Abstract
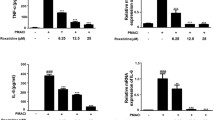
The present study demonstrated that intravenous injection of a high dose of compound 48/80 to the rat induced 50 % drop, within a few min, in the mean arterial pressure and pulse pressure as well as systemic inflammatory plasma leakage that might lead to circulatory and respiratory failure. We also investigated whether pretreatment with Evans blue, a stimulator of BKCa channels, could exert inhibitory effect against compound C48/80-induced allergic circulatory shock and systemic inflammation. Different groups of Sprague–Dawley rats received an intravenous injection of a dose of Evans blue (0, 5, 10, or 50 mg/kg) just 20 s prior to injection of compound 48/80 (200 μg/kg, over 2 min). The present study found that pretreatment with Evans blue in a dose of 10 or 50 mg/kg exerted acute inhibitory effect on compound 48/80-induced sudden drop in mean arterial and pulse pressures. We also showed that pretreatment with Evans blue in a dose of 5, 10, or 50 mg/kg significantly inhibited compound 48/80-induced extensive plasma extravasation, mast cell degranulation, and edema formation in various organs including the airways, esophagus, and skin. Pretreatment with Evans blue 50 mg/kg 1 h earlier exhibited longer-term inhibitory effect on compound 48/80-induced arterial hypotension and systemic inflammation. We concluded that Evans blue pretreatment prevented rats from compound 48/80-triggered allergic shock and systemic inflammation, possibly mainly through inhibition of mast cell degranulation. Evans blue might be potentially useful in elucidating the mechanism and acting as a therapeutic agent of allergic shock and systemic inflammation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baluk P, Hirata A, Thurston G, Fujiwara T, Neal CR, Michel CC, McDonald DM (1997) Endothelial gaps: time course of formation and closure in inflamed venules of rats. Am J Physiol 272 (Lung Cell Mol Physiol 16): L155–L170
Bernik TR, Friedman SG, Ochani M, DiRaimo R, Ulloa L, Yang H, Sudan S, Czura CJ, Ivanova SM, Tracey KJ (2002) Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. J Exp Med 195:781–788
Bolser DC, Del Prado M, O’Reilly S, Mingo G, Hey JA (1995) Evan’s blue dye blocks capsaicin-induced cough and bronchospasm in the guinea pig. Eur J Pharmacol 276:R1–R3
Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, Watkins LR, Wang H, Abumrad N, Eaton JW, Tracey KJ (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405:458–462
Brokaw JJ, Hillenbrand CM, White GW, McDonald DM (1990) Mechanism of tachyphylaxis associated with neurogenic plasma extravasation in rat trachea. Am Rev Respir Dis 141:1434–1440
Chatterjea D, Wetzel A, Mack M, Engblom C, Allen J, Mora-Solano C, Paredes L, Balsells E, Martinov T (2012) Mast cell degranulation mediates compound 48/80-induced hyperalgesia in mice. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 425:237–243
Chen IJ, Chiu HF, Huang HT, Teng CM (1984) Edema formation and degranulation of mast cells by Trimeresurus mucrosquamatus snake venom. Toxicon 22:17–28
Fu YS, Wang PH, Liu SP, Huang WH, Huang H (2010) Warm SPA-induced hyperthermia confers protection to rats against airway inflammation evoked by capsaicin and substance P. Auton Neurosci 155:49–58
Guo JJ, Wang DS, Huang HT (2003) Spontaneous remission of edema and regranulation of goblet cells in rat tracheae after capsaicin-induced acute inflammation. Anat Embryol 206:301–309
Hollywood MA, Cotton KD, McHale NG, Thornbury KD (1998) Enhancement of Ca2+-dependent outward current in sheep bladder myocytes by Evans blue dye. Pflugers Arch 435:631–636
Huang HT, Guo JJ, Huang YH, Fu YS (2013) Histamine-induced changes in rat tracheal goblet cell mucin store and mucosal edema. Histochem Cell Biol 139:717–726
Lidegran M, Domeij S, Carlsoo B, Dahlqvist A (1998) Edema formation in the rat larynx. Cell Tissue Res 292:367–375
Liu SP, Chang CY, Huang WH, Fu YS, Chao D, Huang HT (2010) Dimethylthiourea pretreatment inhibits endotoxin-induced compound exocytosis in goblet cells and plasma leakage of rat small intestine. J Electron Micro 59:127–139
Lo YK, Huang HT (1997) A novel procedure for mediastinal vagotomy inhibits neurogenic inflammation in rat bronchial tree. J Auton Nerv Syst 67:79–88
Lundberg JM, Saria A (1983) Capsaicin-induced desensitization of airway mucosa to cigarette smoke, mechanical and chemical irritants. Nature 302:251–253
McDonald DM (1994) Endothelial gaps and permeability of venules in rat trachea exposed to inflammatory stimuli. Am J Physiol 266:L61–L83
Rohlich P, Anderson P, Uvnas B (1971) Electron microscope observations on compound 48/80-induced degranulation in rat mast cells. Evidence for sequential exocytosis of storage granules. J Cell Biol 51:465–483
Saria A, Lundberg JM (1983) Evans blue fluorescence: quantitative and morphological evaluation of vascular permeability in animal tissues. J Neurosci Methods 8:41–49
Tam EK, Calonico LD, Nadel JA, McDonald DM (1988) Globule leukocytes and mast cells in the rat trachea: their number, distribution, and response to compound 48/80 and dexamethasone. Anat Embryol 178:107–118
Wu SN, Jan CR, Li HF, Chen SA (1999) Stimulation of large-conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels by Evans blue in cultured endothelial cells of human umbilical veins. Biochem Biophys Res Comm 254:666–674
Wu SN, Chen CC, Li HF, Lo YK, Chen SA, Chiang HT (2002) Stimulation of the BKca channel in cultured smooth muscle cells of human trachea by magnolol. Thorax 57:67–74
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by the Grants, KMU-NSYSU 103-I006 and KMU-NSYSU 104-I004 to H.-T.H., Y.-S.F., K.-Z.L and C.-L.C., from cooperated projects of Kaohsiung Medical University and National Sun Yat-Sen University. This study was also supported by a Grant, KMU-O104003 to Y.-S.F., from Kaohsiung Medical University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, YS., Kuo, SY., Lin, HY. et al. Pretreatment with Evans blue, a stimulator of BKCa channels, inhibits compound 48/80-induced shock, systemic inflammation, and mast cell degranulation in the rat. Histochem Cell Biol 144, 237–247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1332-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-015-1332-4