Abstract
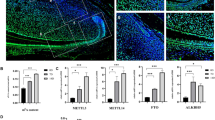
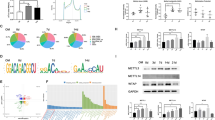
Amelogenesis is a multistep process that relies on specific temporal and spatial signaling networks between the dental epithelium and mesenchymal tissues. Epigenetic modifications of key developmental genes in this process may be closely linked to a network of molecular events. However, the role of epigenetic regulation in amelogenesis remains unclear. Here, we have uncovered the spatial distributions of 5-methylcytosine (5-mC) and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) to determine epigenetic events in the mandibular incisors of mice. Immunohistochemistry and dot blotting showed that 5-hmC in ameloblasts increased from the secretory stage to the later maturation stage. We also demonstrated the distribution of 5-mC-positive ameloblasts with punctate nuclear labeling from sometime after the initiation of the secretory stage to the later maturation stage; however, dot blotting failed to detect this change. No obvious alteration of 5-mC/5-hmC staining in odontoblasts and dental pulp cells was observed. Concomitant with quantitative expression data, immunohistochemistry showed that maintenance DNA methyltransferase DNMT1 was highly expressed in immature dental epithelial cells and subsequently decreased at later stages of development. Meanwhile, de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a and Dnmt3b and DNA demethylase Tet family genes were universally expressed, except Tet1 that was highly expressed in immature dental epithelial cells. Thus, DNMT1 may sustain the undifferentiated status of dental epithelial cells through the maintenance of DNA methylation, while the hydroxylation of 5-mC may occur through the whole differentiation process by TET activity. Taken together, these data indicate that the dynamic changes of 5-mC and 5-hmC may be critical for the regulation of amelogenesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Apostolou E, Hochedlinger K (2013) Chromatin dynamics during cellular reprogramming. Nature 502:462–471. doi:10.1038/nature12749
Biehs B, Hu JK-H, Strauli NB, Sangiorgi E, Jung H, Heber R-P, Ho S, Goodwin AF, Dasen JS, Capecchi MR, Klein OD (2013) BMI1 represses Ink4a/Arf and Hox genes to regulate stem cells in the rodent incisor. Nat Cell Biol 15:846–852. doi:10.1038/ncb2766
Blaschke K, Ebata KT, Karimi MM, Zepeda-Martínez JA, Goyal P, Mahapatra S, Tam A, Laird DJ, Hirst M, Rao A, Lorincz MC, Ramalho-Santos M (2013) Vitamin C induces Tet-dependent DNA demethylation and a blastocyst-like state in ES cells. Nature 500:222–226. doi:10.1038/nature12362
Bleicher F (2014) Odontoblast physiology. Exp Cell Res 325:65–71. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.012
Bronckers A (1983) A histological and biochemical study of the effect of vitamin C-deficiency on induction of amelogenesis in hamster molars in vitro. Arch Oral Biol 28:681–692
Couve E, Osorio R, Schmachtenberg O (2013) The amazing odontoblast: activity, autophagy, and aging. J Dent Res 92:765–772. doi:10.1177/0022034513495874
Delgado-Calle J, Sañudo C, Sanchez-Verde L, Garcia-Renedo RJ, Arozamena J, Riancho JA (2011) Epigenetic regulation of alkaline phosphatase in human cells of the osteoblastic lineage. Bone 49:830–838. doi:10.1016/j.bone.2011.06.006
Delgado-Calle J, Sañudo C, Bolado A, Fernandez AF, Arozamena J, Pascual-Carra MA, Rodriguez-Rey JC, Fraga MF, Bonewald L, Riancho JA (2012) DNA methylation contributes to the regulation of sclerostin expression in human osteocytes. J Bone Miner Res 27:926–937. doi:10.1002/jbmr.1491
Ficz G, Branco MR, Seisenberger S, Santos F, Krueger F, Hore TA, Marques CJ, Andrews S, Reik W (2011) Dynamic regulation of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mouse ES cells and during differentiation. Nature 473:398–402. doi:10.1038/nature10008
Harada H, Kettunen P, Jung HS, Mustonen T, Wang Y, Thesleff I (1999) Localization of putative stem cells in dental epithelium and their association with Notch and FGF signaling. J Cell Biol 147:105–120
He Y-F, Li B-Z, Li Z, Liu P, Wang Y, Tang Q, Ding J, Jia Y, Chen Z, Li L, Sun Y, Li X, Dai Q, Song C-X, Zhang K, He C, Xu G-L (2011) Tet-mediated formation of 5-carboxylcytosine and its excision by TDG in mammalian DNA. Science 333:1303–1307. doi:10.1126/science.1210944
Juuri E, Saito K, Ahtiainen L, Seidel K, Tummers M, Hochedlinger K, Klein OD, Thesleff I, Michon F (2012) Sox2+ stem cells contribute to all epithelial lineages of the tooth via Sfrp5+ progenitors. Dev Cell 23:317–328. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2012.05.012
Kawano S, Saito M, Handa K, Morotomi T, Toyono T, Seta Y, Nakamura N, Uchida T, Toyoshima K, Ohishi M, Harada H (2004) Characterization of dental epithelial progenitor cells derived from cervical-loop epithelium in a rat lower incisor. J Dent Res 83:129–133. doi:10.1177/154405910408300209
Kohli RM, Zhang Y (2013) TET enzymes, TDG and the dynamics of DNA demethylation. Nature 502:472–479. doi:10.1038/nature12750
Lee SK (1996) Full-length sequence, localization, and chromosomal mapping of ameloblastin. J Biol Chem 271:4431–4435. doi:10.1074/jbc.271.8.4431
Morotomi T, Kawano S, Toyono T, Kitamura C, Terashita M, Uchida T, Toyoshima K, Harada H (2005) In vitro differentiation of dental epithelial progenitor cells through epithelial-mesenchymal interactions. Arch Oral Biol 50:695–705. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2004.12.006
Nishikawa K, Iwamoto Y, Kobayashi Y, Katsuoka F, Kawaguchi S, Tsujita T, Nakamura T, Kato S, Yamamoto M, Takayanagi H, Ishii M (2015) DNA methyltransferase 3a regulates osteoclast differentiation by coupling to an S-adenosylmethionine-producing metabolic pathway. Nat Med 21:281–287. doi:10.1038/nm.3774
Pastor WA, Pape UJ, Huang Y, Henderson HR, Lister R, Ko M, McLoughlin EM, Brudno Y, Mahapatra S, Kapranov P, Tahiliani M, Daley GQ, Liu XS, Ecker JR, Milos PM, Agarwal S, Rao A (2011) Genome-wide mapping of 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in embryonic stem cells. Nature 473:394–397. doi:10.1038/nature10102
Ruzov A, Tsenkina Y, Serio A, Dudnakova T, Fletcher J, Bai Y, Chebotareva T, Pells S, Hannoun Z, Sullivan G, Chandran S, Hay DC, Bradley M, Wilmut I, De Sousa P (2011) Lineage-specific distribution of high levels of genomic 5-hydroxymethylcytosine in mammalian development. Cell Res 21:1332–1342. doi:10.1038/cr.2011.113
Seidel K, Ahn CP, Lyons D, Nee A, Ting K, Brownell I, Cao T, Carano RAD, Curran T, Schober M, Fuchs E, Joyner A, Martin GR, de Sauvage FJ, Klein OD (2010) Hedgehog signaling regulates the generation of ameloblast progenitors in the continuously growing mouse incisor. Development 137:3753–3761. doi:10.1242/dev.056358
Sen GL, Reuter JA, Webster DE, Zhu L, Khavari PA (2010) DNMT1 maintains progenitor function in self-renewing somatic tissue. Nature 463:563–567. doi:10.1038/nature08683
Simmer JP, Papagerakis P, Smith CE, Fisher DC, Rountrey N, Zheng L, Hu JCC (2010) Regulation of dental enamel shape and hardness. J Dent Res 89:1024–1038. doi:10.1177/0022034510375829
Smith ZD, Meissner A (2013) DNA methylation: roles in mammalian development. Nat Rev Genet 14:204–220. doi:10.1038/nrg3354
Szulwach KE, Li X, Li Y, Song C-X, Han JW, Kim S, Namburi S, Hermetz K, Kim JJ, Rudd MK, Yoon Y-S, Ren B, He C, Jin P (2011) Integrating 5-hydroxymethylcytosine into the epigenomic landscape of human embryonic stem cells. PLoS Genet 7:e1002154. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1002154
Tsai C-C, Su P-F, Huang Y-F, Yew T-L, Hung S-C (2012) Oct4 and Nanog directly regulate Dnmt1 to maintain self-renewal and undifferentiated state in mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Cell 47:169–182. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2012.06.020
Tucker A, Sharpe P (2004) The cutting-edge of mammalian development; how the embryo makes teeth. Nat Rev Genet 5:499–508. doi:10.1038/nrg1380
Tummers M, Thesleff I (2009) The importance of signal pathway modulation in all aspects of tooth development. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 312B:309–319. doi:10.1002/jez.b.21280
Villagra A, Gutirrez J, Paredes R, Sierra J, Puchi M, Imschenetzky M, Van Wijnen A, Lian J, Stein G, Stein J, Montecino M (2002) Reduced CpG methylation is associated with transcriptional activation of the bone-specific rat osteocalcin gene in osteoblasts. J Cell Biochem 85:112–122. doi:10.1002/jcb.10113
Zentner GE, Henikoff S (2013) Regulation of nucleosome dynamics by histone modifications. Nat Struct Mol Biol 20:259–266. doi:10.1038/nsmb.2470
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Azusa Onishi, Chieko Niwata, and Rina Ohtake for technical assistance with procedures. This work was supported by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists 24791962 to H. Y.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshioka, H., Minamizaki, T. & Yoshiko, Y. The dynamics of DNA methylation and hydroxymethylation during amelogenesis. Histochem Cell Biol 144, 471–478 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1353-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1353-z