the pig, 2nd edn. CAB International, Oxford Shire, pp 426–444
Lepiarczyk E, Bossowska A, Majewski M (2015) Changes in chemical coding of sympathetic chain ganglia (SChG) neurons supplying porcine urinary bladder after botulinum toxin (BTX) treatment. Cell Tissue Res 360(2):263–272. doi:10.1007/s00441-014-2086-3
Levin RM, Ruggieri MR, Wein AJ (1986) Functional effects of the purinergic innervation of the rabbit urinary bladder. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 236:452–457
Lundberg JM, Stjarne L (1984) Neuropeptide Y (NPY) depresses the secretion of 3H-noradrenaline and the contractile response evoked by field stimulation, in rat vas deferens. Acta Physiol Scand 120(3):477–479. doi:10.1111/j.1748-1716.1984.tb07410.x
Majewski M, Bossowska A, Wojtkiewicz J, Kowalska C, Janiuk I, Zapart A, Borkowski A, Radziszewski P (2008) Resiniferatoxin (RTX)-induced changes in the chemical coding of inferior mesenteric ganglion (IMG) neurons supplying porcine urinary bladder. Urologia Polska 61(Supl. 1):60
Morrison J, Birder L, Craggs M et al (2005) Neural control. In: Abrams P, Cardozo L, Khoury S, Wein A (eds) Incontinence. Health Publications Ltd, Jersey, pp 363–422
Ost D, Roskams T, Van Der Aa F, De Ridder D (2002) Topography of the vanilloid receptor in the human bladder: more than just the nerve fibers. J Urol 168(1):293–297. doi:10.1016/S0022-5347(05)64910-5
Persson K, Alm P, Johansson K, Larsson B, Andersson KE (1993) Nitric oxide synthase in pig lower urinary tract: immunohistochemistry, NADPH diaphorase histochemistry and functional effects. Br J Pharmacol 110(2):521–530. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.1993.tb13842.x
Pidsudko Z (2014) Immunohistochemical characteristics and distribution of neurons in the paravertebral, prevertebral and pelvic ganglia supplying the urinary bladder in the male pig. J Mol Neurosci 52(1):56–70. doi:10.1007/s12031-013-0139-9
Ragionieri L, Botti M, Gazza F, Sorteni C, Chiocchetti R, Clavenzani P, Minelli LB, Panu R (2013) Localization of peripheral autonomic neurons innervating the boar urinary bladder trigone and neurochemical features of the sympathetic component. Eur J Histochem 57:93–105. doi:10.4081/ejh.2013.e16
Shi B, Li X, Chen J, Su B, Li X, Yang S, Guan Z, Wang R (2014) Resiniferatoxin for treatment of lifelong premature ejaculation: a preliminary study. Int J Urol 21(9):923–926. doi:10.1111/iju.12471
Skobowiat C, Całka J, Majewski M (2011) Axotomy induced changes in neuron al plasticity of sympathetic chain ganglia (SChG) neurons supplying descending colon in the pig. Exp Mol Pathol 90(1):13–18. doi:10.1016/j.yexmp.2010.11.004
Swindle MM (2012) The development of swine models in drug discovery and development. Future Med Chem 4(14):1771–1772. doi:10.4155/fmc.12.113
Szallasi A, Blumberg PM (1989) Resiniferatoxin, a phorbol-related diterpene, acts as an ultrapotent analog of capsaicin, the irritant constituent in red pepper. Neuroscience 30:515–520. doi:10.1016/0306-4522(89)90269-8
Terai A, Matsui Y, Ichioka K, Ohara H, Terada N, Yoshimura K (2004) Comparative analysis of lower urinary tract symptoms and bother in both sexes. Urology 63(3):487–491. doi:10.1016/j.urology.2003.09.070
Thüroff JW, Bazeed MA, Schmidt RA, Luu DH, Tanagho EA (1982) Regional topography of spinal cord neurons innervating pelvic floor muscles and bladder neck in the dog: a study by combined horseradish peroxidase histochemistry and autoradiography. Urol Int 37:110–120. doi:10.1159/000280804
Tran LV, Somogyi GT, De Groat WC (1994) Inhibitory effect of neuropeptide Y on adrenergic and cholinergic transmission in rat urinary bladder and urethra. Am J Physiol 266(4 Pt 2):R1411–R1417
Vera PL, Nadelhaft I (1992) Afferent and sympathetic innervation of the dome and the base of the urinary bladder of the female rat. Brain Res Bull 29(5):651–658. doi:10.1016/0361-9230(92)90134-J
Wang H, Wang DH, Galligan JJ (2007) Expression of TRPV1 in sensory and sympathetic neurons innervating kidney. FASEB J 21(968):4. doi:10.1096/fj.1530-6860
Yiangou Y, Facer P, Ford A, Brady C, Wiseman O, Fowler CJ, Anand P (2001) Capsaicin receptor VR1 and ATP-gated ion channel P2X3 in human urinary bladder. BJU Int 87:774–779. doi:10.1046/j.1464-410x.2001.02190.x
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
We (all co-authors) confirm that the manuscript “The influence of intravesical administration of resiniferatoxin (RTX) on the chemical coding of sympathetic chain ganglia (SChG) neurons supplying the porcine urinary bladder” by E. Lepiarczyk, M. Majewski, A. Bossowska, has been read and approved by all named authors and that there are no other persons who satisfied the criteria for authorship. We also confirm that neither this manuscript nor one with substantially similar content under our authorship has been published or is being considered for publication elsewhere. All the authors agreed to submit this manuscript to the peer review process of Histochemistry and Cell Biology.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lepiarczyk, E., Majewski, M. & Bossowska, A. The influence of intravesical administration of resiniferatoxin (RTX) on the chemical coding of sympathetic chain ganglia (SChG) neurons supplying the porcine urinary bladder. Histochem Cell Biol 144, 479–489 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1355-x
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1355-x